Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly evolving, and 2025 is shaping up to be the year of AI agents. But what are AI agents, and why are they becoming so important? AI agents represent a shift from traditional AI models to more autonomous systems capable of reasoning, planning, and acting on their own. In this article, we will dive into everything you need to know about AI agents, including what AI agents are good at, the different types of agents in AI, and why they are the next big thing in artificial intelligence.
The way most of us use language models today is a bit like asking someone to sit down at a keyboard and type an essay from start to finish without ever using backspace. Despite how challenging this is, language models do it remarkably well.
Table of contents
- The Shift from Monolithic Models to Compound AI Systems
- Compound AI Systems in Action
- What are AI Agents?
- How do AI Agents work?
- Reasoning Capabilities
- Ability to Act
- Memory Access
- Types of AI Agents
- Multi-Agent Framework
- AI Agents vs. Traditional Compound AI Systems
- Real-World Applications of AI Agents
- Conclusion
The Shift from Monolithic Models to Compound AI Systems
Traditional AI models, while powerful, are limited by the data they are trained on. These models can generate responses to a variety of prompts but often struggle to adapt to tasks outside their specific training. For example, if you ask a basic model about your vacation days, it would likely fail because it lacks access to personal databases or other external resources required to provide a correct answer.
AI models on their own are useful for tasks like summarizing documents, drafting emails, or providing general answers, but their true potential is unlocked when they are integrated into broader systems—what we call compound AI systems. These systems combine multiple components, such as databases, external tools, and different types of AI models, to handle more complex tasks.
Before we get into the defination of AI Agents, let’s look at an example!
Compound AI Systems in Action
Consider this example: if you want to plan a vacation and need to know how many vacation days you have left, a simple AI model would struggle because it doesn’t know your personal data. However, if we build a compound AI system, we can connect the model to a database that holds your vacation information. The system works by:
- Querying the language model for an answer.
- Creating a search query for the vacation database.
- Fetching the information from the database.
- Generating a response based on that information.
This type of compound system uses programmatic components like search queries and data verification to increase accuracy and efficiency, making it more adaptable to specific tasks. This shift to compound systems shows how modular AI components can be assembled to solve more complex problems.
What are AI Agents?
So, now coming to the question – What are AI Agents!
At the core, AI agents are systems that perform tasks autonomously by interacting with their environment. They can perceive inputs (such as data or user queries), process this information, and take actions to achieve a specific goal. Unlike traditional AI models that rely solely on pre-programmed logic or data, intelligent agents in AI are designed to adapt and make decisions based on new information or changing environments.
How do AI Agents work?
So, where do AI agents come into play? AI agents represent the next stage of compound AI systems, taking the system’s logic a step further by giving large language models (LLMs) more control over how tasks are completed. Rather than following a rigid, predefined path, AI agents are designed to reason, plan, and act autonomously to solve complex problems.
Here’s a breakdown of the key features that make AI agents special:
Reasoning Capabilities
AI agents are powered by LLMs that can reason through problems step-by-step. This means that instead of providing a quick (and potentially incorrect) answer, the agent takes the time to break down the problem, plan a solution, and identify external tools or data it might need.
Ability to Act
AI agents can take actions by using external programs or tools, such as searching the web, querying a database, or performing calculations. These tools are known as “external programs” in the AI world, and they allow the agent to go beyond simple question-answering.
For example, if you’re planning a vacation and want to know how many sunscreen bottles you need, the AI agent might:
- Check your vacation days in its memory.
- Look up Florida’s weather forecast for the expected hours of sunlight.
- Search for health recommendations on sunscreen usage.
- Calculate how much sunscreen you’ll need based on these factors.
Memory Access
Another important feature of AI agents is their memory. This doesn’t just refer to remembering previous conversations, but also to storing the internal reasoning process, much like how humans think out loud when solving a problem. This memory allows the agent to retrieve useful information during later stages of the task, making it a more personalized and effective assistant.
Types of AI Agents
Here’s a breakdown of the main types of AI agents:

- Simple Reflex Agents: Respond directly to environmental stimuli with pre-defined rules, without any memory or learning ability. Best for straightforward tasks.
- Model-Based Reflex Agents: Use internal models of the environment to handle more complex tasks by remembering past actions and predicting future states.
- Goal-Based Agents: Act to achieve specific objectives by considering future consequences and planning actions accordingly.
- Utility-Based Agents: Evaluate multiple possible actions to maximize their utility (or benefit), making them ideal for decision-making under uncertainty.
- Learning Agents: Adapt and improve over time by learning from interactions with the environment, becoming more efficient and intelligent as they operate.
To know more about each of these types, checkout our detailed article on Types of AI Agents.
Multi-Agent Framework
A Multi-Agent Framework is a system where multiple AI agents collaborate to solve complex tasks by interacting with each other and their environment. Each agent in the framework has specialized roles, capabilities, or knowledge, and they work together to achieve a common goal. The agents are autonomous, meaning they can perceive their environment, reason about it, take actions, and learn over time.

- User Question: The process starts with a user submitting a query or task. This query is the input that the AI agent must process.
- LLM (Large Language Model): The query is first sent to the LLM, which interprets the question and decides how to process it. The LLM generates an initial response and decides if additional steps are required to address the query fully.
- Action: If further steps are needed, the agent performs actions using various tools or external systems, such as web searches, database queries, or APIs (like WolframAlpha or Wikipedia). These actions help the agent gather additional information or perform specific tasks.
- Observation: The result of the action is fed back into the system as an observation. The agent evaluates this information to determine if it answers the user’s query or if further action is necessary.
- Loop: The system may go through multiple iterations of the Action and Observation stages, continuously refining the response until the final answer is determined.
- Output: Once the agent completes the process and generates the final response, it delivers it to the user.
This loop allows the agent to iteratively improve the accuracy of its answers by incorporating external tools and actions, thus delivering more comprehensive and accurate results.
AI Agents vs. Traditional Compound AI Systems
AI agents represent a significant leap forward from traditional compound AI systems due to their autonomy, reasoning, and adaptability. While traditional systems are still effective for straightforward, well-defined tasks, they lack the dynamic problem-solving capabilities that AI agents possess.
The table below highlights the key differences between Agentic AI Chatbots (representing AI agents) and Non-Agentic AI Chatbots (representing traditional compound systems):
| Feature/Aspect | Agentic AI Chatbots (AI Agents) | Non-Agentic AI Chatbots (Traditional Compound AI Systems) |
| Autonomy | Highly autonomous, capable of reasoning and decision-making. | Limited autonomy, mainly follows pre-programmed rules. |
| Decision-Making Process | Can plan and break down complex tasks into smaller steps for better solutions. | Follows direct logic with no real reasoning capabilities. |
| External Tool Access | Can access and use external tools (e.g., APIs, databases) to enhance responses. | Typically does not access external tools or systems. |
| Learning | Has memory and can improve by learning from past interactions. | May have limited learning, usually within a fixed set of responses. |
| Problem-Solving | Can handle complex, multi-step problems by combining reasoning with external resources. | Handles simple, well-defined problems with scripted responses. |
| Flexibility | Flexible and adaptable to changing queries or tasks. Can adjust its approach based on new information. | Rigid in its responses, unable to adapt beyond predefined logic. |
| Control Logic | Uses a reasoning-based approach to decide the steps needed to achieve a goal. | Follows hardcoded, rule-based logic without deeper reasoning. |
| Response Generation | Iterates on responses by gathering more data and refining the solution until accurate. | Provides an immediate response without revisiting or improving the result. |
| Complex Query Handling | Capable of solving highly complex or ambiguous queries by using multiple resources. | Best suited for straightforward, well-defined queries. |
| Memory & Personalization | Retains past interactions to deliver more personalized and context-aware responses. | Typically lacks memory, providing generic or static responses. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for dynamic, evolving problems such as project management, customer service, or research. | Best for basic customer support, FAQs, or linear conversations. |
Real-World Applications of AI Agents
AI agents have practical applications across various fields, from customer service and project management to software development and research. For example, an AI agent could independently handle GitHub issues by analyzing the problem, retrieving relevant data, and suggesting or even implementing solutions. This level of autonomy allows AI agents to handle a broader spectrum of tasks compared to traditional systems, making them particularly useful in dynamic and unpredictable environments.
