 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Picture 3D display space (3DRoom) implemented by JavaScript_javascript skills
Picture 3D display space (3DRoom) implemented by JavaScript_javascript skillsPicture 3D display space (3DRoom) implemented by JavaScript_javascript skills
The program simulates such a three-dimensional space, and the pictures inside will be displayed in this space according to the three-dimensional coordinates.
I saw a 3DRoom effect a long time ago, which was achieved using complex calculations.
After studying the CSS3 transform in the previous article Image Transformation, I thought of a simpler way to implement it.
Compatible with: ie6/7/8, firefox 3.6.8, opera 10.6, safari 5.0.1, chrome 5.0
Effect preview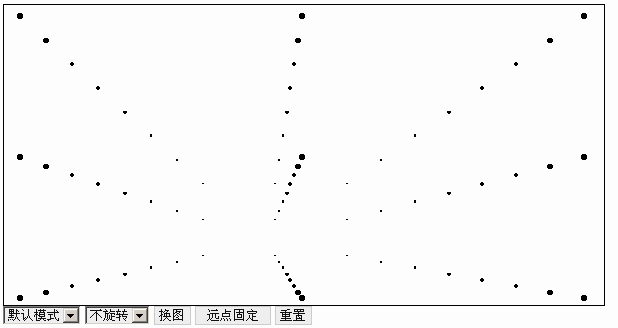
3DRoom
Procedure Description
【Implementation Principle】
The key to 3D effects is the realization of depth.
Think of the 3D container as a space composed of multiple layers of different depths. The dimensions of these layers are the same as the container by default.
A picture of the depth is placed in the layer, and each layer will be scaled and transformed according to the change of depth, resulting in a visual depth difference.
The ratio of the scaling transformation is gradually changed according to the closest point being 1 and the farthest point being 0.
The key point is that the size and coordinates of the image in the layer must be transformed simultaneously with the layer. This can be easily achieved through the CSS3 transform.
In this way, the image only needs to be set in size and positioned relative to the layer, avoiding the trouble of constantly adjusting the image size and positioning as the depth changes.
【Picture loading】
After the program is initialized, you can call the add method to add pictures.
The add method has two parameters: image address and parameter object, and also returns an image operation object.
The operation object contains the following attributes and methods to facilitate the operation of pictures:
img: picture element
src: picture address
options: parameter object
show: display picture method
remove : Remove image method
where options can set the following attributes:
attribute: Default value // Description
x: 0, // Horizontal displacement
y: 0, // Vertical displacement
z: 0,//Depth
width: 0,//Width
height: 0,//Height
scaleW: 1,//Width scaling
scaleH: 1//Height scaling
Among them, x and y are the displacement parameters of the horizontal and vertical coordinates respectively. The coordinate origin is in the middle of the bottom of the container, the horizontal coordinate is to the right, and the vertical coordinate is upward. The unit is px.
Z is the depth, used for calculation of scale, and the direction is from the near point to the origin.
The coordinate system is as shown below: 
After the image is loaded successfully, the _load image loading program will be executed.
First set the image style according to the parameters:
img.style.cssText = "position:absolute;border:0;padding:0;margin:0;-ms-interpolation-mode:nearest-neighbor;"
"z-index:" (99999 - z) ";width:" width "px;height:" height "px;"
"left:" (((clientWidth - width) / 2 opt.x) / clientWidth * 100).toFixed(5) "%; "
"top:" ((clientHeight - height - opt.y) / clientHeight * 100).toFixed(5) "%;";
Absolute positioning is necessary, and the width and height can be set according to the parameters.
Left and top are calculated based on coordinate parameters. They need to be expressed in percentage form, which will be explained in detail later.
Also add a _z attribute to the image to record the depth for easy calling.
Finally insert the layer corresponding to z and redisplay the layer.
【Layer Transformation】
After the image is loaded, the _insertLayer program will be used to insert the image into the corresponding layer.
_insertLayer has two parameters: image element and z-depth.
The program uses the _layers object to record the corresponding layer elements with z as the keyword.
If a layer has not been created at this depth, one will be created automatically:
layer = document.createElement("div");
layer.style.cssText = "position:absolute;border:0;padding:0;margin:0;left:0;top :0;visibility:hidden;background:transparent;width:" this._clientWidth "px;height:" this._clientHeight "px;";
The coordinates and size of the layer must be consistent with the container, because the coordinates of the inserted image are defined relative to the container, which makes it more convenient to use.
A _count attribute will also be added to record the number of pictures contained in the layer, and finally inserted into the container and recorded in the _layers object.
After obtaining the layer object, insert the image into the layer and add 1 to the _count.
Then you can use the _showLayer program to display the corresponding layer according to the depth.
The program contains three coordinate attributes: _x, _y, _z, which represent the offset of the three-dimensional coordinates of the container.
First get the scale of the z-depth through the _getScale method.
The ratio is greater than 1, which means that the image is behind the visual depth and theoretically should not be visible, so it is hidden; if it is less than 0, it means that it is too small to be seen and is hidden.
