A brief introduction to AJAX:
AJAX refers to Asynchronous JavaScript And XML (Asynchronous JavaScript And XML), a web development technology for creating interactive web applications. AJAX allows JavaScript to communicate directly with the server using JavaScript's XMLHttpRequest object. This object allows your JavaScript to exchange data with the web server without reloading the page.
jQuery is a javascript framework, a lightweight encapsulation of javascript that is easy to understand.
Ajax is an asynchronous request technology combined with xml javascript. It can achieve dynamic refresh.
ajax preparation:
1.jquery download:
The latest download address of the official website: http://blog.jquery.com/2011/09/01/jquery-1- 6-3-released/
When downloading, select jQuery 1.6.3 Minified or jQuery 1.6.3 Uncompressed, right-click and select "Download using Thunder"
2. Main knowledge introduction
2.1. Ajax asynchronous transmission steps :
1. Use dom to get the value of the attribute in the text box
document.getElementById("id name").value
2. Create an XMLHttpRequest object
Depending on the browser, there are XMLHttpRequest, ActiveXObject two kinds of objects
3. Register callback function When registering the callback function, only the function name is required, do not add brackets
When registering the callback function, the data returned by the server will be obtained:
The first way: Get the server Plain text data output from the client
The second way: use responseXML to accept the DOM object of the XML data object
4. Set the connection information
5. Send the data and start interacting with the server
Post method/get method
2.2.ajax main method:
(1).getElementById("id attribute value"):
Get the object according to the specified id attribute value
(2 ).getElementsByTagName(tagname):
By searching for any HTML element in the entire HTML document, return a collection of elements with the specified name
(3). Selector:
The selector includes basic selector and hierarchical selection selector, attribute selector, etc. This program only has the basic selector #id, such as:
$("#myDiv"): Find the element with the ID "myDiv"
2.3.XMLHttpRequest object:
XMLHttpRequest can provide the function without reloading the page. When the page is loaded, the web page is updated, the client requests data from the server after the page is loaded, the server receives the data after the page is loaded, and sends data to the client in the background.
2.3.1. Method:
(1)overrideMimeType("text/html"):
Will override the header sent to the server, forcing text/xml as the mime-type
(2) open(method, url, async, username, password):
Initialize HTTP request parameters, such as URL and HTTP method, but do not send the request.
method parameter is the HTTP method used for the request, including GET, POST and HEAD;
url parameter is the body of the request
async parameter indicates whether the request uses synchronous or asynchronous, false request is synchronous, true request is The asynchronous
username and password parameters are optional and provide authentication qualifications for the authorization required by the url. If specified, they override any qualifications specified by url itself.
(3)send(body):
Send an HTTP request, using the parameters passed to the open() method, and the optional request body passed to the method
send(body) If by calling open() ) The specified HTTP method is POST or PUT, and the body parameter specifies the request body, as a string or Document object. If the request body is not required, this parameter will be null.
If the async parameter of the previously called open() is false, this method will block and will not return until readyState is 4 and the server's response is fully received.
If the async parameter is true, or this parameter is omitted, send() returns immediately, and as described later, the server response will be processed in a background thread
(4)setRequestHeader(name, value):
Sets or adds an HTTP request to an open but unsent request
The name parameter is the name of the header to be set. This parameter should not include whitespace, colons, or newlines.
The value parameter is the value of the header. This parameter should not include newlines
2.3.2. Attributes:
(1)onreadystatechange:
The event handler function called every time the readyState attribute changes. It may also be called multiple times when readyState is 3.
(2)readyState:
The status of the HTTP request. When an XMLHttpRequest is first created, the value of this attribute starts from 0 until a complete HTTP response is received, and the value increases to 4.
Each of the 5 states has an associated informal name. The following table lists the states, names and meanings:
The value of readyState will not be decremented except when a request is being processed The abort() or open() method is called during the process. Each time the value of this property is increased, the onreadystatechange event handler is triggered.
(3)status:
The HTTP status code returned by the server, such as 200 for success, and 404 for "Not Found" error. Reading this property when readyState is less than 3 will cause an exception.
(4)responseText:
The response body (excluding headers) received from the server so far, or an empty string if no data has been received yet.
If readyState is less than 3, this property is an empty string.When readyState is 3, this property returns the response part that has been received so far. If readyState is 4, this property holds the complete response body.
If the response contains a header specifying the character encoding for the response body, use that encoding. Otherwise, Unicode UTF-8 is assumed
(5)responseXML: Response to the request, parsed to XML and returned as a Document object
Code example:
Note: This example consists of a frontend and a backend , the backend uses servlet implementation, but does not go to the database to verify the data. The front desk is composed of html and javascript. The front desk verification adopts two methods. One is to use ajax encapsulated by jquery to realize the dynamic verification of the form. The second is to use the XMLHttpRequest object to realize the dynamic verification of the form. The difference between the two verification methods is just that the javascript script is different. , the front page and the background servlet are the same.
Front-end ajax.html
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
< ;/head>
Username:
Background AJAXServer.java:
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http. HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class AJAXServer extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out= response.getWriter();
//1. Get parameters
String old=request.getParameter("name");
//2. Check if there is a problem
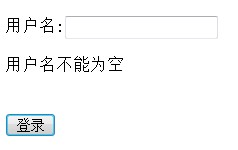
if(old==null ||old.length()==0){
out.println("User name cannot be empty");
}else{
//3. Verification operation
String name= old;
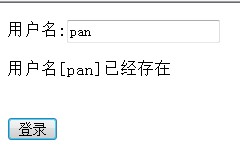
if(name.equals("pan")){
//4. Differences from traditional applications. This step requires returning the data that the user is interested in to the page, rather than to a new page
out.println("Username[" name "] already exists");
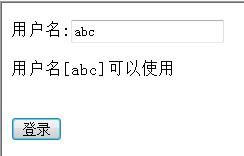
}else{
out .println("Username[" name "] can be used");
}
}
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request,response);
}
}
javascript:verify.js
function verify1(){
//1. Get Content in the text box
//document.getElementById("username");
var jqueryObj= $("#username");
//Get the value of the node
var userName=jqueryObj. val();
//2. Send the data in the text box to the server's servlet
$.get("AJAXServer?name=" username,null,callback);
}
function callback(data){
//3. Receive the data returned by the server
//4. Dynamically display the data returned by the server on the page
//Find the node that saves the information
var resultObj=$("#result");
resultObj.html(data);
}
//Verification method 2 is to write verification method 1 in a method, the effect is the same, both It is ajax dynamic verification form data encapsulated by jquery
function verify2(){
$.get("AJAXServer?name=" $("#username").val(),null,function(data) {
$("#result").html(data);
});
}
var xmlhttp;//Define a global variable
function verify3(){
//1. Use dom to get the value of the attribute in the text box
var username=document.getElementById("username").value;
//2. Create an XMLHttpRequest object
//You need to write different codes in different ways to create this object based on the differences between IE and other types of browsers
if (window. Fix the BUG of the browser
if(xmlhttp.overrideMimeType){
xmlhttp.overrideMimeType("text/html");
}
} else if(window.ActiveXObject){
// For IE6, IE5.5, IE5
//Two control names used to create XMLHttpRequest objects, stored in a js array, the front version is newer
var activexName=["MSXML2.XMLHTTP ","Microsoft.XMLHTTP"];
for(var i=0;i
/ /If the creation fails, an exception will be thrown, and then you can continue to loop and continue to try to create
try{
xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject(activexName[i]);
break;
}catch(e) {
}
}
}
if(!xmlhttp){
alert("XMLHttpRequest object creation failed! ! ");
return;
}
//3. Register the callback function. When registering the callback function, only the function name is required, do not add brackets
//We need to register the function name. If you add brackets, the return value of the function will be registered, which is wrong
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=callback3;
//4. Set the connection information
xmlhttp.open("GET","AJAXServer?name =" username,true);
//5. Send data and start interacting with the server
xmlhttp.send(null);//The username is encapsulated in the GET method url, so you only need to send one null
//POST method to request and send data
}
//Callback function
function callback3(){
//Determine whether the interaction of the object’s status is completed
if(xmlhttp.readyState==4){
//Determine whether the http interaction is successful
if(xmlhttp.status== 200) {
//Get the data returned by the server
//The first way: get the plain text data output by the server
var responseText=xmlhttp.responseText;
//Display the data Find the element node corresponding to the div tag on the page through dom
var divNode=document.getElementById("result");
//Set the content of html in the element node
divNode.innerHTML=responseText ;
}
}
}
web.xml
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com /xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
version="2.5">
web.xml
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment