 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial A brief discussion on Javascript mouse and wheel events_javascript skills
A brief discussion on Javascript mouse and wheel events_javascript skillsMouse event may be the most commonly used event in web pages, because the mouse is the most commonly used navigation device. There are 9 mouse events defined on DOM3 level events. They are:
Click: Triggered when the user clicks the primary mouse button, usually the left mouse button or presses the Enter key.
dbclick: Triggered when the user double-clicks the primary mouse button. This event is not defined in DOM2 level events but is generally supported, and was later standardized in DOM3 level.
Mousedown: It will be triggered when the user presses any mouse button. This event cannot be triggered through the keyboard.
Mouseenter: Triggered when the mouse icon moves from outside the element to within the element boundary. This event does not support bubbling and is triggered when the mouse moves on the upper surface of the element. This event does not belong to DOM2 level event, but is an event added after DOM level 3. IE, FF9, and opera support this event.
mouseleave: This event is triggered when the mouse is over the element and then moves out of the element boundary. It is the same as the mouseenter event. It does not support bubbling. It is not triggered above the element. This event does not belong to DOM2 level events, but belongs to DOM3. An event added later, IE, FF9, and opera support this event.
Mousemove: Triggered repeatedly when the mouse moves around an element. This event cannot be triggered through keyboard events.
Mouseout: Triggered when the mouse is over an element and then moves over other elements. The element moves outside the bounds of the original element, or onto a child element of the original element. This event cannot be triggered by the keyboard.
Mouseover: Triggered when the user moves the mouse from outside the boundary of an element to within the boundary of the element for the first time. This event cannot be triggered through the keyboard.
Mouseup: Triggered when the user releases the mouse button. This event cannot be triggered through the keyboard.
All elements on the page support mouse events. Except for mouseenter and mouseleave, all events bubble up, and their default behaviors can be canceled. But canceling the default behavior of mouse events may affect other events, because some mouse events are dependent on each other.
Only when a mousedown event and a mouseup event are triggered on the same element can the mouse click event be triggered; assuming either event is canceled, the click event will never be triggered. A similar principle is that the dbclick event depends on the click event. If either of the two consecutive click events is canceled, dbclick will not be triggered. Commonly used mouse events are as follows:
1.mousedown, 2.mouseup, 3.click, 4.mousedown, 5.mouseup, 6.click, 7.dbclick.
Whether it is click or dbclick event, both depend on the triggering of other events.
You can use the following code to determine whether the browser supports mouse events on dom2 events,
var isSupport = document.implementation.hasFeature('MouseEvents', '2.0');
However, it is worth noting that the detection on dom3 level events is somewhat different:
var isSupport = document.implementation.hasFeature('MouseEvent','3.0');
The mouse event also contains a subclass event, the wheel event (wheel event). The wheel event contains only one event, the mousewheel event, which reflects the interaction of the mouse wheel or other devices, such as the Mac's touchpad.
b) Associated elements
For mouseover and mouseout events, there are also event-related elements. The actions performed by these events include, move The mouse moves from inside the bounds of one element to inside the bounds of another element. Taking the mouseover event as an example, its main target element is the element that the mouse will move to, and the associated element is the element that loses the mouse. Similarly for the mouseout event, the main target is the element that the mouse moves out, and the related element is the element that gets the mouse. The DOM provides information about the related element through the relatedTarget attribute on the event object. IE8 or earlier versions of IE do not support the relatedTarge attribute. , but provides the fromElement attribute and toElement attribute with similar functions. Under IE, when the mousemove event is triggered, the fromElement of the event object contains the associated element. When the mouseout event is triggered, the toElement attribute of the event contains the associated element. All attributes are supported in IE9. A cross-browser getRelatedTarget method can be written like this:
var eventUtil = {
getRelateTarget:function(event){
if (event.relatedTarget) {
return event.relatedTarget;
}else if(event.fromElement) {
return event.fromElement;
}else if(event.toElement){
return event.toElement;
}else {
return null;
}
}
};
c)buttons
The click event will only be triggered when the mouse primary button clicks on an element (or when an element gets focus and presses Enter key), for mousedown and mouseup, there is an attribute button on the event object event, which can determine which key is pressed or released. There are usually three possible button attribute values implemented in the DOM:
0: represents the primary key,
1: represents the scroll wheel,
2: represents the secondary key.
Generally speaking, the primary key refers to the left mouse button, and the secondary key represents the right mouse button.
