标准参考
根据 W3C DOM 2 Events 描述,EventTarget 接口被所有支持 DOM 事件模型的节点(Node)实现。 该接口提供了 'addEventListener' 和 'removeEventListener' 方法,用来绑定或解绑一个 EventListeners 接口到一个 EventTarget。
DOM 2 Events 中定义了 Event 接口,用来提供事件的上下文信息,它提供了若干标准属性和方法。 实现 Event 接口的对象一般作为第一个参数传入事件处理函数,以用来提供当前事件相关的一些信息。
DOM 2 事件模型允许 DOM 实现支持事件的多模块,如果有必要,事件模型允许附加新的事件模块。 为了共同使用性的目的,DOM 会定义一个包含低级别的,依赖设备的事件模块、一个 UI 逻辑事件模块和一个文档变化事件模块的 UI 事件模块。 第三方实现(比如浏览器厂商)在定义一个新类型事件的时候,事件名称一定不能使用大小写无关的 'DOM' 字符串作开头,该前缀是为未来的 DOM 事件模块保留的。
DOM 2 已经定义了一个 UI 事件类型模块和一个鼠标事件类型的模块,它们分别对应 UEvent models differ across browsers_javascript tipsvent 和 MouseEvent 接口。 这两个接口提供了若干标准属性和方法,以获知事件发生时的一些信息。
关于 EventTarget 接口的详细信息,请参考 DOM 2 Events 1.3. Event listener registration。
关于 Event 接口的详细信息,请参考 DOM 2 Events 1.4. Event interface。
关于事件模块的详细信息,请参考 DOM 2 Events 1.6. Event module definitions。
问题描述
各浏览器对元素绑定、解绑事件监听器的方法,事件对象的获取,以及 Event 对象的实现上存在差异。
造成的影响
如果使用某浏览器特有的事件相关的属性及方法编写代码,则可能造成兼容性问题,导致代码报错,功能失效。
受影响的浏览器
| 所有浏览器 |
|---|
问题分析
1. 只有 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips Opera 支持使用 'attachEvent' 和 'detachEvent' 方法绑定和解绑事件监听器
根据 DOM 2 Events 中描述,节点使用 'addEventListener' 和 'removeEventListener' 方法绑定和解绑事件监听器,但 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips6 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips7 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips8 不支持这两个方法, 而使用 'attachEvent' 和 'detachEvent' 方法作为替代方案,Opera 两类方法都支持。Chrome Safari Firefox 只支持标准方法。
分析以下代码:
<button id="add" type="button">add event listener test</button>
<button id="remove" type="button">remove event listener test</button>
<div id="info"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var add = document.getElementById("add"),
remove = document.getElementById("remove"),
showMsgA = function(){showMsg("attachEvent")},
showMsgB = function(){showMsg("addEventListener")};
if(add.attachEvent){
add.attachEvent("onclick",showMsgA);
remove.attachEvent("onclick",removeE);
}
if(add.addEventListener){
add.addEventListener("click",showMsgB,false);
remove.addEventListener("click",removeE,false);
}
function removeE(){
if(add.detachEvent){
add.detachEvent("onclick",showMsgA);
showMsg("detachEvent");
}
if(add.removeEventListener){
add.removeEventListener("click",showMsgB,false);
showMsg("removeEventListener");
}
}
function showMsg(method){
document.getElementById("info").innerHTML += ("support " + method + "<br />");
}
</script>
依次点击 'add event listener test' >> 'remove event listener test' >> 'add event listener test',测试各浏览器对这些方法的支持,结果如下:
| Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips6 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips7 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips8 | 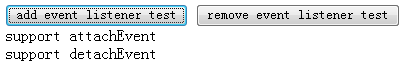 |
|---|---|
| Opera |  |
| Chrome Safari Firefox |  |
关于 'addEventListener' 和 'attachEvent' 有几点需要注意:
- Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips 不支持在捕获阶段触发事件监听器,'attachEvent' 方法没有提供参数说明是否响应在捕获阶段触发的事件;
- 'addEventListener' 和 'attachEvent' 都可以注册多个事件监听器;
- 在 Firefox Chrome Safari Opera 中给同一事件注册同一个事件监听器多次,重复注册的会被丢弃;而在 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips 中重复注册的事件监听器会被重复执行多次;
- 当给同一元素注册了多个事件监听器的时候,Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips6 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips7 的事件监听器执行顺序是随机的,Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips8 是倒序的,Firefox Chrome Safari Opera 是顺序的;
- 当元素注册的事件监听器中有非法的事件监听器时(非函数),在 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips Firefox 中会抛出异常,而在 Chrome Safari Opera 中则会忽略非法的事件监听器,继续执行其他的事件监听器。
2. 各浏览器获取事件对象的差异
