OpenAI's advanced reasoning models, o1 and o3-mini, surpass the capabilities of the base GPT-4 (GPT-4o) by employing sophisticated prompt processing and response generation techniques. These models emulate human-like analytical thinking, dedicating more processing time to complex problems. To maximize their potential, understanding effective prompt crafting is paramount. This article summarizes key insights from OpenAI's prompting guide.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Reasoning Models
- Navigating Long Conversations and Memory Limitations
- Six Key Insights from OpenAI's Prompting Guide:
- Prioritize Simplicity
- Avoid Overly Detailed Instructions
- Leverage Delimiters for Clarity
- Begin with Zero-Shot Prompting
- Employ Mindful Prompt Engineering
- Utilize Model Customization
- Conclusion
Understanding Reasoning Models
OpenAI's o1 and o3-mini leverage reinforcement learning to enhance their reasoning abilities, excelling in fields like mathematics, science, and coding. Unlike standard GPT models, these models dedicate extra processing time to thoughtful analysis before providing answers, resulting in more accurate and thorough solutions for complex tasks.

Managing Long Conversations and Memory Limits
These models possess a limited memory capacity (128,000 tokens), akin to a notebook with a finite number of pages.
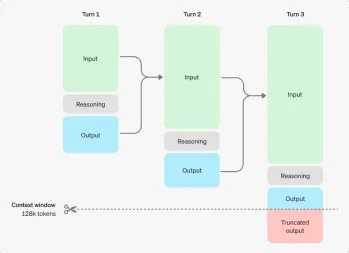
- Initial Interaction: The model receives a question (input), processes it, and provides an answer (output).
- Subsequent Interactions: The model retains previous questions and answers to inform subsequent responses.
- Extended Conversations: As the conversation lengthens, older information may be discarded due to memory limitations, potentially leading to truncated outputs.
Why Memory Limits Matter: Long conversations risk losing crucial details unless the user actively reminds the model of prior information.
Six Key Insights from OpenAI's Prompting Guide
OpenAI's guidance emphasizes optimized prompt engineering for enhanced results.
1. Prioritize Simplicity: Clear, concise prompts are crucial. Complex or ambiguous instructions can hinder the model's performance.
"o1's reasoning capabilities...yielded stronger results on 52% of complex prompts on dense Credit Agreements compared to other models." —Hebbia
Good Prompt: ✅ "What are three primary causes of the Roman Empire's decline?"
Poor Prompt: ❌ "Explain, in exhaustive detail, the economic, social, political, and military factors contributing to the Roman Empire's fall."
2. Avoid Overly Detailed Instructions: Avoid instructing the model to "think step-by-step" or explicitly explain its reasoning. This often hinders performance.
Good Prompt: ✅ "What is the derivative of x² 3x – 5?"
Poor Prompt: ❌ "Calculate the derivative of x² 3x – 5, showing each step as if explaining to a beginner."
3. Leverage Delimiters for Clarity: Use delimiters (quotes, parentheses) to structure inputs, reducing ambiguity and improving interpretation.
Good Prompt: ✅ "Analyze the sentence: 'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.' Identify the subject and verb."
Poor Prompt: ❌ "Analyze this sentence: The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog. Identify the subject and verb and explain their grammatical function."
4. Begin with Zero-Shot Prompting: Start with zero-shot prompting (no examples). Reasoning models often perform well initially. If needed, add examples (few-shot prompting) later.
Good Prompt: ✅ "Translate 'I love learning' into French."
Poor Prompt: ❌ "How would you translate 'I love learning' into French, demonstrating the translation process?"
5. Employ Mindful Prompt Engineering: Some techniques (e.g., step-by-step instructions) may not benefit reasoning models. Adapt your strategy based on the model's behavior.
Good Prompt: ✅ "Solve: 12x 5 = 41"
Poor Prompt: ❌ "Solve 12x 5 = 41, showing each step and explanation."
6. Utilize Model Customization: Experiment with different prompting approaches to find what works best for your specific needs.

This image depicts a foundation plan, detailing structural components with dimensions, annotations, and symbols. Key elements include crawlspace areas, concrete piers, wood posts, glulam beams, and joists. An abbreviations and materials table is included.
Good Prompt: ✅ "Summarize the 2023 IPCC climate report's key findings in three bullet points."
Poor Prompt: ❌ "Provide a comprehensive overview of the 2023 IPCC climate report, explaining its significance and implications for policymakers."
Conclusion
By adhering to these guidelines, users can effectively utilize OpenAI's reasoning models to solve complex problems and obtain accurate, well-structured solutions. Understanding prompt engineering nuances is key to unlocking the full potential of o1 and o3-mini across diverse applications.
References:
- OpenAI Reasoning Best Practices
- OpenAI Reasoning Models Guide
The above is the detailed content of 6 Insights from OpenAI's Prompting Guide for Reasoning Models. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 As AI Use Soars, Companies Shift From SEO To GEOMay 05, 2025 am 11:09 AM
As AI Use Soars, Companies Shift From SEO To GEOMay 05, 2025 am 11:09 AMWith the explosion of AI applications, enterprises are shifting from traditional search engine optimization (SEO) to generative engine optimization (GEO). Google is leading the shift. Its "AI Overview" feature has served over a billion users, providing full answers before users click on the link. [^2] Other participants are also rapidly rising. ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot and Perplexity are creating a new “answer engine” category that completely bypasses traditional search results. If your business doesn't show up in these AI-generated answers, potential customers may never find you—even if you rank high in traditional search results. From SEO to GEO – What exactly does this mean? For decades
 Big Bets On Which Of These Pathways Will Push Today's AI To Become Prized AGIMay 05, 2025 am 11:08 AM
Big Bets On Which Of These Pathways Will Push Today's AI To Become Prized AGIMay 05, 2025 am 11:08 AMLet's explore the potential paths to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). This analysis is part of my ongoing Forbes column on AI advancements, delving into the complexities of achieving AGI and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). (See related art
 Do You Train Your Chatbot, Or Vice Versa?May 05, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Do You Train Your Chatbot, Or Vice Versa?May 05, 2025 am 11:07 AMHuman-computer interaction: a delicate dance of adaptation Interacting with an AI chatbot is like participating in a delicate dance of mutual influence. Your questions, responses, and preferences gradually shape the system to better meet your needs. Modern language models adapt to user preferences through explicit feedback mechanisms and implicit pattern recognition. They learn your communication style, remember your preferences, and gradually adjust their responses to fit your expectations. Yet, while we train our digital partners, something equally important is happening in the reverse direction. Our interactions with these systems are subtly reshaping our own communication patterns, thinking processes, and even expectations of interpersonal conversations. Our interactions with AI systems have begun to reshape our expectations of interpersonal interactions. We adapted to instant response,
 California Taps AI To Fast-Track Wildfire Recovery PermitsMay 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
California Taps AI To Fast-Track Wildfire Recovery PermitsMay 04, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI Streamlines Wildfire Recovery Permitting Australian tech firm Archistar's AI software, utilizing machine learning and computer vision, automates the assessment of building plans for compliance with local regulations. This pre-validation significan
 What The US Can Learn From Estonia's AI-Powered Digital GovernmentMay 04, 2025 am 11:09 AM
What The US Can Learn From Estonia's AI-Powered Digital GovernmentMay 04, 2025 am 11:09 AMEstonia's Digital Government: A Model for the US? The US struggles with bureaucratic inefficiencies, but Estonia offers a compelling alternative. This small nation boasts a nearly 100% digitized, citizen-centric government powered by AI. This isn't
 Wedding Planning Via Generative AIMay 04, 2025 am 11:08 AM
Wedding Planning Via Generative AIMay 04, 2025 am 11:08 AMPlanning a wedding is a monumental task, often overwhelming even the most organized couples. This article, part of an ongoing Forbes series on AI's impact (see link here), explores how generative AI can revolutionize wedding planning. The Wedding Pl
 What Are Digital Defense AI Agents?May 04, 2025 am 11:07 AM
What Are Digital Defense AI Agents?May 04, 2025 am 11:07 AMBusinesses increasingly leverage AI agents for sales, while governments utilize them for various established tasks. However, consumer advocates highlight the need for individuals to possess their own AI agents as a defense against the often-targeted
 A Business Leader's Guide To Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)May 03, 2025 am 11:14 AM
A Business Leader's Guide To Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)May 03, 2025 am 11:14 AMGoogle is leading this shift. Its "AI Overviews" feature already serves more than one billion users, providing complete answers before anyone clicks a link.[^2] Other players are also gaining ground fast. ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, and Pe


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.