Starting from IE8, button attributes are also provided, but they have completely different value ranges:
0: No button is pressed,
1: The primary key has been pressed down,
2: represents the secondary key has been pressed,
3: both the main key and secondary keys have been pressed,
4: represents the middle key has been pressed,
5: Indicates that the primary key and middleware are pressed,
6: Indicates that the secondary key and middle key are pressed,
7: Indicates that all three keys are pressed .
It can be seen that the value range of the button attribute under the DOM model is much simpler than the value range under the IE model, and I personally feel that the operation situation under IE is slightly abnormal.
d) Other event information
On DOM2 level events, the detail attribute is also provided for the event object event to provide more event information, such as click events For example, detail can record the number of clicks at the same pixel position. The value of detail is counted from 1, and one is added after each click. If the mouse moves between mousedown and mouseup, this value will be cleared.
I will write these about mouse events first, and will slowly complete them in the future.
 m590鼠标USB连接上用不了怎么办Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:18 PM
m590鼠标USB连接上用不了怎么办Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:18 PMm590鼠标USB连接上用不了的解决办法:1、查看蓝牙设备,看是否识别为罗技优联连接器,然后下载Logitech Unifying优联软件,运行该软件;2、删除蓝牙设备,再添加蓝牙设备,重新连接m590即可。
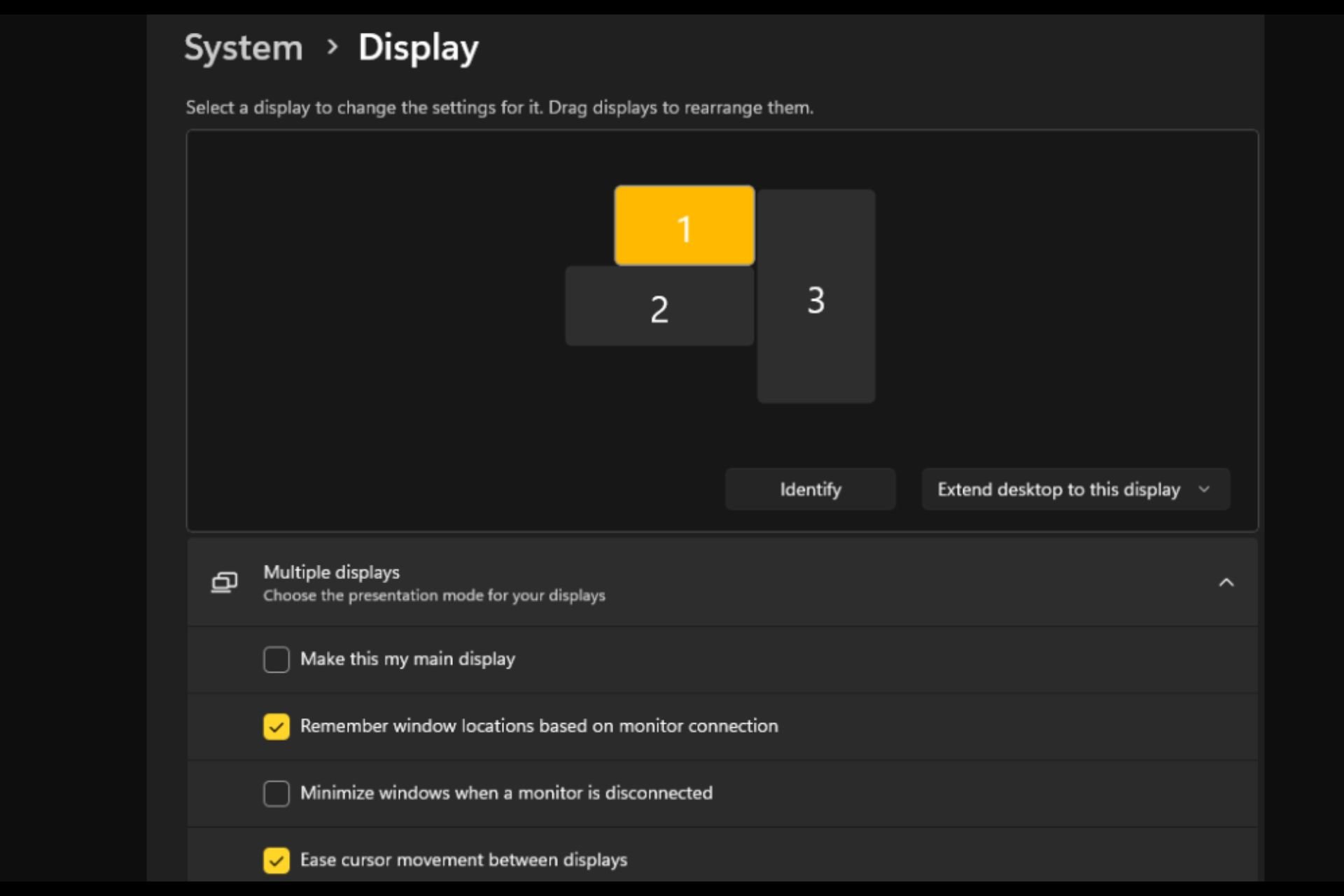 打开或关闭 Easy T光标在 Windows 11 上的显示器之间移动Sep 30, 2023 pm 02:49 PM
打开或关闭 Easy T光标在 Windows 11 上的显示器之间移动Sep 30, 2023 pm 02:49 PM通常,当使用双显示器设置时,会出现如何无缝地让光标从一个显示器移动到另一个显示器的问题。当您的鼠标光标在没有您控制的情况下从一个显示器移动到另一个显示器时,这可能会令人沮丧。如果Windows默认情况下允许您轻松地从一个显示器切换到另一个显示器,那不是很好吗?幸运的是,Windows11具有一个功能可以做到这一点,并且不需要很多技术知识来执行它。缓和光标在显示器之间的移动有什么作用?此功能有助于防止将鼠标从一台显示器移动到另一台显示器时光标漂移。默认情况下,该选项处于禁用状态。如果将其打开,鼠标
