 Backend Development
Backend Development PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial How Can I Secure My Database Against SQL Injection When Using Dynamic Table Names?
How Can I Secure My Database Against SQL Injection When Using Dynamic Table Names?
How to Safeguard Against SQL Injection with Dynamic Table Names
As highlighted in a recent discussion, relying on PDO or mysql_real_escape_string to prevent SQL injection with dynamic tablenames is ineffective. Contrary to the assertion that these measures are "extremely poor quality," understanding why they fall short is crucial for robust security.
mysql_real_escape_string's Limitations
mysql_real_escape_string is designed to escape string data enclosed in quotes. It fails to handle dynamic table names because it does not escape the backtick character (`). This poses a security vulnerability, as injection can be achieved by simply ending the string with a backtick.
PDO's Lack of Support
PDO also does not provide sanitation for dynamic table names. This stems from the fact that it considers table names as identifiers, which it does not escape automatically.
Best Practices
To mitigate these risks, it is advisable to avoid using dynamic table names whenever possible. However, if they are unavoidable, consider the following measures:
- Use a whitelist: Compare the dynamic table name against a pre-defined list of valid table names.
- Implement a system of parameterized queries: Use parameterized queries instead of string concatenation to avoid the need for dynamic table names.
By incorporating these techniques into development practices, developers can effectively prevent SQL injection attacks that exploit dynamic tablenames.
The above is the detailed content of How Can I Secure My Database Against SQL Injection When Using Dynamic Table Names?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PMLaravel simplifies handling temporary session data using its intuitive flash methods. This is perfect for displaying brief messages, alerts, or notifications within your application. Data persists only for the subsequent request by default: $request-
 cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AMThe PHP Client URL (cURL) extension is a powerful tool for developers, enabling seamless interaction with remote servers and REST APIs. By leveraging libcurl, a well-respected multi-protocol file transfer library, PHP cURL facilitates efficient execution of various network protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. This extension offers granular control over HTTP requests, supports multiple concurrent operations, and provides built-in security features.
 Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PMLaravel provides concise HTTP response simulation syntax, simplifying HTTP interaction testing. This approach significantly reduces code redundancy while making your test simulation more intuitive. The basic implementation provides a variety of response type shortcuts: use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http; Http::fake([ 'google.com' => 'Hello World', 'github.com' => ['foo' => 'bar'], 'forge.laravel.com' =>
 12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PMDo you want to provide real-time, instant solutions to your customers' most pressing problems? Live chat lets you have real-time conversations with customers and resolve their problems instantly. It allows you to provide faster service to your custom
 Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PMArticle discusses late static binding (LSB) in PHP, introduced in PHP 5.3, allowing runtime resolution of static method calls for more flexible inheritance.Main issue: LSB vs. traditional polymorphism; LSB's practical applications and potential perfo
 PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PMPHP logging is essential for monitoring and debugging web applications, as well as capturing critical events, errors, and runtime behavior. It provides valuable insights into system performance, helps identify issues, and supports faster troubleshoot
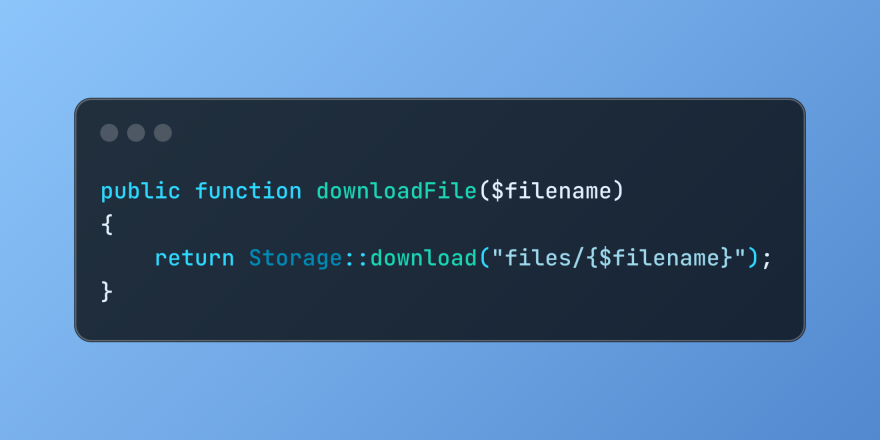 Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::downloadMar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::downloadMar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AMThe Storage::download method of the Laravel framework provides a concise API for safely handling file downloads while managing abstractions of file storage. Here is an example of using Storage::download() in the example controller:
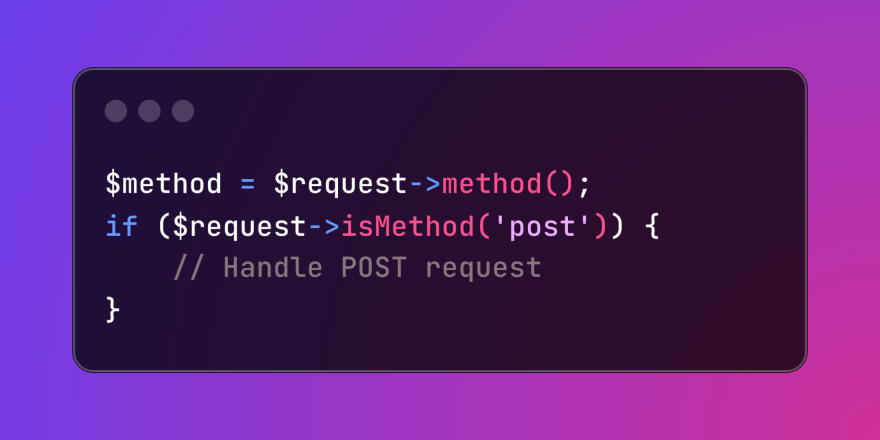 HTTP Method Verification in LaravelMar 05, 2025 pm 04:14 PM
HTTP Method Verification in LaravelMar 05, 2025 pm 04:14 PMLaravel simplifies HTTP verb handling in incoming requests, streamlining diverse operation management within your applications. The method() and isMethod() methods efficiently identify and validate request types. This feature is crucial for building


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft





