 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Building AI Foundational Models And Generative AI That Expertly Performs Mental Health Therapy
Building AI Foundational Models And Generative AI That Expertly Performs Mental Health TherapyBuilding AI Foundational Models And Generative AI That Expertly Performs Mental Health Therapy

Developing AI capable of providing expert mental health therapy is a significant undertaking. Startups are aggressively pursuing this challenging path, attracting substantial venture capital. Academic researchers are actively exploring its feasibility and optimal approaches, with varying degrees of success. Some initiatives are promising, while others appear superficial.
This analysis, part of my ongoing Forbes column on AI advancements, delves into the complexities of AI in mental health. (See link here)
AI in Mental Health Therapy
I've extensively covered AI's role in mental health advice and therapy, fueled by generative AI and large language models (LLMs). While the field offers immense potential, significant risks and challenges remain. I've addressed these concerns publicly, including a 2024 appearance on CBS 60 Minutes. (Summary of related columns here)
For newcomers, I recommend my recent analysis of Stanford University's AI4MH initiative. (Link here)
A key goal is creating AI specifically designed for mental health therapy. This is a complex process, still in its early stages.
While much is already known (and shared in my previous work), a clear path forward remains elusive. Speculation abounds, but this presents an exciting challenge rather than a roadblock. Determined effort is crucial to achieve advancements that will significantly benefit society's mental well-being.
Understanding AI Foundational Models
Let's clarify AI foundational models. For simplicity, I'll provide a concise overview (with links to more detailed explanations).
When using ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, or similar generative AI, you interact with an underlying large language model (LLM), typically a large artificial neural network (ANN). (Detailed explanation here) This massive data structure contains mathematical patterns representing human language.
These patterns are learned by analyzing vast amounts of online text – essays, poems, stories, etc. – to identify statistical relationships between words. After further refinement by developers, the LLM becomes generative AI, responding to prompts with generated text. The fluency of these responses stems from the accurate pattern matching within the model.
The underlying LLM is often called an AI foundational model. Developers build foundational models and then create variations, such as faster (but potentially less accurate) versions or those specializing in logical reasoning (but potentially slower).
Similarities and Limitations of Current AI Foundational Models
Each generative AI app relies on a foundational model (LLM). While developers have choices in design and construction, a surprising similarity exists across many models. This raises concerns about potential limitations and the need for alternative approaches. (Coverage of novel AI model creation here and here)
A common criticism is that current LLMs are "a mile wide and an inch deep." They are versatile but lack deep expertise in any specific area. While capable of handling broad questions, they struggle with in-depth, domain-specific inquiries. Sometimes they admit their limitations; other times, they attempt misleading responses. (Coverage of AI deception here)
Two Main Types of AI Foundational Models
I categorize AI foundational models into:
- (1) General-purpose AI foundational models: The typical generative AI, broad but shallow.
- (2) Domain-specific AI foundational models: Designed for specific domains, aiming for deeper expertise.
Domain-specific models address the limitations of general-purpose models by focusing on a particular area (finance, law, medicine, etc.). While not yet equal to human experts, they can sometimes match or exceed human performance in specific tasks. (Survey paper on domain-specific models here)
Components of AI Foundational Models
Four key components define AI foundational models:
- (1) Structures
- (2) Algorithms
- (3) Data
- (4) Interactivity
These are common to both general-purpose and domain-specific models. Currently, domain-specific models often adapt existing general-purpose structures, but this is likely to change as the need for domain-specific adaptations becomes more apparent. We'll see families of domain-specific models emerge, for example, a library of foundational models for mental health therapy.
The Value of Domain-Specific Models
Developing domain-specific models is a rapidly growing area. The goal is to leverage AI's capabilities for in-depth expertise, addressing the shortcomings of general-purpose models in handling complex, domain-specific questions.
Users are increasingly recognizing the need for specialized AI, potentially switching between general-purpose and domain-specific AI based on their needs. This presents significant opportunities, particularly in mental health.
Domain-Specific Needs
A crucial point: domain-specific models are not interchangeable. The characteristics of each domain dictate the necessary adjustments to structure, algorithms, data, and interactivity. A financial model differs significantly from a mental health therapy model.
AI for Mental Health and Foundational Models
General-purpose AI models offer limited mental health advice, providing shallow responses. While seemingly professional, this advice lacks depth. AI developers often include disclaimers in their licensing agreements to avoid liability. (Discussion on AI disclaimers here and here)
Worse, such AI can generate meaningless psychobabble. (Analysis here)
Three key approaches to AI-driven mental health advice exist:
- (1) Generic generative AI: Broad, shallow advice.
- (2) Customized generative AI: Improved but still unreliable due to variable customization methods.
- (3) Domain-specific generative AI: The preferred approach for providing high-quality mental health therapy.
Domain-specific models are essential for effective AI-driven mental health advice. The other two approaches are insufficient.
Subtypes of Domain-Specific Models
Domain-specific models are further divided into:
- (a) Domain-only type: Models built almost exclusively on domain-specific data (rare).
- (b) Hybrid of domain & general purpose: Models combining domain-specific and general-purpose elements (more common).
The choice depends on the domain's requirements. A mathematical proof model might be domain-only, needing no fluency or broad worldview. However, a mental health therapy model requires both strong fluency and a robust understanding of the world.
(Continued in Part 2)
The above is the detailed content of Building AI Foundational Models And Generative AI That Expertly Performs Mental Health Therapy. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AMScientists have extensively studied human and simpler neural networks (like those in C. elegans) to understand their functionality. However, a crucial question arises: how do we adapt our own neural networks to work effectively alongside novel AI s
 New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AM
New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AMGoogle's Gemini Advanced: New Subscription Tiers on the Horizon Currently, accessing Gemini Advanced requires a $19.99/month Google One AI Premium plan. However, an Android Authority report hints at upcoming changes. Code within the latest Google P
 How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AMDespite the hype surrounding advanced AI capabilities, a significant challenge lurks within enterprise AI deployments: data processing bottlenecks. While CEOs celebrate AI advancements, engineers grapple with slow query times, overloaded pipelines, a
 MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AM
MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AMHandling documents is no longer just about opening files in your AI projects, it’s about transforming chaos into clarity. Docs such as PDFs, PowerPoints, and Word flood our workflows in every shape and size. Retrieving structured
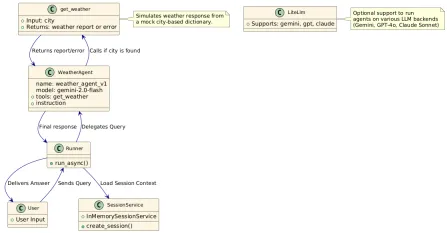 How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AMHarness the power of Google's Agent Development Kit (ADK) to create intelligent agents with real-world capabilities! This tutorial guides you through building conversational agents using ADK, supporting various language models like Gemini and GPT. W
 Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AM
Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AMsummary: Small Language Model (SLM) is designed for efficiency. They are better than the Large Language Model (LLM) in resource-deficient, real-time and privacy-sensitive environments. Best for focus-based tasks, especially where domain specificity, controllability, and interpretability are more important than general knowledge or creativity. SLMs are not a replacement for LLMs, but they are ideal when precision, speed and cost-effectiveness are critical. Technology helps us achieve more with fewer resources. It has always been a promoter, not a driver. From the steam engine era to the Internet bubble era, the power of technology lies in the extent to which it helps us solve problems. Artificial intelligence (AI) and more recently generative AI are no exception
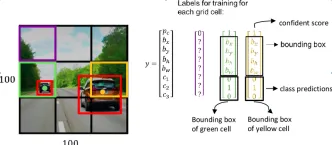 How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AM
How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AMHarness the Power of Google Gemini for Computer Vision: A Comprehensive Guide Google Gemini, a leading AI chatbot, extends its capabilities beyond conversation to encompass powerful computer vision functionalities. This guide details how to utilize
 Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AM
Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AMThe AI landscape of 2025 is electrifying with the arrival of Google's Gemini 2.0 Flash and OpenAI's o4-mini. These cutting-edge models, launched weeks apart, boast comparable advanced features and impressive benchmark scores. This in-depth compariso


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.






