Home >Java >javaTutorial >Inheritance and Polymorphism in Java: Using Superclasses and Subclasses
Inheritance and Polymorphism in Java: Using Superclasses and Subclasses
- Linda HamiltonOriginal
- 2025-01-06 10:31:461015browse
This article explains how Java’s inheritance has an “is-a” relationship between superclasses and subclasses, allowing subclasses to inherit and customize superclass functionality. By using polymorphism, subclasses can define unique behaviors, allowing code reuse and flexibility in object-oriented programming.
In Java, the relationship between super-classes (parent class) and subclasses (child class or derived class) in inheritance is a is-a relationship implying that the subclass is a specialized version of the superclass inheriting the functionality (restrictions can be applied) of a class that it is derived from (CSU Global, n.d). In other words, if class B inherits from class A, then class B “is a” type of class A. This relationship allows class B to use all the functionalities (restrictions can be applied) provided by class A, while also adding its own specific functionalities or/and by overriding some or all of the functionalities of class A. The ability of the child class to override functionality is a form of polymorphism.
“The dictionary definition of polymorphism refers to a principle in biology in which an organism or species can have many different forms or stages. This principle can also be applied to object-oriented programming and languages like the Java language. Subclasses of a class can define their own unique behaviors and yet share some of the same functionality of the parent class” (The Java™ Tutorials, n.d.)This is especially beneficial when dealing with multiple objects from different subclasses that share a common superclass type.
For example: dogs, cats, and owls are animals:
Superclass
public class Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Makes a Sound");
}
}
Subclass of Animals
public class Domesticated extends Animal {
public void friendly() {
System.out.println("This animal is friendly.");
}
}
Subclass of Domesticated
public class Undomesticated extends Animal {
public void notFriendly() {
System.out.println("This animal is not friendly.");
}
}
Subclass of Domesticated
public class Cat extends Domesticated {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow");
}
}
Subclass of Undomesticated
public class Owl extends Undomesticated {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Hoots");
}
}
Main class to output the result
public class inheritanceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog myDog = new Dog();
Cat myCat = new Cat();
Owl redOwl = new Owl();
System.out.println("MY Dog:");
myDog.makeSound(); // Outputs: Bark
myDog.friendly(); // Outputs: This animal is friendly.
System.out.println();
System.out.println("My Cat:");
myCat.makeSound(); // Outputs: Meow
myCat.friendly(); // Outputs: This animal is friendly.
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Red Owl:");
redOwl.makeSound(); // Outputs: Hoot
redOwl.notFriendly(); // Outputs: This animal is not friendly.
}
}
Note: The makeSound() methods in the Dog and Cat classes override the makeSound() method in the Animal class.
Additionally, the Dog class is a subclass of the Domesticated class which is a subclass of the Animal class.
Child of ‘→’

In Java, a subclass can only have one superclass, for example, the Dog class cannot have a superclass Domesticated and a superclass Animal, the following is not allowed.
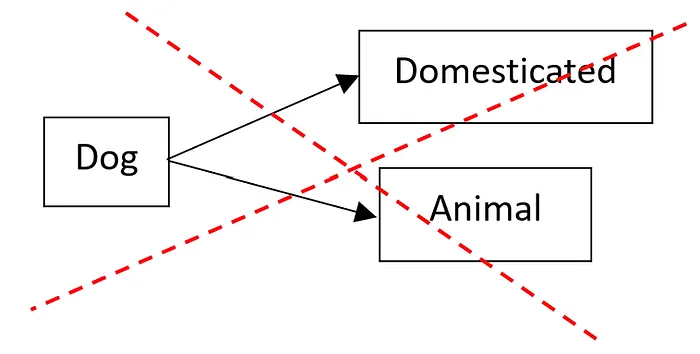
In other words, a subclass can only have one superclass, … and they are not allowed to have multiple parents, grandparents, or great-grandparents.

In conclusion, Java’s inheritance allows subclasses to utilize and extend the functionality of superclasses, embodying the “is-a” relationship and facilitating polymorphism. This enhances code reusability, flexibility, and consistency by enabling specific behaviors in subclasses while maintaining shared characteristics across a common superclass.
References:
CUS Global (n.d.). Module 1: Working with inheritance [Interactive lecture]. In Colorado State University Global, CSC372: Programming II, Computer Science Department. Canvas. Retrieved June 8, 2024, from https://csuglobal.instructure.com/courses/94948/pages/module-1-overview?module_item_id=4868813
The Java™ Tutorials (n.d.). Learning the Java language: Interfaces and inheritance. Oracle. Retrieved June 8, 2024, fromhttps://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/IandI/polymorphism.html
Originally published at Alex.omegapy on Medium published by Level UP Coding on November 1, 2024.
The above is the detailed content of Inheritance and Polymorphism in Java: Using Superclasses and Subclasses. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

