Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Javascript image processing—smoothing processing implementation principle_javascript skills
Javascript image processing—smoothing processing implementation principle_javascript skillsJavascript image processing—smoothing processing implementation principle_javascript skills
Foreword
In the last article, we explained the virtual edge of the image. This article starts with smoothing (that is, blurring) processing.
Basic Principles
Here is a direct reference to the relevant content of OpenCV 2.4 C smoothing processing and OpenCV 2.4 C edge gradient calculation:
Smoothing, also called blurring, is a simple and frequently used image processing method.
A filter
is required for smoothing. The most commonly used filter is the linear filter, the output pixel value of the linear filtering process (for example:) is the weighted average of the input pixel value (for example:
):
, which is just a weighting coefficient.
is called the kernel
This involves an operation called "convolution", so what is convolution?
Convolution is an operation performed between each image block and a certain operator (kernel).
Nuclear? !
nbsp;dsds
The kernel is a fixed-size numerical array. The array has an anchor point
, which is usually located in the center of the array.
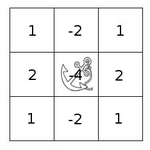
But how does this work?
If you want to get the convolution value at a specific position of the image, you can calculate it with the following method:
Place the anchor point of the kernel on the pixel at that specific position, and at the same time, other values in the kernel coincide with each pixel in the neighborhood of the pixel; multiply each value in the kernel by the corresponding pixel value, and add the products Add; place the result on the pixel corresponding to the anchor point; repeat the above process for all pixels in the image.
The above process is represented by the formula as follows:
What about convolution on the edge of the image?
Before calculating the convolution, you need to create virtual pixels by copying the boundary of the source image, so that there are enough pixels at the edge to calculate the convolution. This is why the previous article required a virtual edge function.
Mean Smoothing
Mean smoothing is actually a convolution operation in which the kernel elements are all 1, and then divided by the size of the kernel. The mathematical expression is:

Let’s implement the mean smoothing function blur:
function blur(__src, __size1, __size2, __borderType, __dst){
if(__src.type && __src.type == "CV_RGBA"){
var height = __src.row,
width = __src. col,
dst = __dst || new Mat(height, width, CV_RGBA),
dstData = dst.data;
var size1 = __size1 || 3,
size2 = __size2 || size1,
size = size1 * size2;
if(size1 % 2 !== 1 || size2 % 2 !== 1){
console.error("size must be an odd number");
return __src;
}
var startX = Math.floor(size1 / 2),
startY = Math.floor(size2 / 2);
var withBorderMat = copyMakeBorder(__src, startY, startX , 0, 0, __borderType),
mData = withBorderMat.data,
mWidth = withBorderMat.col;
var newValue, nowX, offsetY, offsetI;
var i, j, c , y, x;
for(i = height; i--;){
offsetI = i * width;
for(j = width; j--;){
for(c = 3; c--;){
newValue = 0;
for(y = size2; y--;){
offsetY = (y i) * mWidth * 4;
for(x = size1; offsetI) * 4 c] = newValue / size;
}
dstData[(j offsetI) * 4 3] = mData[offsetY startY * mWidth * 4 (j startX) * 4 3];
}
}
}else{
console.error("Type not supported. ");
}
return dst;
}
Where size1 and size2 are the horizontal and vertical sizes of the core respectively, and must be positive odd numbers.
Gaussian smoothing
The most useful filter (although not the fastest). Gaussian filtering is to convolve each pixel of the input array with a Gaussian kernel
and treat the convolution sum as the output pixel value.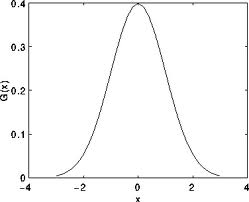
Referring to the one-dimensional Gaussian function, we can see that it is a function that is large in the middle and small on both sides.
So the weighting number of the Gaussian filter is large in the middle and small around it.
The two-dimensional Gaussian function is:

where
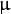 is the mean (the position corresponding to the peak value),
is the mean (the position corresponding to the peak value),
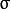 represents the standard deviation (variable
represents the standard deviation (variable
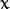 and variables
and variables
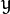 Each has a mean and each has a standard deviation).
Each has a mean and each has a standard deviation).
Here we refer to the implementation of OpenCV, but there should be room for optimization because the separation filter has not been used yet.
