What do PoS and PoW mean? What's the difference? Which one is better?
This article takes an in-depth look at two mainstream consensus mechanisms: Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW). PoS requires validators to pledge tokens to obtain the power to verify transactions. It has the advantages of energy saving and good scalability, but it may also lead to concentration of wealth. PoW requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to verify transactions. It is more secure and decentralized, but it consumes a lot of energy and has poor scalability. This article compares the principles, advantages and disadvantages, and applications of PoS and PoW in the blockchain field to help readers understand the key roles they play in the consensus mechanism.

PoS and PoW: Detailed explanation of the mainstream consensus mechanism in the currency circle
This article will delve into PoS (Proof of Stake) and P oW (proof of work), two consensus mechanisms that are crucial in the currency circle, and compare their main differences to help readers understand their principles, advantages and disadvantages, and applications in the blockchain field.
1. PoS (Proof of Stake)
PoS is a consensus mechanism that requires validators to hold or "pledge" a certain number of tokens. Validators gain the power to validate transactions by holding enough tokens, while malicious behavior or misconduct is punished by having their staked tokens slashed.
- Principle: The PoS system verifies transactions by randomly selecting the validator with the most staked tokens. These validators then vote on the transaction, and if consensus is reached, the transaction is added to the blockchain.
-
Advantages: PoS mechanism has the following advantages:
- Lower energy consumption: PoS verification compared to PoW Transactions do not require extensive computing power, significantly reducing energy consumption.
- Higher security: Attacking a PoS network is more difficult than a PoW network because an attacker needs to obtain a large number of tokens to gain control.
- Better scalability: PoS networks can handle more transactions because verifying transactions does not require expensive computational costs.
-
Disadvantages: PoS mechanism also has some disadvantages:
- Advantage for the rich: Own Validators of more tokens have greater power and access to rewards, which can lead to concentration of wealth.
- Rewards for malicious behavior: If validators engage in malicious behavior, they may receive additional rewards, which may undermine the security of the network.
- Liquidity Restricted: Staked tokens typically cannot be sold immediately, which may limit validator liquidity.
2. PoW (Proof of Work)
PoW is a consensus mechanism that requires miners to verify transactions by solving complex mathematical puzzles. The first or first few miners to solve the puzzle will gain the power to add new blocks on the blockchain.
- Principle: PoW system verifies transactions by randomly selecting the first or first few miners to solve the puzzle. These miners then vote on the transaction, and if consensus is reached, the transaction is added to the blockchain.
-
Advantages: PoW mechanism has the following advantages:
- Higher decentralization: PoW network does not require verification or stake tokens, which makes it more decentralized and censorship-resistant.
- Stronger security: It is very difficult to attack a PoW network because the attacker needs to control more than 51% of the network's computing power.
-
Disadvantages: The PoW mechanism also has some disadvantages:
- Higher energy consumption: PoW verification of transactions requires a large amount of computing power, which results in high energy consumption.
- Poor scalability: PoW networks can only handle a limited number of transactions because of the high cost of verifying transactions.
- Costly: Mining equipment and energy costs are expensive, which may limit the number of people who can participate in mining.
3. Comparison of PoS and PoW
| 特征 | PoS | PoW |
|---|---|---|
| 共识机制 | 持有或质押代币 | 解决数学难题 |
| 能耗 | 低能耗 | 高能耗 |
| 可扩展性 | 高可扩展性 | 低可扩展性 |
| 安全性 | 相对较高 | 相对较高 |
| 去中心化程度 | 较低 | 较高 |
| 财富集中 | 可能导致 | 不太可能 |
| 恶意行为的奖励 | 可能发生 | 不太可能 |
Summary:
Both PoS and PoW are important consensus mechanisms, each with its own pros and cons. The PoS mechanism is more energy-efficient and scalable, but may lead to concentration of wealth. The PoW mechanism is more decentralized and more secure, but has higher energy consumption and poor scalability. Depending on the needs and goals of a specific project, the most appropriate consensus mechanism can be selected for a blockchain.
The above is the detailed content of What do PoS and PoW mean? What's the difference? Which one is better?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Meme Coins' Hot Streak Cooled Dramatically in Q1 2025Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Meme Coins' Hot Streak Cooled Dramatically in Q1 2025Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:24 PMThis sharp drop happened as investor interest faded and a major scandal hit the highly speculative market.