DOM 2 Events 中规定使用事件监听器的第一个参数作为事件对象,而 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips Opera Chrome Safari 还支持通过 window.event 获取事件对象。
分析以下代码:
<button type="button" id="attach">attachEvent</button>
<button type="button" id="addE">addEventListener</button>
<button type="button" id="byclick">onClick</button>
<br>
INFO :
<div id="info"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $(id){return document.getElementById(id);}
var attach = $("attach"),
addE = $("addE"),
byClick = $("byclick");
attach.attachEvent && attach.attachEvent("onclick", handler);
addE.addEventListener && addE.addEventListener("click", handler, false);
byClick.onclick = handler;
function handler(){
var src = window === this ? window.event.srcElement : this, type = src.innerHTML;
window.event && showMsg(window.event.type, type + " + window.event");
arguments[0] && showMsg(arguments[0].type, type + " + arguments[0]");
}
function showMsg(type, msg){
$("info").innerHTML += (msg + "(type : " + type + ")<br />");
}
</script>
以上代码组合不同的事件监听器绑定方式和事件对象获取方法,测试各浏览器的支持程度。
依次点击 'attachEvent' >> 'addEventListener' >> 'onClick',结果如下:
| Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips6 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips7 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips8 |  |
|---|---|
| Chrome Safari |  |
| Opera |  |
| Firefox |  |
汇总测试结果如下表:1
| 事件对象获取方式 | Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips6 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips7 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips8 | Chrome Safari | Opera | Firefox |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| window.event | Y | Y | Y | N |
| arguments[0] | Y2 | Y | Y | Y |
注1: Y 表示支持该事件对象获取方式,N 表示不支持。
注2: 部分支持。
从上表出可以看出:
- 只有在使用 attachEvent 方法注册事件监听器的时候,Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips 才支持使用事件监听器传入的第一个参数作为事件对象的方式;
- Chrome Safari Opera 两种获取事件对象的方式都支持;
- Firefox 只支持获取事件对象的标准方式。
3. 各浏览器中事件对象的属性和方法的差异
Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips 对事件对象的标准属性和方法支持有限,针对大部分属性和方法,Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips 都提供了一套替代非标准的替代方案; 而 Firefox Chrome Safari Opera 除了全面支持事件对象的标准属性和方法外,还在不同程度上支持了 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips 提供的非标准替代方案。
以下代码检测了 Event、UEvent models differ across browsers_javascript tipsvent、MouseEvent 接口以及事件对象的非标准属性在各浏览器下的支持程度:
<button type="button" id="iEvent">Interface Event</button> <button type="button" id="iUIMouse">Interface UEvent models differ across browsers_javascript tipsvent & MouseEvent</button> <input type="text" id="nosK"> <p id="wrap" style="border:3px solid;padding:5px;width:500px;"><a id="nosCM" href="#"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="google.gif" class="lazy" alt="Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips"></a></p> <br>
| Interface Event | |
|---|---|
| Interface UEvent models differ across browsers_javascript tipsvent & MouseEvent |
|
| Non-standard & click |
|
| Non-standard & mouseover mouseout |
|
| Non-standard & keyCode |
执行以上测试代码,分别点击 'Interface Event' 按钮、'Interface UEvent models differ across browsers_javascript tipsvent & MouseEvent' 按钮和图片,鼠标移到图片上再移开,在文本框中输入 'a',得到结果整理如下表:3
| Interface & Non-standard | Property & method | Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips6 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips7 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips8 | Chrome Safari Opera | Firefox |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interface Event | type | Y | Y | Y |
| target | N | Y | Y | |
| currentTarget | N | Y | Y | |
| eventPhase | N | Y | Y | |
| bubbles | N | Y | Y | |
| cancelable | N | Y | Y | |
| timeStamp | N | Y | Y | |
| initEvent | N | Y | Y | |
| preventDefault | N | Y | Y | |
| stopPropagation | N | Y | Y | |
| Interface UEvent models differ across browsers_javascript tipsvent | view | N | Y | Y |
| detail | N | Y | Y | |
| initUEvent models differ across browsers_javascript tipsvent | N | Y | Y | |
| Interface MouseEvent | screenX | Y | Y | Y |
| screenY | Y | Y | Y | |
| clientX | Y | Y | Y | |
| clientY | Y | Y | Y | |
| ctrlKey | Y | Y | Y | |
| shiftKey | Y | Y | Y | |
| altKey | Y | Y | Y | |
| metaKey | N | Y | Y | |
| button | Y | Y | Y | |
| relatedTarget | N | Y | Y | |
| initMouseEvent | N | Y | Y | |
| Non-standard | cancelBubble | Y | Y | Y |
| offsetX | Y | Y | N | |
| offsetY | Y | Y | N | |
| returnValue | Y | Y | N | |
| srcElement | Y | Y | N | |
| x | Y | Y | N | |
| y | Y | Y | N | |
| fromElement | Y | Y | N | |
| toElement | Y | Y | N | |
| keyCode | Y | Y | Y |
注3: Y 代表事件对象支持该属性或方法,N 代表不支持。
从上表中可以看出:
- Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips 支持事件对象的所有非标准属性,不支持除 'type' 外 Event 接口的所有方法属性及方法,不支持 UEvent models differ across browsers_javascript tipsvent 接口的所有属性和方法,不支持 MouseEvent 接口的 'metaKey'、'relatedTarget' 属性和 'initMouseEvent' 方法;
- Chrome Safari Opera 支持事件对象的所有标准及非标准的属性和方法;
- Firefox 支持事件对象的所有标准属性和方法,但仅支持非标准属性中的 'cancelBubble' 和 'keyCode'。
需要注意的是:
- Firefox 不支持事件对象的 'returnValue' 属性,测试样例中虽然显示 'returnValue' 值为 false,但这仅仅是因为给事件对象添加了 'returnValue' 属性,并没有起到取消事件默认动作的作用,这从地址栏可以看出,多了 '#' 号,这是 A 标签的 'href' 属性造成的。
- 各浏览器对 Event 接口的 'timeStamp' 属性返回值都不同。
关于 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips 实现的事件对象非标准的属性及方法的详细信息,请参考 MSDN event Object。
关于 Firefox 对事件对象实现的详细信息,请参考 MDC event。
解决方案
1. 使用特性判断创建无兼容性问题的事件监听器绑定和解绑函数
如:
function addEvent(elem, type, handler, useCapture){
elem.addEventListener ? elem.addEventListener(type, handler, useCapture) :
elem.attachEvent("on" + type, handler);
}
function removeEvent(elem, type, handler, useCapture){
elem.removeEventListener ? elem.removeEventListener(type, handler, useCapture) :
elem.detachEvent("on" + type, handler);
}
2. 使用特性判断获得有效的事件对象
在事件监听器中判断传入的第一个参数或 window.event 是否有效,如:
function handler(e){
e = e || window.event;
}
3. 使用特性判断使用与标准对应的非标准方法及属性
尽管 Event models differ across browsers_javascript tips 对事件对象的标准属性和方法支持有限,但它自己实现的事件模型也基本能够替代或实现标准属性或方法的功能。
下表总结了部分与标准事件对象对应的,或可以实现标准属性或方法功能的非标准属性:
| Standard | Non-standard |
|---|---|
| target | srcElement |
| preventDefault() | returnValue |
| stopPropagation() | cancelBubble |
| relatedTarget | fromElement toElement |
另,标准的 'clientX' 属性和非标准的 'x' 属性作用是相同的,同样 'clientY' 和 'y' 也是。
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr
 Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AM
Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AMNode.js excels at efficient I/O, largely thanks to streams. Streams process data incrementally, avoiding memory overload—ideal for large files, network tasks, and real-time applications. Combining streams with TypeScript's type safety creates a powe
 Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AMThe differences in performance and efficiency between Python and JavaScript are mainly reflected in: 1) As an interpreted language, Python runs slowly but has high development efficiency and is suitable for rapid prototype development; 2) JavaScript is limited to single thread in the browser, but multi-threading and asynchronous I/O can be used to improve performance in Node.js, and both have advantages in actual projects.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.







