 System Tutorial
System Tutorial Windows Series
Windows Series Understanding and Customizing the Windows 11 Hosts File for Improved Network Management
Understanding and Customizing the Windows 11 Hosts File for Improved Network ManagementUnderstanding and Customizing the Windows 11 Hosts File for Improved Network Management
This article explains the Windows 11 hosts file, a local DNS resolver allowing users to manage network traffic by mapping hostnames to IP addresses. It details how to block malicious websites and improve network management, emphasizing best practice

Understanding and Customizing the Windows 11 Hosts File for Improved Network Management
The Windows hosts file is a simple text file that acts as a local DNS (Domain Name System) resolver. It maps hostnames (website addresses like www.example.com) to IP addresses. When you type a website address into your browser, your computer first checks the hosts file. If it finds a matching entry, it uses the IP address specified in the file to connect to the website. If it doesn't find a match, it then queries your DNS server to resolve the hostname. This means you can override the DNS resolution for specific websites by adding entries to your hosts file. This offers a degree of control over your network traffic, allowing you to block certain websites, redirect traffic, or even test local web servers. It's a powerful tool for network management, particularly useful for troubleshooting, security, and local development. However, it's important to remember that the hosts file only affects the machine it's located on; it doesn't affect other devices on your network.
How can I use the Windows 11 hosts file to block malicious websites?
To block malicious websites using the Windows 11 hosts file, you need to add entries that map the malicious website's domain names to the loopback IP address, 127.0.0.1. This effectively prevents your computer from connecting to those websites. For example, if you want to block maliciouswebsite.com, you would add the following line to your hosts file:
<code>127.0.0.1 maliciouswebsite.com</code>
You can add multiple lines, each blocking a different malicious website. To find the domain names of malicious websites, you can consult online resources like threat intelligence feeds or security advisories from reputable sources. Remember that simply blocking a domain may not be sufficient; many malicious websites use multiple domains or IP addresses. Therefore, combining the hosts file with other security measures like a robust antivirus and firewall is crucial for comprehensive protection. After adding entries, save the file and restart your browser or flush your DNS cache (ipconfig /flushdns in Command Prompt) for the changes to take effect.
What are the best practices for editing and managing the Windows 11 hosts file?
Editing the hosts file requires caution. Incorrectly editing it can disrupt your internet connectivity. Here are some best practices:
- Backup your hosts file: Before making any changes, create a backup copy of the original file. This allows you to revert to the original configuration if something goes wrong. You can simply copy the file to a different location.
- Use a text editor with administrator privileges: Open the file using Notepad (or a similar text editor) as an administrator. Right-click the Notepad icon, select "Run as administrator". This ensures you have the necessary permissions to save changes.
-
Understand the file format: The hosts file uses a simple format: each line contains an IP address followed by one or more hostnames, separated by spaces or tabs. Blank lines and lines starting with
#are comments and are ignored. - Use accurate information: Ensure the IP addresses and hostnames are correct. Typos can lead to connectivity issues.
- Test your changes: After making changes, test your internet connectivity to ensure that the changes have the intended effect. Check whether the blocked websites are inaccessible and that other websites are still accessible.
- Regularly review your entries: Periodically review your hosts file to remove outdated or unnecessary entries. A cluttered hosts file can become difficult to manage.
- Consider using a dedicated hosts file manager: Several third-party tools are available that provide a user-friendly interface for managing the hosts file, offering features like import/export, search, and backup functionality.
The location of the hosts file is typically C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts.
Can I use the Windows 11 hosts file to speed up my internet connection by blocking ads?
While you can use the Windows 11 hosts file to block ads by adding entries for ad servers' IP addresses or domain names, this is not a guaranteed or highly effective method for speeding up your internet connection. Ad blockers are generally more effective because they use sophisticated techniques to identify and block ads across multiple domains and even dynamically generated content. The hosts file is limited in its ability to keep up with the constantly changing landscape of advertising networks. Many ad networks use dynamic IP addresses or multiple domains, making it difficult to completely block them with a hosts file. While blocking some ads might result in a marginal improvement in browsing speed, it's likely to be insignificant compared to the impact of other factors like your internet connection speed, browser performance, and the websites you visit. Dedicated ad blockers integrated into your browser or as standalone applications are generally a far more effective solution for blocking ads and improving browsing speed.
The above is the detailed content of Understanding and Customizing the Windows 11 Hosts File for Improved Network Management. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 iFixit Is Helping Make HP Laptops More RepairableMay 04, 2025 am 12:53 AM
iFixit Is Helping Make HP Laptops More RepairableMay 04, 2025 am 12:53 AMRelated ##### Samsung hinders mobile phone repair iFixit's partnership with Samsung broke down, and Samsung reportedly forced repair shops to share customer information. Article The blog post also mentioned: "A interesting feature worth watching is the new battery replacement tool, which [HP] calls it the Revivekit. There are two smaller boxes in the box - one with a new battery, and the other designed to safely store the old battery after replacement. The cardboard profile design allows it to cover the old battery and protect it from accidental poking when you do repairs. It also comes with some strategically placed adhesive pads to help securely hold it to the battery when you work - and it is designed to still stick to the battery when you lift it, which you can fold and store after that.
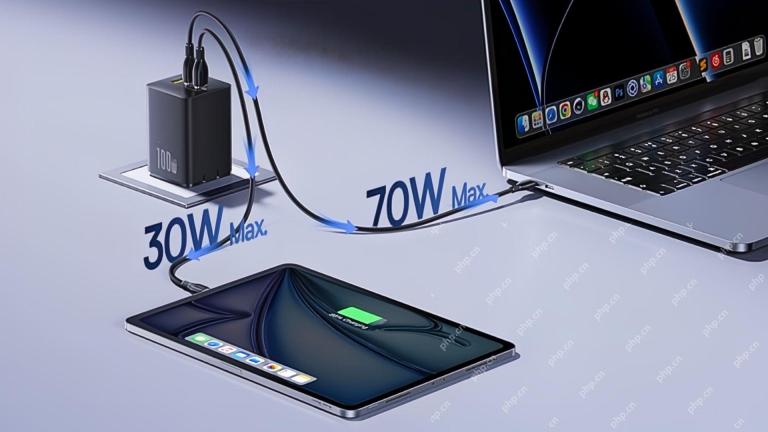 This 100W USB-C Baseus Charger Is 45% OffMay 04, 2025 am 12:52 AM
This 100W USB-C Baseus Charger Is 45% OffMay 04, 2025 am 12:52 AMBaseus 100W Three-Port USB-C Charger: Great Value! The Baseus 100W three-port USB-C charger provides ultra-high speed charging for up to three devices at the same time. The two USB-C ports each provide 100W output, while one USB-A port adds more compatibility. Its compact and portable design and foldable plug are perfect for traveling. Advanced cooling system and intelligent power distribution technology ensure safe and efficient charging. Amazon Baseus flagship store is currently in a big promotion. If you purchase Baseus 100W three-port USB-C charger, you will get two 45W USB-C chargers and charging cables. The total price is only
 How to Transfer Windows to Another DriveMay 02, 2025 pm 02:01 PM
How to Transfer Windows to Another DriveMay 02, 2025 pm 02:01 PMPerhaps your old hard drive is starting to slow down and fail, or maybe you’re looking to migrate your files to a disk with much more space. There are plenty of reasons to migrate Windows from one drive to another, and just as many
 How to Add a User Interface to Windows' Winget UtilityMay 02, 2025 am 06:04 AM
How to Add a User Interface to Windows' Winget UtilityMay 02, 2025 am 06:04 AMDoes Windows lack a convenient package manager? UniGetUI is here to help you! The package manager for Linux systems is very convenient, but Windows systems lack similar tools. However, with a free open source project UniGetUI and Windows built-in command line tool winget, you can get the same functionality on Windows. The best feature for Windows missing: a convenient package manager Package Manager allows you to add and remove programs, system libraries, and drivers. You can search for programs almost instantly, retrieve information about them, and adjust settings. In other words, they are features that Microsoft stores dream of. Every Linux distribution has one
 Arch Linux Is Now in the Windows Subsystem for LinuxMay 02, 2025 am 06:02 AM
Arch Linux Is Now in the Windows Subsystem for LinuxMay 02, 2025 am 06:02 AMArch Linux officially joins the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) family! No external downloads are needed; installation is a breeze using PowerShell: wsl --install archlinux First-time WSL users will need to run this command first, followed by a sy
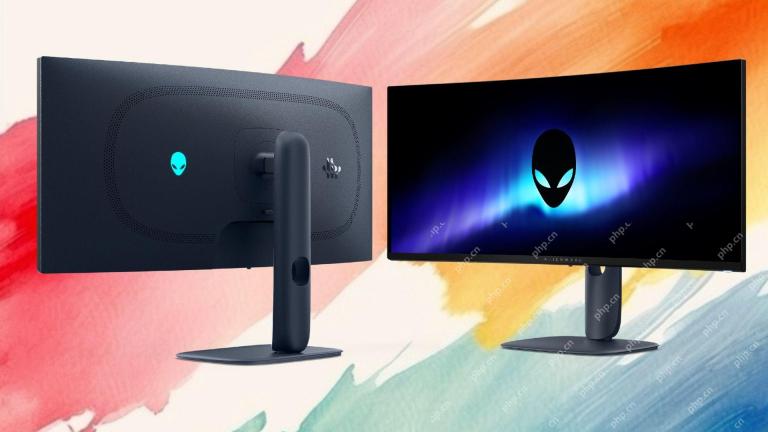 Alienware's New 240Hz 34-Inch QD-OLED Monitor Is Finally OutMay 02, 2025 am 03:05 AM
Alienware's New 240Hz 34-Inch QD-OLED Monitor Is Finally OutMay 02, 2025 am 03:05 AMThis monitor boasts extensive connectivity, featuring a DisplayPort 1.4 port (supporting up to 3440 x 1440 at 240Hz, DSC, and HDR) and two HDMI 2.1 FRL ports (also supporting 3440 x 1440 at 240Hz, FRL, HDR, and VRR). These high-speed HDMI 2.1 ports
 How to Install Windows 11 With No TPM 2.0May 01, 2025 pm 08:01 PM
How to Install Windows 11 With No TPM 2.0May 01, 2025 pm 08:01 PMWindows 10 support is ending in late 2025, prompting many users to upgrade to Windows 11. However, the TPM 2.0 requirement can be a significant hurdle. This guide outlines methods to install Windows 11 even without TPM 2.0, but proceed with caution.
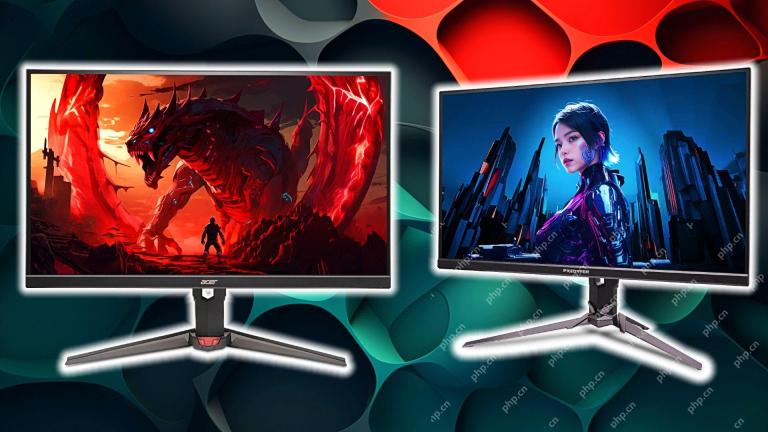 Acer Has Two New Monitors for GamingMay 01, 2025 am 06:06 AM
Acer Has Two New Monitors for GamingMay 01, 2025 am 06:06 AMThe Acer Predator XB323QK V4 and Nitro XV240 F6: A Tale of Two Monitors Acer offers two distinct gaming monitors catering to different needs: the color-focused XB323QK V4 and the speed-demon XV240 F6. Let's break down their key features. The XB323QK


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)