 We Tend to Think Coin Flips Are Unfair When We LoseApr 18, 2025 pm 12:22 PM
We Tend to Think Coin Flips Are Unfair When We LoseApr 18, 2025 pm 12:22 PMDespite being pretty much the iconic example of “random” – well, that and dice rolls – we can't help but feel like there's some element of skill involved. Especially when we lose.
 Bitwise Announces the Listing of Four of Its Crypto ETPs on the London Stock Exchange (LSE)Apr 18, 2025 am 11:24 AM
Bitwise Announces the Listing of Four of Its Crypto ETPs on the London Stock Exchange (LSE)Apr 18, 2025 am 11:24 AMBitwise, a leading digital asset manager, has announced the listing of four of its crypto Exchange-Traded Products (ETPs) on the London Stock Exchange (LSE).
 Bitcoin Set to Explode After Gold's Rally: Here's When BTC Could Break All-Time HighsApr 18, 2025 am 11:22 AM
Bitcoin Set to Explode After Gold's Rally: Here's When BTC Could Break All-Time HighsApr 18, 2025 am 11:22 AMBitcoin may be poised for a massive rally—but only if gold continues its upward climb, according to Joe Consorti, Head of Growth at Theya.
 Shiba Inu (SHIB) Price Prediction 2025: Targeting $0.0000399 By Year-EndApr 18, 2025 am 11:20 AM
Shiba Inu (SHIB) Price Prediction 2025: Targeting $0.0000399 By Year-EndApr 18, 2025 am 11:20 AMThe Shiba Inu price continues to attract the attention of analysts, who are watching for its next potential move. By Samuele Piar. Updated April 14, 2025.
 Ripple and U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Agree to Hold the Appeal in AbeyanceApr 18, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Ripple and U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Agree to Hold the Appeal in AbeyanceApr 18, 2025 am 11:18 AMThe joint motion of Ripple and U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to hold the appeal in abeyance has been granted by the Circuit Judge Jose A. Cabranes.
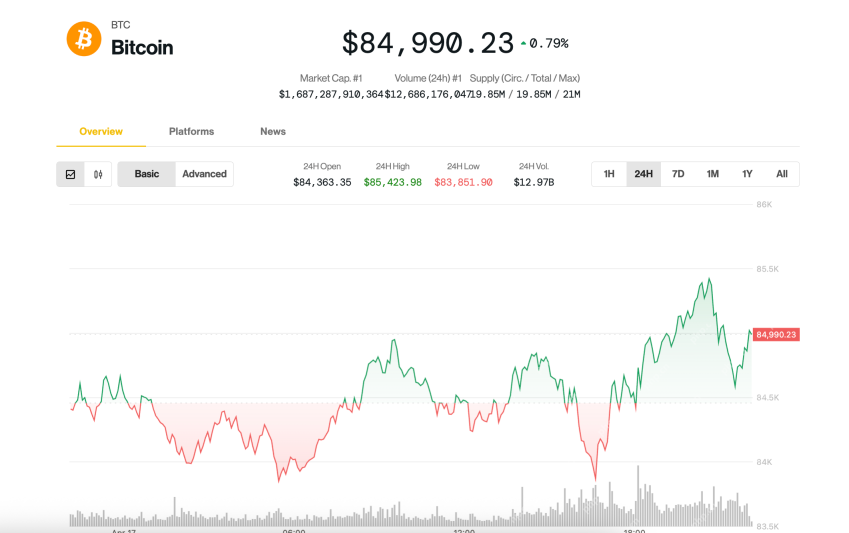 Bitcoin (BTC) was treading water just below $85,000Apr 18, 2025 am 11:14 AM
Bitcoin (BTC) was treading water just below $85,000Apr 18, 2025 am 11:14 AMBitcoin (BTC) was treading water just below $85,000 late Thursday as tensions between U.S. President Donald Trump and Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell added another layer of uncertainty for investors.
 AB DAO Launches Dual Reward Campaign in Collaboration with Bitget to Celebrate Its Token Generation EventApr 18, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AB DAO Launches Dual Reward Campaign in Collaboration with Bitget to Celebrate Its Token Generation EventApr 18, 2025 am 11:12 AMToday, AB DAO officially announced the launch of a dual reward campaign in collaboration with Bitget (bitget.com), the world's second-largest digital asset trading platform.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor





