This tutorial demonstrates fine-tuning the cost-effective GPT-4o Mini large language model for stress detection in social media text. We'll leverage the OpenAI API and playground for both fine-tuning and evaluation, comparing performance before and after the process.

Introducing GPT-4o Mini:
GPT-4o Mini stands out as a highly affordable general-purpose LLM. Boasting an 82% score on the MMLU benchmark and surpassing Claude 3.5 Sonnet in chat preferences (LMSYS leaderboard), it offers significant cost savings (60% cheaper than GPT-3.5 Turbo) at 15 cents per million input tokens and 60 cents per million output tokens. It accepts text and image inputs, features a 128K token context window, supports up to 16K output tokens, and its knowledge cutoff is October 2023. Its compatibility with non-English text, thanks to the GPT-4o tokenizer, adds to its versatility. For a deeper dive into GPT-4o Mini, explore our blog post: "What Is GPT-4o Mini?"
Setting Up the OpenAI API:
- Create an OpenAI account. Fine-tuning incurs costs, so ensure a minimum of $10 USD credit before proceeding.
- Generate an OpenAI API secret key from your dashboard's "API keys" tab.
- Configure your API key as an environment variable (DataCamp's DataLab is used in this example).
- Install the OpenAI Python package:
%pip install openai - Create an OpenAI client and test it with a sample prompt.



New to the OpenAI API? Our "GPT-4o API Tutorial: Getting Started with OpenAI's API" provides a comprehensive introduction.
Fine-tuning GPT-4o Mini for Stress Detection:
We'll fine-tune GPT-4o Mini using a Kaggle dataset of Reddit and Twitter posts labeled as "stress" or "non-stress."
1. Dataset Creation:
- Load and process the dataset (e.g., the top 200 rows of a Reddit post dataset).
- Retain only the 'title' and 'label' columns.
- Map numerical labels (0, 1) to "non-stress" and "stress".
- Split into training and validation sets (80/20 split).
- Save both sets in JSONL format, ensuring each entry includes a system prompt, user query (post title), and the "assistant" response (label).
2. Dataset Upload:
Use the OpenAI client to upload the training and validation JSONL files.
3. Fine-tuning Job Initiation:
Create a fine-tuning job specifying the file IDs, model name (gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18), and hyperparameters (e.g., 3 epochs, batch size 3, learning rate multiplier 0.3). Monitor the job's status via the dashboard or API.



Accessing the Fine-tuned Model:
Retrieve the fine-tuned model name from the API and use it to generate predictions via the API or the OpenAI playground.


Model Evaluation:
Compare the base and fine-tuned models using accuracy, classification reports, and confusion matrices on the validation set. A custom predict function generates predictions, and an evaluate function provides the performance metrics.
Conclusion:
This tutorial provides a practical guide to fine-tuning GPT-4o Mini, showcasing its effectiveness in improving text classification accuracy. Remember to explore the linked resources for further details and alternative approaches. For a free, open-source alternative, consider our "Fine-tuning Llama 3.2 and Using It Locally" tutorial.
The above is the detailed content of Fine-tuning GPT-4o Mini: A Step-by-Step Guide. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 AI Game Development Enters Its Agentic Era With Upheaval's Dreamer PortalMay 02, 2025 am 11:17 AM
AI Game Development Enters Its Agentic Era With Upheaval's Dreamer PortalMay 02, 2025 am 11:17 AMUpheaval Games: Revolutionizing Game Development with AI Agents Upheaval, a game development studio comprised of veterans from industry giants like Blizzard and Obsidian, is poised to revolutionize game creation with its innovative AI-powered platfor
 Uber Wants To Be Your Robotaxi Shop, Will Providers Let Them?May 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
Uber Wants To Be Your Robotaxi Shop, Will Providers Let Them?May 02, 2025 am 11:16 AMUber's RoboTaxi Strategy: A Ride-Hail Ecosystem for Autonomous Vehicles At the recent Curbivore conference, Uber's Richard Willder unveiled their strategy to become the ride-hail platform for robotaxi providers. Leveraging their dominant position in
 AI Agents Playing Video Games Will Transform Future RobotsMay 02, 2025 am 11:15 AM
AI Agents Playing Video Games Will Transform Future RobotsMay 02, 2025 am 11:15 AMVideo games are proving to be invaluable testing grounds for cutting-edge AI research, particularly in the development of autonomous agents and real-world robots, even potentially contributing to the quest for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). A
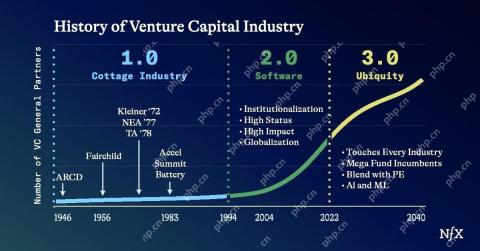 The Startup Industrial Complex, VC 3.0, And James Currier's ManifestoMay 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
The Startup Industrial Complex, VC 3.0, And James Currier's ManifestoMay 02, 2025 am 11:14 AMThe impact of the evolving venture capital landscape is evident in the media, financial reports, and everyday conversations. However, the specific consequences for investors, startups, and funds are often overlooked. Venture Capital 3.0: A Paradigm
 Adobe Updates Creative Cloud And Firefly At Adobe MAX London 2025May 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Adobe Updates Creative Cloud And Firefly At Adobe MAX London 2025May 02, 2025 am 11:13 AMAdobe MAX London 2025 delivered significant updates to Creative Cloud and Firefly, reflecting a strategic shift towards accessibility and generative AI. This analysis incorporates insights from pre-event briefings with Adobe leadership. (Note: Adob
 Everything Meta Announced At LlamaConMay 02, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Everything Meta Announced At LlamaConMay 02, 2025 am 11:12 AMMeta's LlamaCon announcements showcase a comprehensive AI strategy designed to compete directly with closed AI systems like OpenAI's, while simultaneously creating new revenue streams for its open-source models. This multifaceted approach targets bo
 The Brewing Controversy Over The Proposition That AI Is Nothing More Than Just Normal TechnologyMay 02, 2025 am 11:10 AM
The Brewing Controversy Over The Proposition That AI Is Nothing More Than Just Normal TechnologyMay 02, 2025 am 11:10 AMThere are serious differences in the field of artificial intelligence on this conclusion. Some insist that it is time to expose the "emperor's new clothes", while others strongly oppose the idea that artificial intelligence is just ordinary technology. Let's discuss it. An analysis of this innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column that covers the latest advancements in the field of AI, including identifying and explaining a variety of influential AI complexities (click here to view the link). Artificial intelligence as a common technology First, some basic knowledge is needed to lay the foundation for this important discussion. There is currently a large amount of research dedicated to further developing artificial intelligence. The overall goal is to achieve artificial general intelligence (AGI) and even possible artificial super intelligence (AS)
 Model Citizens, Why AI Value Is The Next Business YardstickMay 02, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Model Citizens, Why AI Value Is The Next Business YardstickMay 02, 2025 am 11:09 AMThe effectiveness of a company's AI model is now a key performance indicator. Since the AI boom, generative AI has been used for everything from composing birthday invitations to writing software code. This has led to a proliferation of language mod


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools






