Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >Big O Notation - Python
Big O Notation - Python
- Barbara StreisandOriginal
- 2024-11-18 08:43:01846browse
1. Definition
Mathematical notation that describes the upper limit of the execution time or space usage of an algorithm. It is denoted as O(f(n)), where f(n) is a function that represents time or space as a function of the size of the input n.
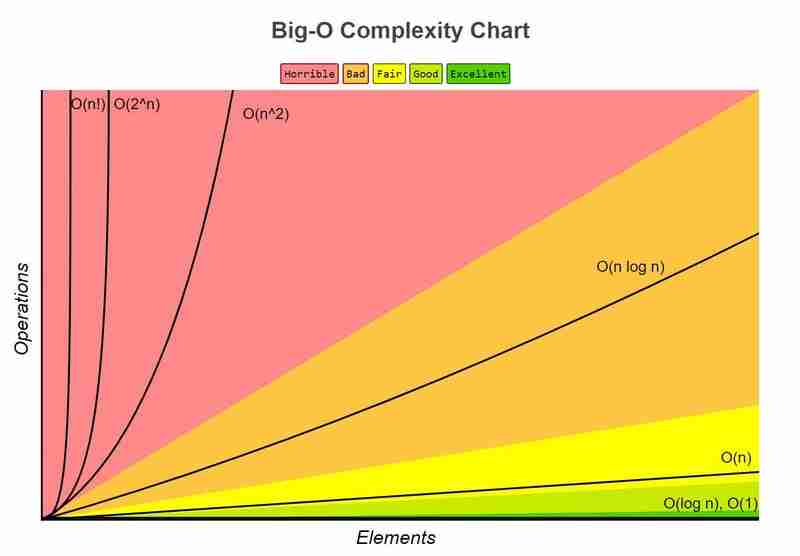
More information visit: http://bigocheatsheet.com
2. Purpose
- Algorithm Comparison: Allows you to compare different algorithms and choose the most efficient one for a given problem.
- Scalability: Helps predict how an algorithm will behave when the amount of data increases.
3. Complexity Analysis
- Worst Case: Refers to the scenario where the algorithm takes longer or uses more resources. Big O usually refers to this case.
- Best Case and Average Case: Although important, they are used less frequently for Big O notation.
4. Space vs. Time
- Temporal Complexity: Refers to the time it takes for an algorithm to execute.
- Space Complexity: Refers to the amount of additional memory it uses. It can have notations like O(1) (constant space) or O(n) (linear space).
Example:
import timeit
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cProfile
# O(1)
def constant_time_operation():
return 42
# O(log n)
def logarithmic_time_operation(n):
count = 0
while n > 1:
n //= 2
count += 1
return count
# O(n)
def linear_time_operation(n):
total = 0
for i in range(n):
total += i
return total
# O(n log n)
def linear_logarithmic_time_operation(n):
if n <= 1:
return n
else:
return linear_logarithmic_time_operation(n - 1) + n
# O(n^2)
def quadratic_time_operation(n):
total = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
total += i + j
return total
# O(2^n)
def exponential_time_operation(n):
if n <= 1:
return 1
else:
return exponential_time_operation(n - 1) + exponential_time_operation(n - 1)
# O(n!)
def factorial_time_operation(n):
if n == 0:
return 1
else:
return n * factorial_time_operation(n - 1)
# Function to measure execution time using timeit
def measure_time(func, *args):
execution_time = timeit.timeit(lambda: func(*args), number=1000)
return execution_time
def plot_results(results):
functions, times = zip(*results)
colors = ['skyblue', 'orange', 'green', 'red', 'purple', 'brown', 'pink']
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 8))
plt.bar(functions, times, color=colors)
for i, v in enumerate(times):
plt.text(i, v + 0.5, f"{v:.6f}", ha='center',
va='bottom', rotation=0, color='black')
plt.xlabel('Function Complexity')
plt.ylabel('Average Time (s)')
plt.title('Execution Time of Different Algorithm Complexities')
plt.grid(axis='y', linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5, color='gray', alpha=0.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
def main():
results = []
results.append(("O(1)", measure_time(constant_time_operation)))
results.append(("O(log n)", measure_time(logarithmic_time_operation, 10)))
results.append(("O(n)", measure_time(linear_time_operation, 10)))
results.append(("O(n log n)", measure_time(
linear_logarithmic_time_operation, 10)))
results.append(("O(n^2)", measure_time(quadratic_time_operation, 7)))
results.append(("O(2^n)", measure_time(exponential_time_operation, 7)))
results.append(("O(n!)", measure_time(factorial_time_operation, 112)))
plot_results(results)
if __name__ == '__main__':
cProfile.run("main()", sort="totime", filename="output_profile.prof")
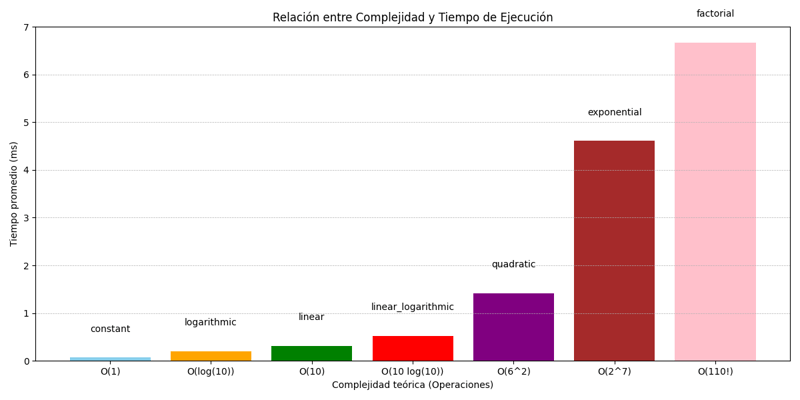
Remember that it is not enough to simply apply big notation or, although this is the first step, there are other ways to optimize memory, for example the use of slots, cache, threads, parallelism, processes, etc.
Thank you for reading!!
Support me by reacting and giving your opinion.
The above is the detailed content of Big O Notation - Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