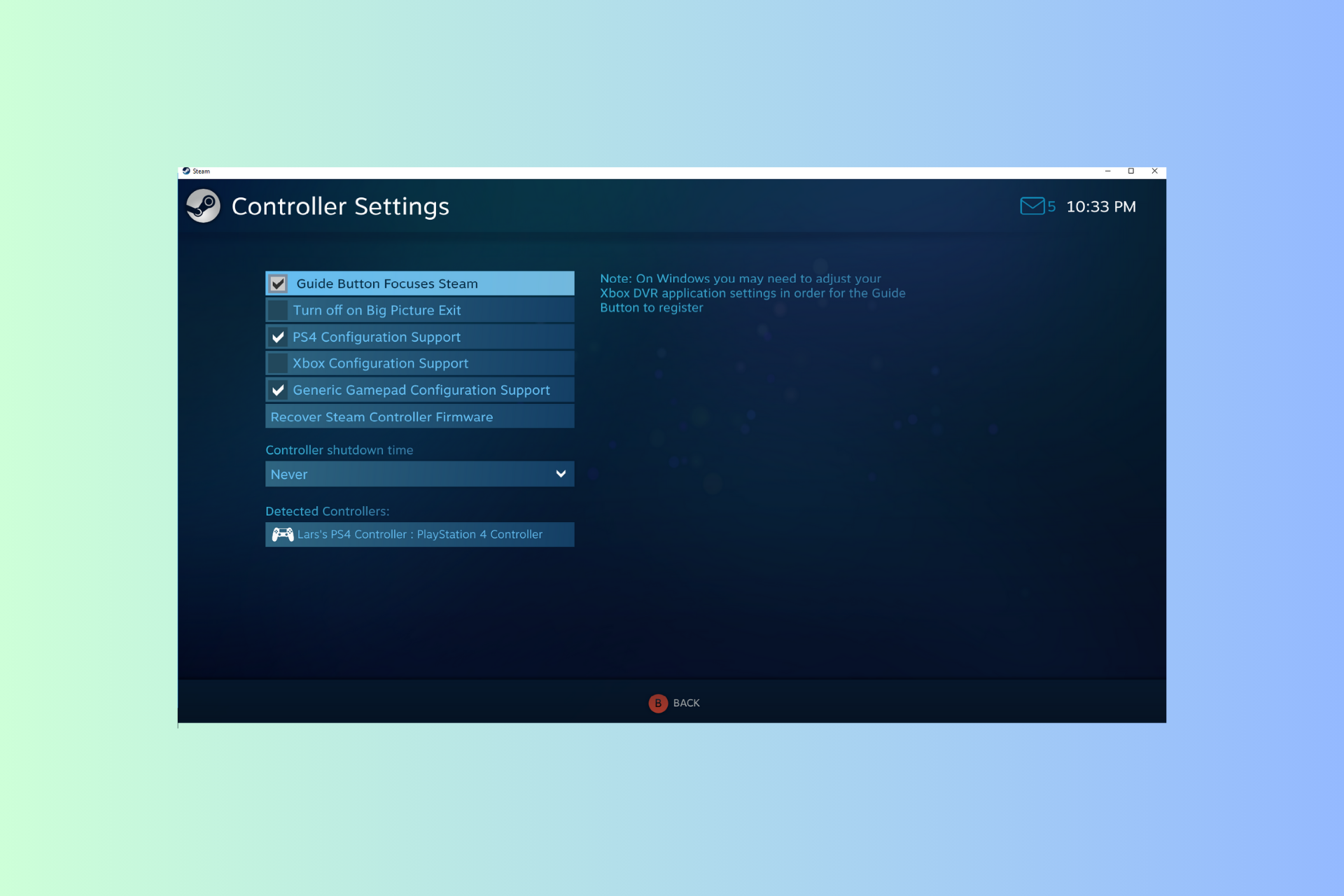 Windows 11 控制器像鼠标一样运行?如何阻止它Sep 26, 2023 pm 04:53 PM
Windows 11 控制器像鼠标一样运行?如何阻止它Sep 26, 2023 pm 04:53 PM如果您的控制器在加载游戏时就像Windows11上的鼠标一样,扰乱了您的游戏体验,本指南可以提供帮助!在解释其可能的原因后,我们将立即讨论一些经过专家测试的解决方案,并附上分步说明。为什么我的控制器像鼠标一样工作?Steam上的控制器设置配置错误。在控制面板设置中作为鼠标启用。软件冲突。过时的驱动程序。如何阻止我的控制器在Windows11上像鼠标一样运行?在移动详细的故障排除步骤之前,请尝试以下修复程序以消除问题:重新启动计算机并检查挂起的Windows更新。先让游戏加载,然后插入或连接控制器
 mac鼠标滚轮相反怎么办Mar 16, 2023 pm 05:44 PM
mac鼠标滚轮相反怎么办Mar 16, 2023 pm 05:44 PMmac鼠标滚轮相反的解决办法:1、打开mac电脑,点击屏幕的苹果标志,然后选择“系统偏好设置”;2、在“系统偏好设置”窗口中,选择“鼠标”;3、在“鼠标”窗口中,将“滚动方向:自然”前面的勾去掉即可。
 电脑鼠标能动但点什么都没反应怎么办Jul 06, 2023 pm 02:23 PM
电脑鼠标能动但点什么都没反应怎么办Jul 06, 2023 pm 02:23 PM电脑鼠标能动但点什么都没反应解决方法:1、检查鼠标连接,确认鼠标连接到电脑的USB接口上;2、重启电脑,断开鼠标连接,然后重新启动电脑并重新连接鼠标;3、更换鼠标电池或充电,如果使用的是无线鼠标,可能是因为鼠标电池电量低了,导致无法正常工作。
 鼠标左键失灵Jul 20, 2023 pm 03:21 PM
鼠标左键失灵Jul 20, 2023 pm 03:21 PM鼠标是我们使用电脑时必不可少的设备。鼠标是否易于使用也直接关系到我们的操作体验、工作效率和游戏体验,鼠标左键使用最频繁。如何解决鼠标左键失灵、鼠标左键不敏感的问题?让我们来看看解决方案。解决方法一:开机后鼠标左键暂时失灵。1.打开任务管理器,如果鼠标将来可以使用,那就是鼠标的问题!这是一个系统过程问题——conime.exe问题!conime.exe过程,通常刚刚开始,只有一段时间,是一个输入编辑器,允许用户使用标准键盘输入复杂的字符和符号。关闭它,无法输入汉字。如果您不想要这个过程,您可以禁止
 Win10鼠标dpi怎么调?Win10系统调节鼠标灵敏度实例教程Jul 11, 2023 pm 03:13 PM
Win10鼠标dpi怎么调?Win10系统调节鼠标灵敏度实例教程Jul 11, 2023 pm 03:13 PMWin10鼠标dpi怎么调?鼠标dpi实际上简单点来说便是鼠标的敏感度。dpi值越高,鼠标灵敏度越高。许多好朋友全是应用Win10系统,要想了解如何修改鼠标dpi值,小编今日就告知各位朋友们怎么修改鼠标dpi值,期待对您有协助。Win10系统调节鼠标灵敏度实例教程1.鼠标右键点一下菜单栏,挑选设定,进到Windows设定页面,挑选开启机器设备;2.在左边的选择栏中转换到鼠标,随后在右边有关设定下挑选别的鼠标选择项;3.在鼠标特性对话框,将上边菜单栏转换到表针选择项,在下边挑选表针挪动速率来调节鼠
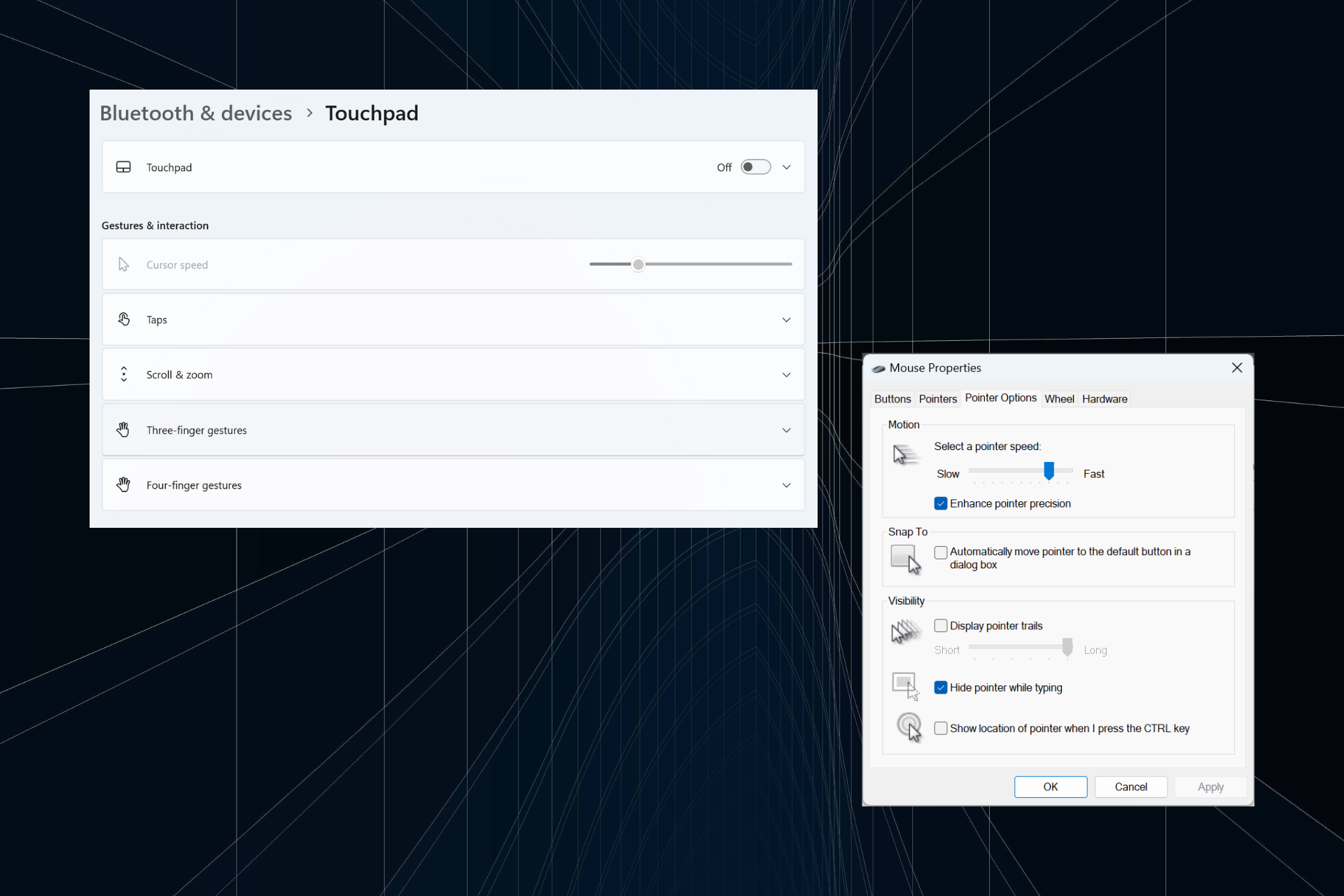 解决:在 Windows 11 上键入时光标持续向左移动的问题Sep 10, 2023 pm 09:29 PM
解决:在 Windows 11 上键入时光标持续向左移动的问题Sep 10, 2023 pm 09:29 PM不规则或无意的鼠标移动会影响任务并令人愤怒。在某些情况下,用户发现在Windows11中键入时光标不断向左移动。在命名或重命名文件时,它更加突出。令人惊讶的是,根据论坛上的报道,这个问题很普遍。但通常情况下,它被证明是用户端的问题,尽管我们不能排除操作系统的问题。为什么我的光标一直向左移动?鼠标设置配置错误您不停地敲击触摸板,或者您的手擦过它。过时、损坏或不兼容的鼠标驱动程序。已安装的Windows11版本中的错误。触发冲突的第三方应用。如何在Windows11上键入时阻止光标跳来跳去?在我们进


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version





