Satya Nadella just announced the release of Microsoft’s Majorana 1, the world’s first quantum processing unit (QPU) powered by a unique “Topological Core” architecture. The announcement has stirred some serious excitement in the quantum community. Majorana 1 is a step toward the future of quantum computing, promising to tackle problems that are currently too complex for today’s classical computers. This chip, built on topological qubits, is a fresh approach, different from what competitors like Google and IBM are doing with superconducting or trapped-ion qubits. Let’s break it down.
Table of contents
- What is Majorana 1?
- Development History
- Technical Details
- Core Innovation: Topoconductors
- Qubit Design
- Measurement Breakthrough
- Architecture
- Performance and Claims
- What’s Next for Microsoft’s Majorana 1?
- End Note
What is Majorana 1?
Microsoft’s Majorana 1 is an ambitious piece of tech that brings a topological twist to quantum computing. Named after the Majorana fermion—an elusive quasiparticle theorized by Ettore Majorana back in 1937—the chip uses topological qubits. These are a far cry from the superconducting qubits or trapped-ion qubits commonly used by Google and IBM. Majorana 1 is designed to scale to one million qubits on a single palm-sized device, a size Microsoft says is key to achieving fault-tolerant quantum computing capable of solving some seriously complex industrial and societal challenges.
A couple reflections on the quantum computing breakthrough we just announced…
— Satya Nadella (@satyanadella) February 19, 2025
Most of us grew up learning there are three main types of matter that matter: solid, liquid, and gas. Today, that changed.
After a nearly 20 year pursuit, we’ve created an entirely new state of… pic.twitter.com/Vp4sxMHNjc
Development History
Timeline: The Majorana 1 isn’t something that happened overnight. It’s the result of nearly two decades of research, making it Microsoft’s longest-running R&D project. The journey started back in 2005 under the Station Q program, with experts like Chetan Nayak (Microsoft’s Technical Fellow and Quantum Hardware VP) leading the charge.
Milestones:
- 2022: Microsoft finally saw experimental evidence of Majorana zero modes (MZMs) in nanowires— a critical moment after a few earlier setbacks.
- 2023: The team managed to demonstrate control over these Majorana quasiparticles, validating their approach.
- February 19, 2025: The official unveiling is set to happen, complete with a peer-reviewed paper in Nature and data shared at the Station Q meeting.
Team: With over 160 researchers, scientists, and engineers working on the project, it’s safe to say this wasn’t a solo effort – it was a massive, interdisciplinary team effort.
Technical Details
The chip itself is quite striking, with its golden-hued circuits delicately held in hand—a compact marvel compared to some of the sprawling quantum setups we’re used to seeing. But the insides? Well, let’s learn more about it:
Core Innovation: Topoconductors
So what exactly makes this chip tick? Majorana 1 relies on a new class of materials called “topoconductors” (topological superconductors), which combine indium arsenide (a semiconductor) and aluminum (a superconductor). These materials are fabricated atom by atom using molecular beam epitaxy, cooled to near absolute zero (-273°C), and tuned with magnetic fields to create a state of matter that’s neither solid, liquid, nor gas.
This special state enables the creation of Majorana zero modes (MZMs) at the ends of nanowires. These MZMs have some unique properties, like non-Abelian statistics, meaning they store quantum information in a non-local way, making them resistant to environmental noise. In other words, they’re naturally more stable than traditional qubits.
Qubit Design
The topological qubits in Majorana 1 are formed from an “H”-shaped unit, consisting of two parallel topological nanowires connected by a trivial superconducting wire. Microsoft calls this a “tetron.” Currently, the Majorana 1 chip hosts eight of these qubits, but the idea is to scale up to one million qubits on a single chip—roughly the size of a watch face or a palm.

And here’s the fun part: Unlike traditional qubits that require complex analog signals, these topological qubits are digitally controlled with simple pulses connecting quantum dots to nanowires. This makes operations simpler and less prone to errors.
Measurement Breakthrough
In a world where quantum states are notoriously finicky, Microsoft developed a precise method to measure these states. Using quantum dots (tiny capacitors), they can detect parity—whether there’s an even or odd number of electrons in the system—in microseconds. This allows them to distinguish between different states, an important step for computation.
The cool part? This non-destructive measurement supports a “measurement-based” computing approach, which is different from the rotation-based methods used by many competitors.
Architecture
The architecture of Majorana 1 is designed with scalability in mind. The chip uses tetrons arranged in arrays (think 4×2 or 27×13 setups), supporting quantum error correction (QEC) via lattice surgery and braiding transformations. These arrays are designed to be easily integrated into Azure data centers, making the setup much more compact than some rival quantum computers that require sprawling physical spaces.
Performance and Claims
- Current State: As of now, Majorana 1 is still a research device. It only has eight qubits—far fewer than the 156 qubits in IBM’s latest processor or Google’s Willow chip. But Microsoft isn’t too worried about quantity— they’re all about quality.
- Error Resistance: Topological qubits are hardware-protected, meaning they’re inherently more stable than traditional qubits, which often rely on software-driven error correction. Exact error rates haven’t been disclosed, but early data suggests significant improvements in stability.
- Scalability: Microsoft claims they have a “clear path” to scaling up to a million qubits. This is a bold claim, especially since other companies estimate that it would take thousands of physical qubits to achieve the same logical output due to error correction overhead. Majorana 1’s design, however, theoretically requires fewer physical qubits to reach the same result.
- Timeline: Microsoft suggests that practical quantum computing could arrive in the next few years—perhaps by 2030. This puts them ahead of rivals like Nvidia (which predicts 15-30 years) or IBM (2033).
What’s Next for Microsoft’s Majorana 1?
- Two-Qubit Device: Demonstrate measurement-based braiding for Clifford operations.
- Eight-Qubit Array: Implement error correction on logical qubits.
- Larger Arrays: Move toward a fault-tolerant prototype (27×13 tetrons) as part of DARPA’s US2QC program, where Microsoft is a finalist.
- Commercialization: No firm commercialization date yet, but Microsoft plans to share Majorana 1 with labs and universities in the coming years for research purposes.
Beyond Scale: Microsoft envisions that a million-qubit chip is just the beginning—Nayak believes they’ll need about 1,000 of these chips for true utility-scale impact.
End Note
Microsoft’s Majorana 1 is an intriguing step forward in quantum computing. While it might not have the raw qubit power yet to compete with Google or IBM in sheer numbers, its topological approach holds a lot of promise. If Microsoft can scale it up as claimed, Majorana 1 might not just be another flash in the quantum pan—it could be the beginning of something much bigger. But only time will tell.
Stay updated with the latest happenings of the AI world with Analytics Vidhya News!
The above is the detailed content of Microsoft's Majorana 1 Explained: The Path to a Million Qubits. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Personal Hacking Will Be A Pretty Fierce BearMay 11, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Personal Hacking Will Be A Pretty Fierce BearMay 11, 2025 am 11:09 AMCyberattacks are evolving. Gone are the days of generic phishing emails. The future of cybercrime is hyper-personalized, leveraging readily available online data and AI to craft highly targeted attacks. Imagine a scammer who knows your job, your f
 Pope Leo XIV Reveals How AI Influenced His Name ChoiceMay 11, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Pope Leo XIV Reveals How AI Influenced His Name ChoiceMay 11, 2025 am 11:07 AMIn his inaugural address to the College of Cardinals, Chicago-born Robert Francis Prevost, the newly elected Pope Leo XIV, discussed the influence of his namesake, Pope Leo XIII, whose papacy (1878-1903) coincided with the dawn of the automobile and
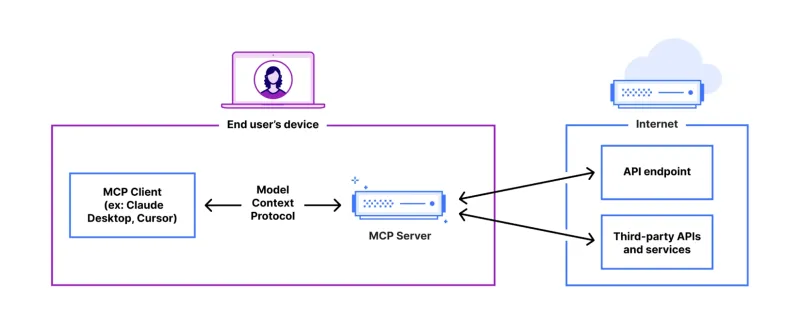 FastAPI-MCP Tutorial for Beginners and Experts - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:56 AM
FastAPI-MCP Tutorial for Beginners and Experts - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:56 AMThis tutorial demonstrates how to integrate your Large Language Model (LLM) with external tools using the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and FastAPI. We'll build a simple web application using FastAPI and convert it into an MCP server, enabling your L
 Dia-1.6B TTS : Best Text-to-Dialogue Generation Model - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:27 AM
Dia-1.6B TTS : Best Text-to-Dialogue Generation Model - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:27 AMExplore Dia-1.6B: A groundbreaking text-to-speech model developed by two undergraduates with zero funding! This 1.6 billion parameter model generates remarkably realistic speech, including nonverbal cues like laughter and sneezes. This article guide
 3 Ways AI Can Make Mentorship More Meaningful Than EverMay 10, 2025 am 11:17 AM
3 Ways AI Can Make Mentorship More Meaningful Than EverMay 10, 2025 am 11:17 AMI wholeheartedly agree. My success is inextricably linked to the guidance of my mentors. Their insights, particularly regarding business management, formed the bedrock of my beliefs and practices. This experience underscores my commitment to mentor
 AI Unearths New Potential In The Mining IndustryMay 10, 2025 am 11:16 AM
AI Unearths New Potential In The Mining IndustryMay 10, 2025 am 11:16 AMAI Enhanced Mining Equipment The mining operation environment is harsh and dangerous. Artificial intelligence systems help improve overall efficiency and security by removing humans from the most dangerous environments and enhancing human capabilities. Artificial intelligence is increasingly used to power autonomous trucks, drills and loaders used in mining operations. These AI-powered vehicles can operate accurately in hazardous environments, thereby increasing safety and productivity. Some companies have developed autonomous mining vehicles for large-scale mining operations. Equipment operating in challenging environments requires ongoing maintenance. However, maintenance can keep critical devices offline and consume resources. More precise maintenance means increased uptime for expensive and necessary equipment and significant cost savings. AI-driven
 Why AI Agents Will Trigger The Biggest Workplace Revolution In 25 YearsMay 10, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Why AI Agents Will Trigger The Biggest Workplace Revolution In 25 YearsMay 10, 2025 am 11:15 AMMarc Benioff, Salesforce CEO, predicts a monumental workplace revolution driven by AI agents, a transformation already underway within Salesforce and its client base. He envisions a shift from traditional markets to a vastly larger market focused on
 AI HR Is Going To Rock Our Worlds As AI Adoption SoarsMay 10, 2025 am 11:14 AM
AI HR Is Going To Rock Our Worlds As AI Adoption SoarsMay 10, 2025 am 11:14 AMThe Rise of AI in HR: Navigating a Workforce with Robot Colleagues The integration of AI into human resources (HR) is no longer a futuristic concept; it's rapidly becoming the new reality. This shift impacts both HR professionals and employees, dem


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.







