Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): A Comprehensive Guide
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are a powerful type of artificial neural network (ANN) used in applications like Apple's Siri and Google's voice search. Their unique ability to retain past inputs through internal memory makes them ideal for tasks such as stock price prediction, text generation, transcription, and machine translation. Unlike traditional neural networks where inputs and outputs are independent, RNN outputs depend on previous elements in a sequence. Furthermore, RNNs share parameters across network layers, optimizing weight and bias adjustments during gradient descent.

The diagram above illustrates a basic RNN. In a stock price forecasting scenario using data like [45, 56, 45, 49, 50,...], each input (X0 to Xt) incorporates past values. For instance, X0 would be 45, X1 would be 56, and these values contribute to predicting the next sequence element.
How RNNs Function
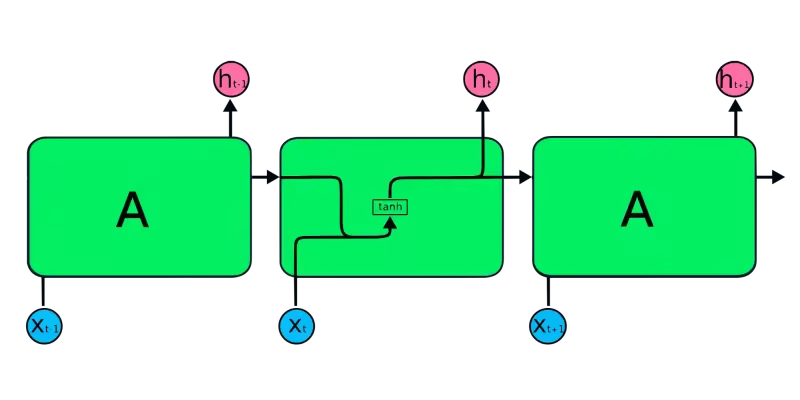
In RNNs, information cycles through a loop, making the output a function of both the current and previous inputs.

The input layer (X) processes the initial input, passing it to the middle layer (A), which comprises multiple hidden layers with activation functions, weights, and biases. These parameters are shared across the hidden layer, creating a single looped layer instead of multiple distinct layers. RNNs employ backpropagation through time (BPTT) instead of traditional backpropagation to compute gradients. BPTT sums errors at each time step due to the shared parameters.
Types of RNNs
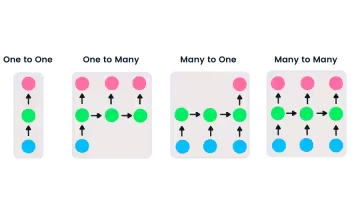
RNNs offer flexibility in input and output lengths, unlike feedforward networks with single inputs and outputs. This adaptability allows RNNs to handle diverse tasks, including music generation, sentiment analysis, and machine translation. Four main types exist:
- One-to-one: A simple neural network suitable for single input/output problems.
- One-to-many: Processes a single input to generate multiple outputs (e.g., image captioning).
- Many-to-one: Takes multiple inputs to predict a single output (e.g., sentiment classification).
- Many-to-many: Handles multiple inputs and outputs (e.g., machine translation).
Recommended Machine Learning Courses
Learn more about RNNs for language modeling
Explore Introduction to Deep Learning in Python
CNNs vs. RNNs
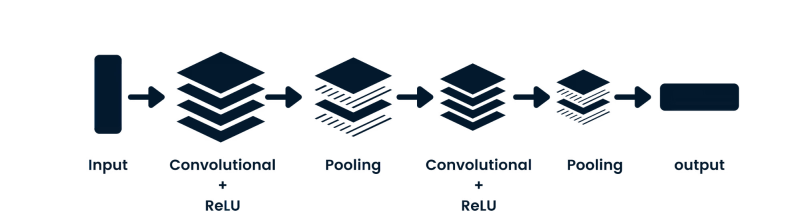
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are feedforward networks processing spatial data (like images), commonly used in computer vision. Simple neural networks struggle with image pixel dependencies, while CNNs, with their convolutional, ReLU, pooling, and fully connected layers, excel in this area.
Key Differences:
- CNNs handle sparse data (images), while RNNs manage time series and sequential data.
- CNNs use standard backpropagation, RNNs use BPTT.
- CNNs have finite inputs/outputs; RNNs are flexible.
- CNNs are feedforward; RNNs use loops for sequential data.
- CNNs are used for image/video processing; RNNs for speech/text analysis.
RNN Limitations
Simple RNNs face two primary challenges related to gradients:
- Vanishing Gradient: Gradients become too small, hindering parameter updates and learning.
- Exploding Gradient: Gradients become excessively large, causing model instability and longer training times.
Solutions include reducing hidden layers or using advanced architectures like LSTM and GRU.
Advanced RNN Architectures
Simple RNNs suffer from short-term memory limitations. LSTM and GRU address this by enabling the retention of information over extended periods.
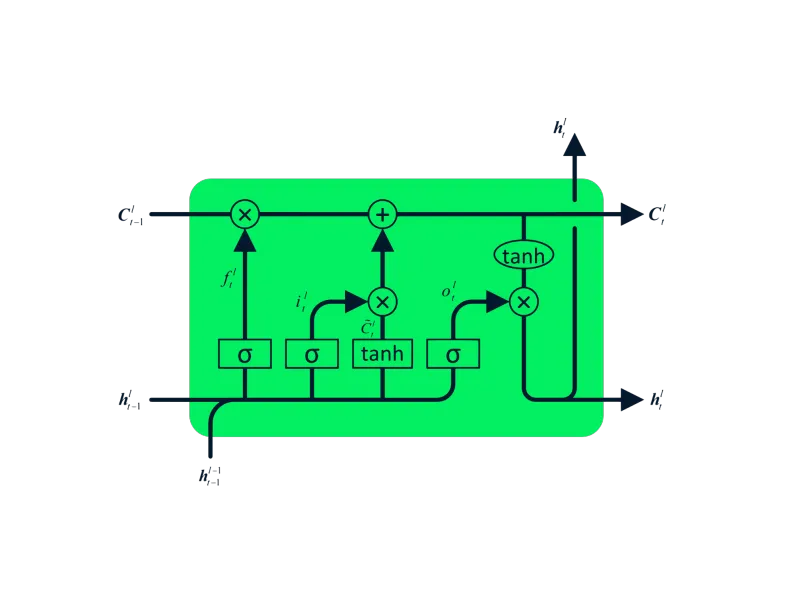
- Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): An advanced RNN designed to mitigate vanishing/exploding gradients. Its four interacting layers facilitate long-term memory retention, making it suitable for machine translation, speech synthesis, and more.
- Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU): A simpler variation of LSTM, using update and reset gates to manage information flow. Its streamlined architecture often leads to faster training compared to LSTM.

MasterCard Stock Price Prediction Using LSTM & GRU
This section details a project using LSTM and GRU to predict MasterCard stock prices. The code utilizes libraries like Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, scikit-learn, and TensorFlow.
(The detailed code example from the original input is omitted here for brevity. The core steps are summarized below.)
- Data Analysis: Import and clean the MasterCard stock dataset.
-
Data Preprocessing: Split the data into training and testing sets, scale using
MinMaxScaler, and reshape for model input. - LSTM Model: Build and train an LSTM model.
- LSTM Results: Evaluate the LSTM model's performance using RMSE.
- GRU Model: Build and train a GRU model with similar architecture.
- GRU Results: Evaluate the GRU model's performance using RMSE.
- Conclusion: Compare the performance of LSTM and GRU models.


Conclusion
Hybrid CNN-RNN networks are increasingly used for tasks requiring both spatial and temporal understanding. This tutorial provided a foundational understanding of RNNs, their limitations, and solutions offered by advanced architectures like LSTM and GRU. The project demonstrated the application of LSTM and GRU for stock price prediction, highlighting GRU's superior performance in this specific case. The complete project is available on the DataCamp workspace.
Remember to replace https://www.php.cn/link/cc6a6632b380f3f6a1c54b1222cd96c2 and https://www.php.cn/link/8708107b2ff5de15d0244471ae041fdb with actual links to the relevant courses. The image URLs are assumed to be correct and accessible.
The above is the detailed content of Recurrent Neural Network Tutorial (RNN). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 From Friction To Flow: How AI Is Reshaping Legal WorkMay 09, 2025 am 11:29 AM
From Friction To Flow: How AI Is Reshaping Legal WorkMay 09, 2025 am 11:29 AMThe legal tech revolution is gaining momentum, pushing legal professionals to actively embrace AI solutions. Passive resistance is no longer a viable option for those aiming to stay competitive. Why is Technology Adoption Crucial? Legal professional
 This Is What AI Thinks Of You And Knows About YouMay 09, 2025 am 11:24 AM
This Is What AI Thinks Of You And Knows About YouMay 09, 2025 am 11:24 AMMany assume interactions with AI are anonymous, a stark contrast to human communication. However, AI actively profiles users during every chat. Every prompt, every word, is analyzed and categorized. Let's explore this critical aspect of the AI revo
 7 Steps To Building A Thriving, AI-Ready Corporate CultureMay 09, 2025 am 11:23 AM
7 Steps To Building A Thriving, AI-Ready Corporate CultureMay 09, 2025 am 11:23 AMA successful artificial intelligence strategy cannot be separated from strong corporate culture support. As Peter Drucker said, business operations depend on people, and so does the success of artificial intelligence. For organizations that actively embrace artificial intelligence, building a corporate culture that adapts to AI is crucial, and it even determines the success or failure of AI strategies. West Monroe recently released a practical guide to building a thriving AI-friendly corporate culture, and here are some key points: 1. Clarify the success model of AI: First of all, we must have a clear vision of how AI can empower business. An ideal AI operation culture can achieve a natural integration of work processes between humans and AI systems. AI is good at certain tasks, while humans are good at creativity and judgment
 Netflix New Scroll, Meta AI's Game Changers, Neuralink Valued At $8.5 BillionMay 09, 2025 am 11:22 AM
Netflix New Scroll, Meta AI's Game Changers, Neuralink Valued At $8.5 BillionMay 09, 2025 am 11:22 AMMeta upgrades AI assistant application, and the era of wearable AI is coming! The app, designed to compete with ChatGPT, offers standard AI features such as text, voice interaction, image generation and web search, but has now added geolocation capabilities for the first time. This means that Meta AI knows where you are and what you are viewing when answering your question. It uses your interests, location, profile and activity information to provide the latest situational information that was not possible before. The app also supports real-time translation, which completely changed the AI experience on Ray-Ban glasses and greatly improved its usefulness. The imposition of tariffs on foreign films is a naked exercise of power over the media and culture. If implemented, this will accelerate toward AI and virtual production
 Take These Steps Today To Protect Yourself Against AI CybercrimeMay 09, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Take These Steps Today To Protect Yourself Against AI CybercrimeMay 09, 2025 am 11:19 AMArtificial intelligence is revolutionizing the field of cybercrime, which forces us to learn new defensive skills. Cyber criminals are increasingly using powerful artificial intelligence technologies such as deep forgery and intelligent cyberattacks to fraud and destruction at an unprecedented scale. It is reported that 87% of global businesses have been targeted for AI cybercrime over the past year. So, how can we avoid becoming victims of this wave of smart crimes? Let’s explore how to identify risks and take protective measures at the individual and organizational level. How cybercriminals use artificial intelligence As technology advances, criminals are constantly looking for new ways to attack individuals, businesses and governments. The widespread use of artificial intelligence may be the latest aspect, but its potential harm is unprecedented. In particular, artificial intelligence
 A Symbiotic Dance: Navigating Loops Of Artificial And Natural PerceptionMay 09, 2025 am 11:13 AM
A Symbiotic Dance: Navigating Loops Of Artificial And Natural PerceptionMay 09, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe intricate relationship between artificial intelligence (AI) and human intelligence (NI) is best understood as a feedback loop. Humans create AI, training it on data generated by human activity to enhance or replicate human capabilities. This AI
 AI's Biggest Secret — Creators Don't Understand It, Experts SplitMay 09, 2025 am 11:09 AM
AI's Biggest Secret — Creators Don't Understand It, Experts SplitMay 09, 2025 am 11:09 AMAnthropic's recent statement, highlighting the lack of understanding surrounding cutting-edge AI models, has sparked a heated debate among experts. Is this opacity a genuine technological crisis, or simply a temporary hurdle on the path to more soph
 Bulbul-V2 by Sarvam AI: India's Best TTS ModelMay 09, 2025 am 10:52 AM
Bulbul-V2 by Sarvam AI: India's Best TTS ModelMay 09, 2025 am 10:52 AMIndia is a diverse country with a rich tapestry of languages, making seamless communication across regions a persistent challenge. However, Sarvam’s Bulbul-V2 is helping to bridge this gap with its advanced text-to-speech (TTS) t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)