The _x and _y offsets also need to be recalculated based on the depth. The program has two offset methods: far point fixed and near point fixed.
Far point fixation means that the plane displacement offset gradually becomes smaller with depth, resulting in the effect of using the farthest point as the fixed point movement direction. Near point fixation is just the opposite.
To achieve this effect, as long as the displacement offset also changes with the proportion, that is, when the far point is fixed, the offset is proportional to the proportion, and when the far point is fixed, it is inversely proportional:
var moveScale = this.fixedFar ? scale : (1 - scale);
Then give these parameters to the _show program for processing and display the effect.
In order to maximize the use of layer elements, the program will put the layers without pictures into the _invalid discarded layer collection in the _remove picture removal program. When a layer needs to be inserted, it will be obtained from _invalid first.
【Scale ratio】
As mentioned above, the scaling ratio should gradually change according to the closest point being 1 and the farthest point being 0.
The program defaults to calculation based on the following formula:
But when you use this formula to achieve the 3DRoom effect, you will find that the proportion changes too quickly and is not as smooth as this 3DRoom.
After studying the code, I found that the formula it used is this:
where FL and Z are constants, that is, the formula can be expressed as:
According to this formula, when the depth is 0, the scale is 1, when the depth is constant, the scale is 0.5, and when the depth is infinity, the scale is 0.
You can refer to the following procedure for changing effects:
[Ctrl A Select all Note: If you need to introduce external Js, you need to refresh to execute
As you can see, the scaling ratio The default formula changes evenly, while the 3DRoom formula is first fast and then slow, and it becomes gradually slower, so it has that smooth feeling. According to the actual situation, you can also design a suitable formula yourself, as long as it changes between 1 and 0.
[css3 mode]
There are three zoom transformation methods in the program: css3, zoom and base. The program structure of the mode is similar to the previous one.
The css3 mode uses the CSS3 transform. In the previous article, we have introduced the use of the transform matrix for scaling and rotation. This time we also need the next two parameters for position transformation. Pay attention to the setting of the units for the last two parameters, which are explained in MDC's -moz-transform
:
Gecko (Firefox) accepts a
Safari (WebKit) and Opera currently support a unitless
It means that the displacement parameters tx and ty need to have units in Firefox, while WebKit and Opera only need numbers (without units, default px).
Using css3 mode, you can also rotate by modifying the _r arc attribute.
Finally set the matrix to implement the transformation:
layer.style [ css3Transform ] = "matrix("
( Cos * scale).toFixed(5) "," (Sin * scale).toFixed(5) ","
(-Sin * scale).toFixed(5 ) "," (Cos * scale).toFixed(5) ", "
Math.round(x) unit ", " Math.round(y) unit ")";
There is another issue to note here. The calculated ratio may be a very long decimal, which will cause problems when spelling characters.
For example, if you execute: alert(0.0000001), you will get "1e-7". JS will use this result to spell characters and get wrong results. So when splicing numbers and characters, those that can use integers should be converted into integers first, and decimals should also be converted using toFixed.
【zoom mode】
IE does not support transform yet, but there is a zoom style that can achieve similar effects.
In addition to ie, webkit (chrome/safari) also supports zoom, but the implementations of ie6/7, ie8 and webkit are not exactly the same.
.inner{ width:100px; height:100px; position:absolute; background:#0CF; zoom:0.5; top:50px; left:50px;}
The desired effect is achieved in ie6/7, but the position displayed in webkit is wrong.
The reason is that after using zoom, the left and top of the element will also be scaled, so it only needs to be recalculated according to the proportion.
Like the example above, just change left and top to 50/0.5, which is 100, and it will be correct.
ie8 is even more troublesome. The content inside is scaled according to zoom, but the left and top are still the original size.
I have been troubled by this problem for a long time, and finally found that it can be solved by using percentage positioning. This is why percentages are used for left and top when loading images.
For example, in the example, just modify the left and top, and change the left of the innermost div to 25%.
I also saw a problem in IE8. After zooming, the content was reduced, but the size of the container and internal elements did not change. Fortunately, this will not affect the display of the image. You also need to use left and top for positioning, so as not to trouble.
Also, if the size of the zoom element is set in percentage, the size of the element will not be scaled according to zoom.
There is another issue to pay attention to when calculating. As mentioned above, in webkit and ie8, left and top need to be divided by scale to correct. When scale is close to 0 to a certain extent, the result will become Infinity (infinity).
An error will occur when using Infinity to perform operations. This problem needs to be corrected:
top = Math.min(MAX, Math. max(-MAX, top )) | 0;
Where MAX is Number.MAX_VALUE (the maximum number that js can express).
【base mode】
There is also a base mode that is compatible with all browsers, using the traditional method, that is, calculating and setting the size and position of each image based on the scaling ratio.
Every time it is displayed, the images in the layer are traversed and the settings are calculated one by one.
The calculation requires the original position and size of the image. During the first calculation, the data will be saved in the _original attribute:
width: img.offsetWidth, height: img.offsetHeight,
left: img.offsetLeft, top: img.offsetTop
};
The size only needs to be scaled according to the ratio. In addition to calculating the relative layer scaling, the position also needs to add the relative container displacement. This is the same as the calculation in zoom mode.
After understanding the method of layer transformation, it is not difficult to understand this.
[zIndex]
In addition to scaling and positioning, depth also requires reasonable front and rear covering.
Front and rear masking needs to be implemented using zIndex, which can be set on the image or layer.
First and easiest way is to set it on the layer:
To achieve general 3D effects, you can set it up like this.
But when you click on the test, the ones in front of ff and webkit can be triggered, but the ones behind cannot be triggered, while ie and opera can be triggered both before and after.
ps: If img is replaced by div, the elements behind ie and opera cannot be triggered. The reason is still unclear.
In this way, if you want to trigger the picture event like 3DRoom, you cannot set zIndex on the layer.
You can also set it on the picture:
这样图片在所有浏览器都能正常触发,但在ie6/7层叠的效果失效了,看来在ie6/7只能在层用zIndex。
还有一个问题,如果给div加上变换效果:
div{-moz-transform:scale(1);-webkit-transform:scale(1);-o-transform:scale(1);}
那图片上的zIndex就会失效,那css3模式就只能在层设置zIndex了。
总结一下:
在css3模式肯定要在层设置zIndex,但图片也不能触发事件。
在zoom和base模式,应该在图片设置zIndex,但在ie6/7就要在层设置。
这样至少在base模式层叠和图片触发事件都是正常的。
【msInterpolationMode】
开始做的时候,效果在ie8下会很卡,但这个3DRoom却不会卡,最后发现是使用了-ms-interpolation-mode。
这个东西在aoao的文章中看过,但没想到可以用在这里。
在MSDN有msInterpolationMode的介绍:
Gets or sets the interpolation (resampling) method used to stretch images.
即获取或设置用于拉伸图像的插值(重采样)方法。
它有两个值:
nearest-neighbor:使用近邻插值模式。
bicubic:使用高品质的双三次插值模式。
这些名词比较专业,我们只要知道使用nearest-neighbor效率高但效果差,而bicubic效果好效率低就够了。
程序把它设为nearest-neighbor提高效率,这样在ie8中也不会卡了。
【拖动方向变换/滚轮深度变换】
程序扩展了拖动视觉变换和滚轮深度变换。
拖动和滚动的做法跟上一个的做法差不多,这里拖动是实现方向的变换,滚轮是实现深度的变换。
移动是通过修改_x和_y属性来实现,缩放是通过修改_z来实现。
修改属性之后再调用show方法显示效果。
使用技巧
【3DRoom】
在3DRoom效果中,因为要实现图片的触发事件,所以不能用css3模式,原因是上面提到的层叠问题。
上面也提到在ie8被zoom的元素尺寸不会改变,导致触发范围错误,所以也不用zoom模式。
使用base模式就不会有问题了。
在点击图片时,视觉会移动到图片上面,这个通过点击图片后根据本身的三维参数修改_x/_y/_z来实现:
i3D._z = -options.z | 0;
i3D._x = -options.x | 0;
i3D._y = options.y | 0;
i3D.show();
}
The picture will display a border when mouseover. In order to prevent the picture from being displaced after adding a border, a "-1px" margin is added and removed when mouseout.
There is still a gap between the effects of 3DRoom and the reference here. This article is mainly about the implementation and research of 3D effects.
【Mode Selection】
CSS3 mode is stable and supported by most browsers except IE.
Zoom mode has poor compatibility, but IE supports it.
base is the slowest, but has good compatibility and no bugs.
Generally, css3 mode should be used first, then zoom, and finally base. However, in cases like 3DRoom, the actual choice must be made.
When designing, IE planned to use Matrix filters, but some problems were discovered during development and the efficiency was too low, so it was not considered.
Instructions for use
When instantiating, there must be a container as a parameter:
Then call the i3D method to add the image:
Optional parameters are used to set the default attributes of the system, including:
Attribute: Default value // Description
mode: "css3|zoom|base", //Mode
x: 0,//Horizontal offset value
y: 0,//Vertical offset value
z: 0,//Depth offset value
r: 0,//Rotation angle (css3 support)
fixedFar: false,//Whether the far point is fixed
getScale: function(z){ return 1 - z / 1000; },//Get the scale method
onError: function(err){}//Error Execute when
The optional parameters of the add method have been explained in image loading.
also provides the following methods:
add: add pictures;
show: display effects;
reset: reset the default state;
dispose: destroy the program.
After adding the drag direction transformation or wheel depth transformation extension, the transformation range can be defined by setting relevant parameters.
Package download addresshttp://demo.jb51.net/js/Image3D/index.htm
Demo address/201010/yuanma/Image3D.rar
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMThis article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future ProspectsApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future ProspectsApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AMThe latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.