First we make a getGaussianKernel to return a one-dimensional array of Gaussian filters.
function getGaussianKernel(__n, __sigma){
var SMALL_GAUSSIAN_SIZE = 7,
smallGaussianTab = [[1],
[0.25, 0.5, 0.25],
[0.0625, 0.25, 0.375, 0.25, 0.0625],
[0.03125, 0.10937 5,0.21875, 0.28125, 0.21875, 0.109375, 0.03125]
];
var fixedKernel = __n & 2 == 1 && __n & gt; 1] : 0;
var sigmaX = __sigma > 0 ? __sigma : ((__n - 1) * 0.5 - 1) * 0.3 0.8,
scale2X = -0.5 / (sigmaX * sigmaX),
sum = 0;
var i, x, t, kernel = [];
for(i = 0; i x = i - (__n - 1) * 0.5;
t = fixedKernel ? fixedKernel[i] : Math.exp(scale2X * x * x);
kernel[i] = t;
sum = t;
}
sum = 1 / sum;
for(i = __n; i--;){
kernel[i] *= sum;
}
return kernel;
};
Then through two one-dimensional arrays, a complete Gaussian kernel can be calculated, and then using the loop method used in blur, The Gaussian smoothed matrix can be calculated.
function GaussianBlur(__src, __size1, __size2, __sigma1, __sigma2, __borderType, __dst){
if(__src.type && __src.type == "CV_RGBA"){
var height = __src.row,
width = __src.col,
dst = __dst || new Mat(height, width, CV_RGBA),
dstData = dst.data;
var sigma1 = __sigma1 || 0,
sigma2 = __sigma2 || __sigma1;
var size1 = __size1 || Math.round(sigma1 * 6 1) | 1,
size2 = __size2 || Math.round(sigma2 * 6 1) | 1,
size = size1 * size2;
if(size1 % 2 !== 1 || size2 % 2 !== 1){
console.error("size必须是奇数。");
return __src;
}
var startX = Math.floor(size1 / 2),
startY = Math.floor(size2 / 2);
var withBorderMat = copyMakeBorder(__src, startY, startX, 0, 0, __borderType),
mData = withBorderMat.data,
mWidth = withBorderMat.col;
var kernel1 = getGaussianKernel(size1, sigma1),
kernel2,
kernel = new Array(size1 * size2);
if(size1 === size2 && sigma1 === sigma2)
kernel2 = kernel1;
else
kernel2 = getGaussianKernel(size2, sigma2);
var i, j, c, y, x;
for(i = kernel2.length; i--;){
for(j = kernel1.length; j--;){
kernel[i * size1 j] = kernel2[i] * kernel1[j];
}
}
var newValue, nowX, offsetY, offsetI;
for(i = height; i--;){
offsetI = i * width;
for(j = width; j--;){
for(c = 3; c--;){
newValue = 0;
for(y = size2; y--;){
offsetY = (y i) * mWidth * 4;
for(x = size1; x--;){
nowX = (x j) * 4 c;
newValue = (mData[offsetY nowX] * kernel[y * size1 x]);
}
}
dstData[(j offsetI) * 4 c] = newValue;
}
dstData[(j offsetI) * 4 3] = mData[offsetY startY * mWidth * 4 (j startX) * 4 3];
}
}
}else{
console.error("不支持的类型");
}
return dst;
}
中值平滑
中值滤波将图像的每个像素用邻域 (以当前像素为中心的正方形区域)像素的
中值代替 。依然使用blur里面用到的循环,只要得到核中的所有值,再通过sort排序便可以得到中值,然后锚点由该值替代。
function medianBlur(__src, __size1, __size2, __borderType, __dst){
if(__src.type && __src.type == "CV_RGBA"){
var height = __src.row,
width = __src.col,
dst = __dst || new Mat(height, width, CV_RGBA),
dstData = dst.data;
var size1 = __size1 || 3,
size2 = __size2 || size1,
size = size1 * size2;
if(size1 % 2 !== 1 || size2 % 2 !== 1){
console.error("size必须是奇数");
return __src;
}
var startX = Math.floor(size1 / 2),
startY = Math.floor(size2 / 2);
var withBorderMat = copyMakeBorder(__src, startY, startX, 0, 0, __borderType),
mData = withBorderMat.data,
mWidth = withBorderMat.col;
var newValue = [], nowX, offsetY, offsetI;
var i, j, c, y, x;
for(i = height; i--;){
offsetI = i * width;
for(j = width; j--;){
for(c = 3; c--;){
for(y = size2; y--;){
offsetY = (y i) * mWidth * 4;
for(x = size1; x--;){
nowX = (x j) * 4 c;
newValue[y * size1 x] = mData[offsetY nowX];
}
}
newValue.sort();
dstData[(j offsetI) * 4 c] = newValue[Math.round(size / 2)];
}
dstData[(j offsetI) * 4 3] = mData[offsetY startY * mWidth * 4 (j startX) * 4 3];
}
}
}else{
console.error("类型不支持");
}
return dst;
};
 The Future of Python and JavaScript: Trends and PredictionsApr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AM
The Future of Python and JavaScript: Trends and PredictionsApr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AMThe future trends of Python and JavaScript include: 1. Python will consolidate its position in the fields of scientific computing and AI, 2. JavaScript will promote the development of web technology, 3. Cross-platform development will become a hot topic, and 4. Performance optimization will be the focus. Both will continue to expand application scenarios in their respective fields and make more breakthroughs in performance.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and ToolsApr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and ToolsApr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AMBoth Python and JavaScript's choices in development environments are important. 1) Python's development environment includes PyCharm, JupyterNotebook and Anaconda, which are suitable for data science and rapid prototyping. 2) The development environment of JavaScript includes Node.js, VSCode and Webpack, which are suitable for front-end and back-end development. Choosing the right tools according to project needs can improve development efficiency and project success rate.