Here are some of our latest articles where you can see AI Agents in action:
- Building Agentic Chatbots Using AutoGen
- Build an AI Pair Programmer
- Automating Email Sorting and Labelling with CrewAI
- Scaling Multi-Document Agentic RAG to Handle 10 Documents
- Creating a Personalized News Digest Using AI Agents
Other Helpful Resources
- 4 Agentic AI Design Patterns for Architecting AI Systems
- Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraph
- 5 Frameworks for Building AI Agents in 2024
- 5 AI Agent Projects to Try
If you want to learn how to build these agents then consider enrolling in our exclusive Agentic AI Pioneer Program!
Conclusion
AI agents represent the next big leap in artificial intelligence, offering a level of reasoning, planning, and autonomy that surpasses traditional compound AI systems. As these agents become more integrated into our daily lives and professional workflows, they will play a critical role in helping us navigate increasingly complex challenges with ease. Whether it’s managing your vacation plans or tackling complex tasks like software troubleshooting, AI agents are poised to revolutionize the way we interact with AI.
Stay tuned as we continue to explore this exciting frontier in AI.
The above is the detailed content of What are AI Agents? - Analytics Vidhya. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AMScientists have extensively studied human and simpler neural networks (like those in C. elegans) to understand their functionality. However, a crucial question arises: how do we adapt our own neural networks to work effectively alongside novel AI s
 New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AM
New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AMGoogle's Gemini Advanced: New Subscription Tiers on the Horizon Currently, accessing Gemini Advanced requires a $19.99/month Google One AI Premium plan. However, an Android Authority report hints at upcoming changes. Code within the latest Google P
 How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AMDespite the hype surrounding advanced AI capabilities, a significant challenge lurks within enterprise AI deployments: data processing bottlenecks. While CEOs celebrate AI advancements, engineers grapple with slow query times, overloaded pipelines, a
 MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AM
MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AMHandling documents is no longer just about opening files in your AI projects, it’s about transforming chaos into clarity. Docs such as PDFs, PowerPoints, and Word flood our workflows in every shape and size. Retrieving structured
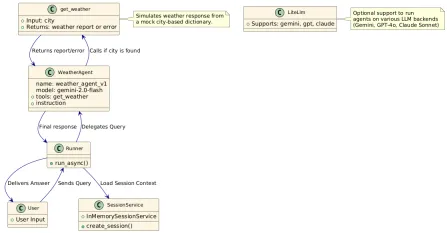 How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AMHarness the power of Google's Agent Development Kit (ADK) to create intelligent agents with real-world capabilities! This tutorial guides you through building conversational agents using ADK, supporting various language models like Gemini and GPT. W
 Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AM
Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AMsummary: Small Language Model (SLM) is designed for efficiency. They are better than the Large Language Model (LLM) in resource-deficient, real-time and privacy-sensitive environments. Best for focus-based tasks, especially where domain specificity, controllability, and interpretability are more important than general knowledge or creativity. SLMs are not a replacement for LLMs, but they are ideal when precision, speed and cost-effectiveness are critical. Technology helps us achieve more with fewer resources. It has always been a promoter, not a driver. From the steam engine era to the Internet bubble era, the power of technology lies in the extent to which it helps us solve problems. Artificial intelligence (AI) and more recently generative AI are no exception
 How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AM
How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AMHarness the Power of Google Gemini for Computer Vision: A Comprehensive Guide Google Gemini, a leading AI chatbot, extends its capabilities beyond conversation to encompass powerful computer vision functionalities. This guide details how to utilize
 Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AM
Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AMThe AI landscape of 2025 is electrifying with the arrival of Google's Gemini 2.0 Flash and OpenAI's o4-mini. These cutting-edge models, launched weeks apart, boast comparable advanced features and impressive benchmark scores. This in-depth compariso


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor







