Detailed explanation of QuickSort algorithm: an efficient sorting tool
QuickSort is an efficient sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer strategy. The divide-and-conquer method decomposes the problem into smaller sub-problems, solves these sub-problems separately, and then combines the solutions of the sub-problems to obtain the final solution. In quick sort, an array is divided by selecting a partition element, which determines the split point of the array. Before partitioning, the position of the partitioning element is rearranged so that it is before the element that is larger than it and after the element that is smaller than it. The left and right subarrays will be divided recursively in this manner until each subarray contains only one element, at which point the array is sorted.
How quick sort works
Let us sort the following array in ascending order as an example:

Step 1: Select the pivot element
We choose the last element as the pivot:

Step 2: Rearrange pivot elements
We place the pivot element before elements that are larger than it and after elements that are smaller than it. To do this, we will iterate through the array and compare the pivot to each element before it. If an element larger than the pivot is found, we create a second pointer for it:

If an element smaller than the pivot is found, we swap it with the second pointer:
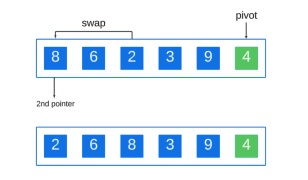
Repeat this process, setting the next element larger than the pivot to the second pointer, swapping if an element smaller than the pivot is found:
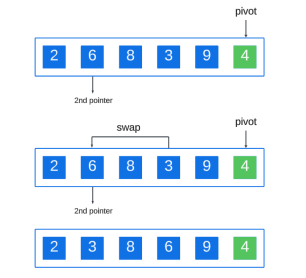
Continue this process until you reach the end of the array:
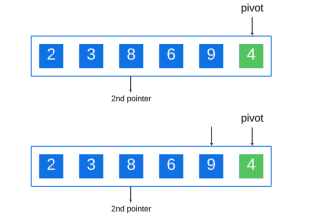
After completing the element comparison, the element smaller than the pivot has been moved to the right, then we swap the pivot with the second pointer:
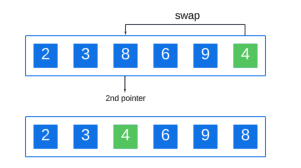
Step 3: Divide the array
Divide the array according to the partition index. If we represent the array as arr[start..end], then by dividing the array by partition, we can get the left subarray arr[start..partitionIndex-1] and the right subarray arr[partitionIndex 1..end].

Continue dividing the subarrays in this way until each subarray contains only one element:
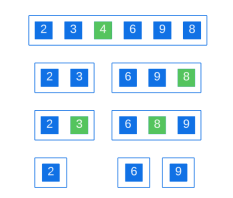
At this point, the array is sorted.

Quick sort code implementation
import java.util.Arrays;
public class QuickSortTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 4};
System.out.println("未排序数组: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length-1);
System.out.println("已排序数组: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static int partition(int[] arr, int start, int end){
// 将最后一个元素设置为枢轴
int pivot = arr[end];
// 创建指向下一个较大元素的指针
int secondPointer = start-1;
// 将小于枢轴的元素移动到枢轴左侧
for (int i = start; i < end; i++){
if (arr[i] < pivot){
secondPointer++;
// 交换元素
int temp = arr[secondPointer];
arr[secondPointer] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
// 将枢轴与第二个指针交换
int temp = arr[secondPointer+1];
arr[secondPointer+1] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
// 返回分区索引
return secondPointer+1;
}
public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int start, int end){
if (start < end){
// 找到分区索引
int partitionIndex = partition(arr, start, end);
// 递归调用快速排序
quickSort(arr, start, partitionIndex-1);
quickSort(arr, partitionIndex+1, end);
}
}
}
Code interpretation
quickSort method: First call the partition method to divide the array into two sub-arrays, and then call quickSort recursively to sort the left and right sub-arrays. This process continues until all subarrays contain exactly one element, at which point the array is sorted.
partition Method: Responsible for dividing the array into two sub-arrays. It first sets the pivot and the pointer to the next larger element, then iterates through the array, moving elements smaller than the pivot to the left. After that it swaps the pivot with the second pointer and returns the partition position.
Run the above code, the console will output the following:
Unsorted array: [8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 4] Sorted array: [2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9]
Time complexity
Best case (O(n log n)): The best case occurs when the pivot splits the array into two nearly equal parts every time.
Average case (O(n log n)): In the average case, the pivot splits the array into two unequal parts, but the recursion depth and number of comparisons are still proportional to n log n.
Worst case (O(n²)): The worst case occurs when the pivot always splits the array into very unequal parts (e.g. one part has only one element and the other has n-1 elements) . This can happen, for example, when sorting an array in reverse order, and the pivot is chosen poorly.
Space complexity (O(log n)): Quick sort is usually implemented in-place and does not require additional arrays.
The above is the detailed content of Understanding Quick Sort Algorithm (with Examples in Java). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Explain how the JVM acts as an intermediary between the Java code and the underlying operating system.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:23 AM
Explain how the JVM acts as an intermediary between the Java code and the underlying operating system.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:23 AMJVM works by converting Java code into machine code and managing resources. 1) Class loading: Load the .class file into memory. 2) Runtime data area: manage memory area. 3) Execution engine: interpret or compile execution bytecode. 4) Local method interface: interact with the operating system through JNI.
 Explain the role of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) in Java's platform independence.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:21 AM
Explain the role of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) in Java's platform independence.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:21 AMJVM enables Java to run across platforms. 1) JVM loads, validates and executes bytecode. 2) JVM's work includes class loading, bytecode verification, interpretation execution and memory management. 3) JVM supports advanced features such as dynamic class loading and reflection.
 What steps would you take to ensure a Java application runs correctly on different operating systems?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What steps would you take to ensure a Java application runs correctly on different operating systems?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:11 AMJava applications can run on different operating systems through the following steps: 1) Use File or Paths class to process file paths; 2) Set and obtain environment variables through System.getenv(); 3) Use Maven or Gradle to manage dependencies and test. Java's cross-platform capabilities rely on the JVM's abstraction layer, but still require manual handling of certain operating system-specific features.
 Are there any areas where Java requires platform-specific configuration or tuning?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Are there any areas where Java requires platform-specific configuration or tuning?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:11 AMJava requires specific configuration and tuning on different platforms. 1) Adjust JVM parameters, such as -Xms and -Xmx to set the heap size. 2) Choose the appropriate garbage collection strategy, such as ParallelGC or G1GC. 3) Configure the Native library to adapt to different platforms. These measures can enable Java applications to perform best in various environments.
 What are some tools or libraries that can help you address platform-specific challenges in Java development?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:01 AM
What are some tools or libraries that can help you address platform-specific challenges in Java development?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:01 AMOSGi,ApacheCommonsLang,JNA,andJVMoptionsareeffectiveforhandlingplatform-specificchallengesinJava.1)OSGimanagesdependenciesandisolatescomponents.2)ApacheCommonsLangprovidesutilityfunctions.3)JNAallowscallingnativecode.4)JVMoptionstweakapplicationbehav
 How does the JVM manage garbage collection across different platforms?Apr 28, 2025 am 12:23 AM
How does the JVM manage garbage collection across different platforms?Apr 28, 2025 am 12:23 AMJVMmanagesgarbagecollectionacrossplatformseffectivelybyusingagenerationalapproachandadaptingtoOSandhardwaredifferences.ItemploysvariouscollectorslikeSerial,Parallel,CMS,andG1,eachsuitedfordifferentscenarios.Performancecanbetunedwithflagslike-XX:NewRa
 Why can Java code run on different operating systems without modification?Apr 28, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Why can Java code run on different operating systems without modification?Apr 28, 2025 am 12:14 AMJava code can run on different operating systems without modification, because Java's "write once, run everywhere" philosophy is implemented by Java virtual machine (JVM). As the intermediary between the compiled Java bytecode and the operating system, the JVM translates the bytecode into specific machine instructions to ensure that the program can run independently on any platform with JVM installed.
 Describe the process of compiling and executing a Java program, highlighting platform independence.Apr 28, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Describe the process of compiling and executing a Java program, highlighting platform independence.Apr 28, 2025 am 12:08 AMThe compilation and execution of Java programs achieve platform independence through bytecode and JVM. 1) Write Java source code and compile it into bytecode. 2) Use JVM to execute bytecode on any platform to ensure the code runs across platforms.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