 Is JavaScript Written in C? Examining the EvidenceApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Is JavaScript Written in C? Examining the EvidenceApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AMYes, the engine core of JavaScript is written in C. 1) The C language provides efficient performance and underlying control, which is suitable for the development of JavaScript engine. 2) Taking the V8 engine as an example, its core is written in C, combining the efficiency and object-oriented characteristics of C. 3) The working principle of the JavaScript engine includes parsing, compiling and execution, and the C language plays a key role in these processes.
 JavaScript's Role: Making the Web Interactive and DynamicApr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript's Role: Making the Web Interactive and DynamicApr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript is at the heart of modern websites because it enhances the interactivity and dynamicity of web pages. 1) It allows to change content without refreshing the page, 2) manipulate web pages through DOMAPI, 3) support complex interactive effects such as animation and drag-and-drop, 4) optimize performance and best practices to improve user experience.
 C and JavaScript: The Connection ExplainedApr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C and JavaScript: The Connection ExplainedApr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AMC and JavaScript achieve interoperability through WebAssembly. 1) C code is compiled into WebAssembly module and introduced into JavaScript environment to enhance computing power. 2) In game development, C handles physics engines and graphics rendering, and JavaScript is responsible for game logic and user interface.
 From Websites to Apps: The Diverse Applications of JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
From Websites to Apps: The Diverse Applications of JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AMJavaScript is widely used in websites, mobile applications, desktop applications and server-side programming. 1) In website development, JavaScript operates DOM together with HTML and CSS to achieve dynamic effects and supports frameworks such as jQuery and React. 2) Through ReactNative and Ionic, JavaScript is used to develop cross-platform mobile applications. 3) The Electron framework enables JavaScript to build desktop applications. 4) Node.js allows JavaScript to run on the server side and supports high concurrent requests.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications ComparedApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications ComparedApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AMPython is more suitable for data science and automation, while JavaScript is more suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 1. Python performs well in data science and machine learning, using libraries such as NumPy and Pandas for data processing and modeling. 2. Python is concise and efficient in automation and scripting. 3. JavaScript is indispensable in front-end development and is used to build dynamic web pages and single-page applications. 4. JavaScript plays a role in back-end development through Node.js and supports full-stack development.
 The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and CompilersApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and CompilersApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AMC and C play a vital role in the JavaScript engine, mainly used to implement interpreters and JIT compilers. 1) C is used to parse JavaScript source code and generate an abstract syntax tree. 2) C is responsible for generating and executing bytecode. 3) C implements the JIT compiler, optimizes and compiles hot-spot code at runtime, and significantly improves the execution efficiency of JavaScript.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment



 ) is the weighted average of the input pixel value (for example:
) is the weighted average of the input pixel value (for example:  ):
):
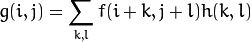
 is called the kernel
is called the kernel