In the age of increasingly large language models and complex neural networks, optimizing model efficiency has become paramount. Weight quantization stands out as a crucial technique for reducing model size and improving inference speed without significant performance degradation. This guide provides a hands-on approach to implementing and understanding weight quantization, using GPT-2 as our practical example.
Learning Objectives
- Understand the fundamentals of weight quantization and its importance in model optimization.
- Learn the differences between absmax and zero-point quantization techniques.
- Implement weight quantization methods on GPT-2 using PyTorch.
- Analyze the impact of quantization on memory efficiency, inference speed, and accuracy.
- Visualize quantized weight distributions using histograms for insights.
- Evaluate model performance post-quantization through text generation and perplexity metrics.
- Explore the advantages of quantization for deploying models on resource-constrained devices.
This article was published as a part of theData Science Blogathon.
Table of contents
- Understanding Weight Quantization Fundamentals
- Practical Implementation
- Quantization Process: Weights and Model
- Visualizing Quantized Weight Distributions
- Performance Evaluation
- Advantages of Weight Quantization
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Weight Quantization Fundamentals
Weight quantization converts high-precision floating-point weights (typically 32-bit) to lower-precision representations (commonly 8-bit integers). This process significantly reduces model size and memory usage while attempting to preserve model performance. The key challenge lies in maintaining model accuracy while reducing numerical precision.
Why Quantize?
- Memory Efficiency: Reducing precision from 32-bit to 8-bit can theoretically reduce model size by 75%
- Faster Inference: Integer operations are generally faster than floating-point operations
- Lower Power Consumption: Reduced memory bandwidth and simpler computations lead to energy savings
- Deployment Flexibility: Smaller models can be deployed on resource-constrained devices
Practical Implementation
Let’s dive into implementing two popular quantization methods: absmax quantization and zero-point quantization.
Setting Up the Environment
First, we’ll set up our development environment with necessary dependencies:
import seaborn as sns import torch import numpy as np from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer from copy import deepcopy import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.ticker as ticker import seaborn as sns
Below we will look into implementing quantization methods:
Absmax Quantization
The absmax quantization method scales weights based on the maximum absolute value in the tensor:
import seaborn as sns import torch import numpy as np from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer from copy import deepcopy import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.ticker as ticker import seaborn as sns
This method works by:
- Finding the maximum absolute value in the weight tensor
- Computing a scaling factor to fit values within int8 range
- Scaling and rounding the values
- Providing both quantized and dequantized versions
Key advantages:
- Simple implementation
- Good preservation of large values
- Symmetric quantization around zero
Zero-point Quantization
Zero-point quantization adds an offset to better handle asymmetric distributions:
# Define quantization functions
def absmax_quantize(X):
scale = 100 / torch.max(torch.abs(X)) # Adjusted scale
X_quant = (scale * X).round()
X_dequant = X_quant / scale
return X_quant.to(torch.int8), X_dequant
Output:
def zeropoint_quantize(X):
x_range = torch.max(X) - torch.min(X)
x_range = 1 if x_range == 0 else x_range
scale = 200 / x_range
zeropoint = (-scale * torch.min(X) - 128).round()
X_quant = torch.clip((X * scale + zeropoint).round(), -128, 127)
X_dequant = (X_quant - zeropoint) / scale
return X_quant.to(torch.int8), X_dequant
This method:
- Calculates the full range of values
- Determines scale and zero-point parameters
- Applies scaling and shifting
- Clips values to ensure int8 bounds
Benefits:
- Better handling of asymmetric distributions
- Improved representation of near-zero values
- Often results in better overall accuracy
Loading and Preparing the Model
Let’s apply these quantization methods to a real model. We’ll use GPT-2 as our example:
Using device: cuda
Output:
Quantization Process: Weights and Model
Dive into applying quantization techniques to both individual weights and the entire model. This step ensures reduced memory usage and computational efficiency while maintaining performance.
# Load model and tokenizer
model_id = 'gpt2'
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id).to(device)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
# Print model size
print(f"Model size: {model.get_memory_footprint():,} bytes")
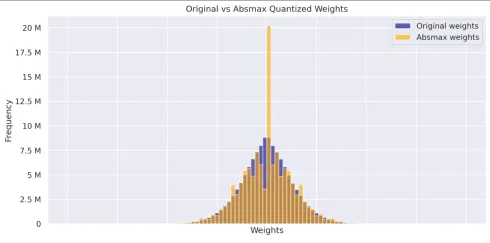
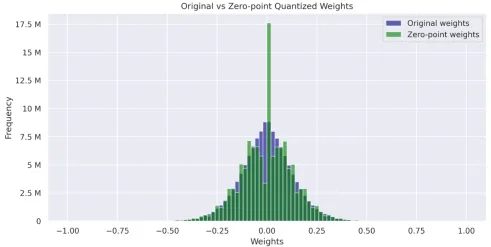
Visualizing Quantized Weight Distributions
Visualize and compare the weight distributions of the original, absmax quantized, and zero-point quantized models. These histograms provide insights into how quantization impacts weight values and their overall distribution.
# Quantize and visualize weights
weights_abs_quant, _ = absmax_quantize(weights)
weights_zp_quant, _ = zeropoint_quantize(weights)
# Quantize the entire model
model_abs = deepcopy(model)
model_zp = deepcopy(model)
for param in model_abs.parameters():
_, dequantized = absmax_quantize(param.data)
param.data = dequantized
for param in model_zp.parameters():
_, dequantized = zeropoint_quantize(param.data)
param.data = dequantized
The code includes a comprehensive visualization function:
- Graph displaying Original Weights vs Absmax Weights
- Graph displaying Original Weights vs Zero-point Weights
Output:
Performance Evaluation
Evaluating the impact of quantization on model performance is essential to ensure efficiency and accuracy. Let’s measure how well the quantized models perform compared to the original.
Text Generation
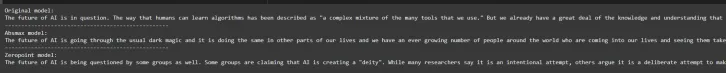
Explore how the quantized models generate text and compare the quality of outputs to the original model’s predictions.
import seaborn as sns import torch import numpy as np from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer from copy import deepcopy import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.ticker as ticker import seaborn as sns
This code compares text generation outputs from three models: the original, an “absmax” quantized model, and a “zeropoint” quantized model. It uses a generate_text function to generate text based on an input prompt, applying sampling with a top-k value of 30. Finally, it prints the results from all three models.
Output:
# Define quantization functions
def absmax_quantize(X):
scale = 100 / torch.max(torch.abs(X)) # Adjusted scale
X_quant = (scale * X).round()
X_dequant = X_quant / scale
return X_quant.to(torch.int8), X_dequant
The code calculates the perplexity (a measure of how well a model predicts text) for a given input using three models: the original, “absmax” quantized, and “zeropoint” quantized models. Lower perplexity indicates better performance. It prints the perplexity scores for comparison.
Output:

You can access colab link here.
Advantages of Weight Quantization
Below we will look into the advantages of weight quantization:
- Memory Efficiency: Quantization reduces model size by up to 75%, enabling faster loading and inference.
- Faster Inference: Integer operations are faster than floating-point operations, leading to quicker model execution.
- Lower Power Consumption: Reduced memory bandwidth and simplified computation lead to energy savings, essential for edge devices and mobile deployment.
- Deployment Flexibility: Smaller models are easier to deploy on hardware with limited resources (e.g., mobile phones, embedded devices).
- Minimal Performance Degradation: With the right quantization strategy, models can retain most of their accuracy despite the reduced precision.
Conclusion
Weight quantization plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of large language models, particularly when it comes to deploying them on resource-constrained devices. By converting high-precision weights to lower-precision integer representations, we can significantly reduce memory usage, improve inference speed, and lower power consumption, all without severely affecting the model’s performance.
In this guide, we explored two popular quantization techniques—absmax quantization and zero-point quantization—using GPT-2 as a practical example. Both techniques demonstrated the ability to reduce the model’s memory footprint and computational requirements while maintaining a high level of accuracy in text generation tasks. However, the zero-point quantization method, with its asymmetric approach, generally resulted in better preservation of model accuracy, especially for non-symmetric weight distributions.
Key Takeaways
- Absmax Quantization is simpler and works well for symmetric weight distributions, though it might not capture asymmetric distributions as effectively as zero-point quantization.
- Zero-point Quantization offers a more flexible approach by introducing an offset to handle asymmetric distributions, often leading to better accuracy and a more efficient representation of weights.
- Quantization is essential for deploying large models in real-time applications where computational resources are limited.
- Despite the quantization process reducing precision, it’s possible to maintain model performance close to the original with proper tuning and quantization strategies.
- Visualization techniques like histograms can provide insights into how quantization affects model weights and the distribution of values in the tensors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is weight quantization?A. Weight quantization reduces the precision of a model’s weights, typically from 32-bit floating-point values to lower-precision integers (e.g., 8-bit integers), to save memory and computation while maintaining performance.
Q2. How does weight quantization affect model performance?A. While quantization reduces the model’s memory footprint and inference time, it can lead to a slight degradation in accuracy. However, if done correctly, the loss in accuracy is minimal.
Q3. Can quantization be applied to any model?A. Yes, quantization can be applied to any neural network model, including language models, vision models, and other deep learning architectures.
Q4. How do I implement weight quantization in my model?A. You can implement quantization by creating functions to scale and round the model’s weights, then apply them across all parameters. Libraries like PyTorch provide native support for some quantization techniques, though custom implementations, as shown in the guide, offer flexibility.
Q5. Does quantization work for all types of models?A. Weight quantization is most effective for large models where reducing memory footprint and computation is critical. However, very small models may not benefit as much from quantization.
The media shown in this article is not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.
The above is the detailed content of Neural Network Weight Quantization. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 From Friction To Flow: How AI Is Reshaping Legal WorkMay 09, 2025 am 11:29 AM
From Friction To Flow: How AI Is Reshaping Legal WorkMay 09, 2025 am 11:29 AMThe legal tech revolution is gaining momentum, pushing legal professionals to actively embrace AI solutions. Passive resistance is no longer a viable option for those aiming to stay competitive. Why is Technology Adoption Crucial? Legal professional
 This Is What AI Thinks Of You And Knows About YouMay 09, 2025 am 11:24 AM
This Is What AI Thinks Of You And Knows About YouMay 09, 2025 am 11:24 AMMany assume interactions with AI are anonymous, a stark contrast to human communication. However, AI actively profiles users during every chat. Every prompt, every word, is analyzed and categorized. Let's explore this critical aspect of the AI revo
 7 Steps To Building A Thriving, AI-Ready Corporate CultureMay 09, 2025 am 11:23 AM
7 Steps To Building A Thriving, AI-Ready Corporate CultureMay 09, 2025 am 11:23 AMA successful artificial intelligence strategy cannot be separated from strong corporate culture support. As Peter Drucker said, business operations depend on people, and so does the success of artificial intelligence. For organizations that actively embrace artificial intelligence, building a corporate culture that adapts to AI is crucial, and it even determines the success or failure of AI strategies. West Monroe recently released a practical guide to building a thriving AI-friendly corporate culture, and here are some key points: 1. Clarify the success model of AI: First of all, we must have a clear vision of how AI can empower business. An ideal AI operation culture can achieve a natural integration of work processes between humans and AI systems. AI is good at certain tasks, while humans are good at creativity and judgment
 Netflix New Scroll, Meta AI's Game Changers, Neuralink Valued At $8.5 BillionMay 09, 2025 am 11:22 AM
Netflix New Scroll, Meta AI's Game Changers, Neuralink Valued At $8.5 BillionMay 09, 2025 am 11:22 AMMeta upgrades AI assistant application, and the era of wearable AI is coming! The app, designed to compete with ChatGPT, offers standard AI features such as text, voice interaction, image generation and web search, but has now added geolocation capabilities for the first time. This means that Meta AI knows where you are and what you are viewing when answering your question. It uses your interests, location, profile and activity information to provide the latest situational information that was not possible before. The app also supports real-time translation, which completely changed the AI experience on Ray-Ban glasses and greatly improved its usefulness. The imposition of tariffs on foreign films is a naked exercise of power over the media and culture. If implemented, this will accelerate toward AI and virtual production
 Take These Steps Today To Protect Yourself Against AI CybercrimeMay 09, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Take These Steps Today To Protect Yourself Against AI CybercrimeMay 09, 2025 am 11:19 AMArtificial intelligence is revolutionizing the field of cybercrime, which forces us to learn new defensive skills. Cyber criminals are increasingly using powerful artificial intelligence technologies such as deep forgery and intelligent cyberattacks to fraud and destruction at an unprecedented scale. It is reported that 87% of global businesses have been targeted for AI cybercrime over the past year. So, how can we avoid becoming victims of this wave of smart crimes? Let’s explore how to identify risks and take protective measures at the individual and organizational level. How cybercriminals use artificial intelligence As technology advances, criminals are constantly looking for new ways to attack individuals, businesses and governments. The widespread use of artificial intelligence may be the latest aspect, but its potential harm is unprecedented. In particular, artificial intelligence
 A Symbiotic Dance: Navigating Loops Of Artificial And Natural PerceptionMay 09, 2025 am 11:13 AM
A Symbiotic Dance: Navigating Loops Of Artificial And Natural PerceptionMay 09, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe intricate relationship between artificial intelligence (AI) and human intelligence (NI) is best understood as a feedback loop. Humans create AI, training it on data generated by human activity to enhance or replicate human capabilities. This AI
 AI's Biggest Secret — Creators Don't Understand It, Experts SplitMay 09, 2025 am 11:09 AM
AI's Biggest Secret — Creators Don't Understand It, Experts SplitMay 09, 2025 am 11:09 AMAnthropic's recent statement, highlighting the lack of understanding surrounding cutting-edge AI models, has sparked a heated debate among experts. Is this opacity a genuine technological crisis, or simply a temporary hurdle on the path to more soph
 Bulbul-V2 by Sarvam AI: India's Best TTS ModelMay 09, 2025 am 10:52 AM
Bulbul-V2 by Sarvam AI: India's Best TTS ModelMay 09, 2025 am 10:52 AMIndia is a diverse country with a rich tapestry of languages, making seamless communication across regions a persistent challenge. However, Sarvam’s Bulbul-V2 is helping to bridge this gap with its advanced text-to-speech (TTS) t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.







