The
each() function is a tool function provided by basically all frameworks. Through it, you can traverse the attribute values of objects and arrays and process them. Both jQuery and jQuery objects implement this method. For jQuery objects, the each method is simply delegated: the jQuery object is passed as the first parameter to jQuery's each method. In other words: the each method provided by jQuery is All sub-elements in the object provided by parameter 1 are called one by one. The each method provided by the jQuery object calls the sub-elements inside jQuery one by one.
The effects of each function are not completely consistent depending on the type of parameters:
1. Traverse objects (with additional parameters)
$.each(Object, function(p1, p2) {
This; //This here points to the current property value of Object in each traversal
p1; p2; //Access additional parameters
}, ['Parameter 1', 'Parameter 2']);
2. Traverse the array (with attachment parameters)
$.each(Array, function(p1, p2){
This; //This here points to the current element of Array in each traversal
p1; p2; //Access additional parameters
}, ['Parameter 1', 'Parameter 2']);
3. Traverse objects (no additional parameters)
$.each(Object, function(name, value) {
This; //this points to the value of the current attribute
Name; //name represents the name of the current property of the Object
Value; //value represents the value of the current property of the Object
});
4. Traverse the array (no additional parameters)
$.each(Array, function(i, value) {
This; //this points to the current element
i; //i represents the current subscript of Array
value; //value represents the current element of Array
});
Here are some common uses of jQuery’s each method
var arr = [ "one", "two", "three", "four"];
$.each(arr, function(){
alert(this);
});
//上面这个each输出的结果分别为:one,two,three,four
var arr1 = [[1, 4, 3], [4, 6, 6], [7, 20, 9]]
$.each(arr1, function(i, item){
alert(item[0]);
});
//其实arr1为一个二维数组,item相当于取每一个一维数组,
//item[0]相对于取每一个一维数组里的第一个值
//所以上面这个each输出分别为:1 4 7
var obj = { one:1, two:2, three:3, four:4};
$.each(obj, function(key, val) {
alert(obj[key]);
});
//这个each就有更厉害了,能循环每一个属性
//输出结果为:1 2 3 4
The each function in JQuery is described as follows in the official documentation of 1.3.2:
each(callback)
Execute a function with each matching element as context.
This means that each time the function passed in is executed, the this keyword in the function points to a different DOM element (a different matching element each time). Moreover, every time the function is executed, a numeric value representing the position of the element as the execution environment in the set of matching elements is passed to the function as a parameter (an integer starting from zero). Returning 'false' will stop the loop (just like using 'break' in a normal loop). Returns 'true' to jump to the next loop (just like using 'continue' in a normal loop).
The subsequent callback is a callback function that indicates the operation that should be assigned when traversing elements. Let’s take a look at a simple example below:
Iterate over the two images and set their src attributes. Note: here this refers to the DOM object rather than the jQuery object.
HTML code:

 jQuery code:
jQuery code: $("img").each(function(i){
this.src = "test" i ".jpg";
});
Result:[
 ,
,  ]
] Of course, when traversing elements, jquery allows customized jumps. Please see the sample code: you can use 'return' to jump out of the each() loop in advance.
HTML code:
jQuery code:
$("button").click(function(){
$("div").each(function(index,domEle){
$(domEle).css("backgroundColor","wheat");
if($(this).is("#stop")){
$("span").text("Stop at div block #" index ".");
return false;
}
});
Or write this:
$("button").click(function(){
$("div").each(function(index){
$(this).css("backgroundColor","wheat");
if($(this).is("#stop")){
$("span").text("Stop at div block #" index ".");
return false;
}
});
Illustration:
The each() method specifies a function to run for each matching element.
Tip: Returning false can be used to stop the loop early.
Grammar
$(selector).each(function(index,element)) Parameter Description
function(index,element) required. Specifies the function to run for each matching element.
•index - the index position of the selector
•element - the current element (can also use the "this" selector
Example
Output the text of each li element:
$("button").click(function(){
$("li").each(function(){
alert($(this).text())
});
});
Example
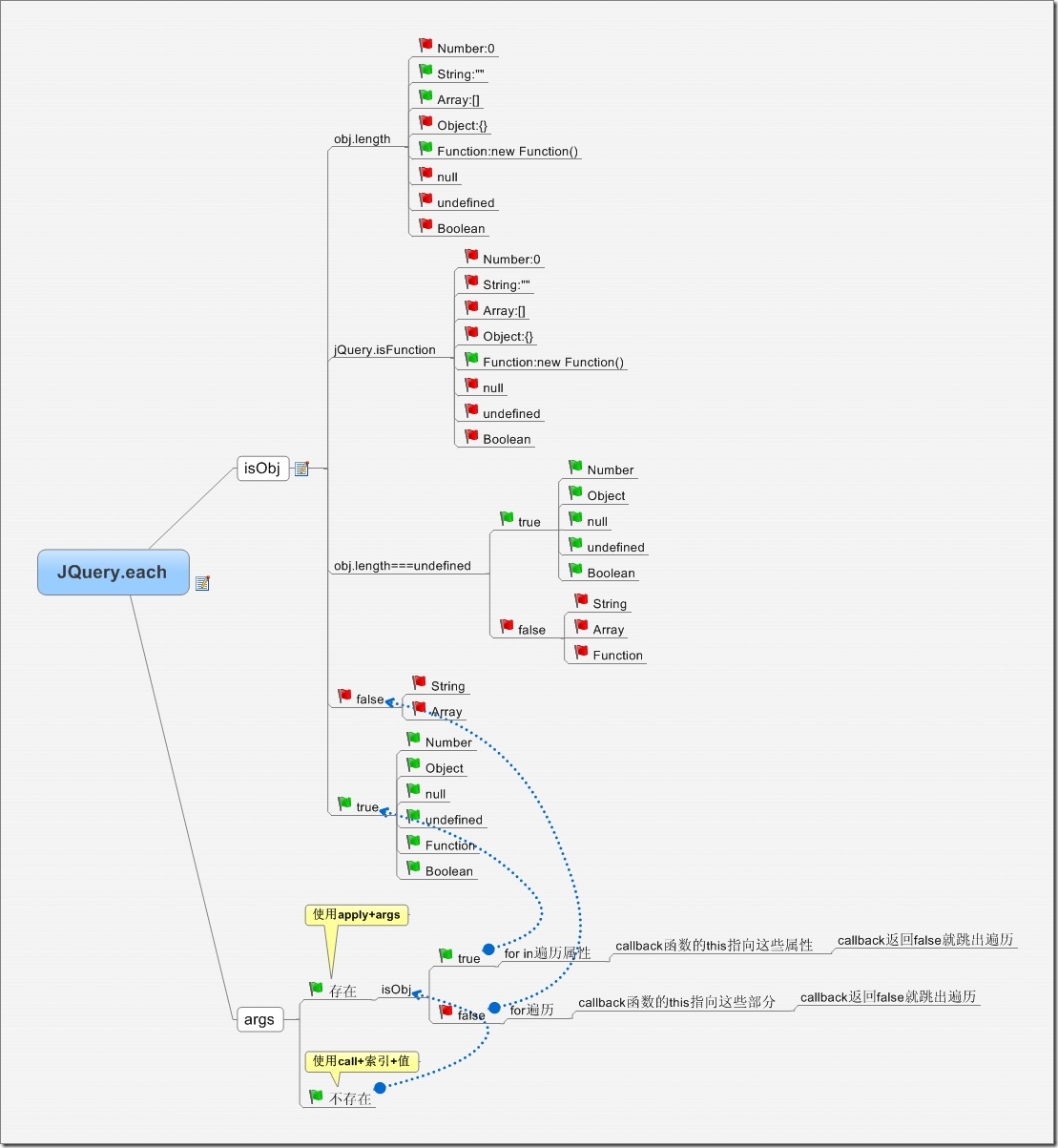
obj object is not an array
The biggest difference between this method and 1 is that the fn method will be executed one after another without considering the return value. In other words, all properties of the obj object will be called by the fn method, even if the fn function returns false. The parameters passed in the call are similar to 1.
jQuery.each=function( obj, fn, args ) {
if (args) {
if ( obj.length == undefined ){
for (var i in obj)
fn.apply( obj, args );
}else{
for ( var i = 0, ol = obj.length; i if ( fn.apply( obj, args ) === false )
break;
}
}
} else {
if ( obj.length == undefined ) {
for (var i in obj)
fn.call( obj, i, obj );
}else{
for ( var i = 0, ol = obj.length, val = obj[0]; i }
}
return obj;
}
It should be noted that the specific calling method of fn in each method is not simple fn(i, val) or fn(args), but fn.call(val,i,val) or fn.apply(obj .args), which means that in your own fn implementation, you can directly use this pointer to reference the sub-elements of the array or object.
Then how to jump out of each
It is more convenient to use each when jquery traverses the selected objects. There is an application that needs to break out of this loop after finding an object that meets the conditions.
To break out of a loop in JavaScript, break is generally used.
When a colleague encountered this problem, he subconsciously used break to get out of this cycle. The result is an error
SyntaxError: unlabeled break must be inside loop or switch
After checking, I should use one
Just return false in the callback function, most jq methods are like this
Returning 'false' will stop the loop (just like using 'break' in a normal loop).
Returns 'true' to jump to the next loop (just like using 'continue' in a normal loop).
 jquery实现多少秒后隐藏图片Apr 20, 2022 pm 05:33 PM
jquery实现多少秒后隐藏图片Apr 20, 2022 pm 05:33 PM实现方法:1、用“$("img").delay(毫秒数).fadeOut()”语句,delay()设置延迟秒数;2、用“setTimeout(function(){ $("img").hide(); },毫秒值);”语句,通过定时器来延迟。
 axios与jquery的区别是什么Apr 20, 2022 pm 06:18 PM
axios与jquery的区别是什么Apr 20, 2022 pm 06:18 PM区别:1、axios是一个异步请求框架,用于封装底层的XMLHttpRequest,而jquery是一个JavaScript库,只是顺便封装了dom操作;2、axios是基于承诺对象的,可以用承诺对象中的方法,而jquery不基于承诺对象。
 jquery怎么修改min-height样式Apr 20, 2022 pm 12:19 PM
jquery怎么修改min-height样式Apr 20, 2022 pm 12:19 PM修改方法:1、用css()设置新样式,语法“$(元素).css("min-height","新值")”;2、用attr(),通过设置style属性来添加新样式,语法“$(元素).attr("style","min-height:新值")”。
 jquery怎么在body中增加元素Apr 22, 2022 am 11:13 AM
jquery怎么在body中增加元素Apr 22, 2022 am 11:13 AM增加元素的方法:1、用append(),语法“$("body").append(新元素)”,可向body内部的末尾处增加元素;2、用prepend(),语法“$("body").prepend(新元素)”,可向body内部的开始处增加元素。
 jquery中apply()方法怎么用Apr 24, 2022 pm 05:35 PM
jquery中apply()方法怎么用Apr 24, 2022 pm 05:35 PM在jquery中,apply()方法用于改变this指向,使用另一个对象替换当前对象,是应用某一对象的一个方法,语法为“apply(thisobj,[argarray])”;参数argarray表示的是以数组的形式进行传递。
 jquery怎么删除div内所有子元素Apr 21, 2022 pm 07:08 PM
jquery怎么删除div内所有子元素Apr 21, 2022 pm 07:08 PM删除方法:1、用empty(),语法“$("div").empty();”,可删除所有子节点和内容;2、用children()和remove(),语法“$("div").children().remove();”,只删除子元素,不删除内容。
 jquery怎么去掉只读属性Apr 20, 2022 pm 07:55 PM
jquery怎么去掉只读属性Apr 20, 2022 pm 07:55 PM去掉方法:1、用“$(selector).removeAttr("readonly")”语句删除readonly属性;2、用“$(selector).attr("readonly",false)”将readonly属性的值设置为false。
 jquery on()有几个参数Apr 21, 2022 am 11:29 AM
jquery on()有几个参数Apr 21, 2022 am 11:29 AMon()方法有4个参数:1、第一个参数不可省略,规定要从被选元素添加的一个或多个事件或命名空间;2、第二个参数可省略,规定元素的事件处理程序;3、第三个参数可省略,规定传递到函数的额外数据;4、第四个参数可省略,规定当事件发生时运行的函数。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.





