 Backend Development
Backend Development PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial How to Implement Pagination in MySQL: A Comprehensive Guide Using LIMIT and OFFSET?
How to Implement Pagination in MySQL: A Comprehensive Guide Using LIMIT and OFFSET?
Pagination using MySQL LIMIT and OFFSET: A Comprehensive Guide
Pagination is a crucial technique used to display data in manageable chunks on web pages. In this context, MySQL's LIMIT and OFFSET operators play a vital role in achieving pagination. This article provides a detailed explanation of pagination using these operators, along with a real-world example.
Consider a scenario where you have a table named menuitem containing 20-30 menu items. Your goal is to display these items in a paginated manner, with four items per page. To achieve this, you initially use the following code to display the first page:
$result = mysqli_query($con,"SELECT * FROM menuitem LIMIT 4");
This query displays the first four items. However, to handle additional pages, you need a mechanism to determine the number of available pages dynamically. This can be achieved by calculating the total row count in the table:
$sql = "SELECT your_primary_key_field FROM menuitem"; $result = mysqli_query($con, $sql); $row_count = mysqli_num_rows($result);
Next, calculate the number of pages based on the total row count and the number of items per page:
$page_count = 0;
if (0 === $row_count) {
// Handle the case where the table is empty
} else {
$page_count = (int)ceil($row_count / $items_per_page);
}
To navigate between pages, you can use a URL parameter such as page. For example, the URL http://yoursite.com/itempage.php?page=2 would display the second page. To handle this request, you can modify your SQL query as follows:
// determine page number from $_GET
$page = 1;
if(!empty($_GET['page'])) {
$page = filter_input(INPUT_GET, 'page', FILTER_VALIDATE_INT);
if(false === $page) {
$page = 1;
}
}
// set the number of items to display per page
$items_per_page = 4;
// build query
$offset = ($page - 1) * $items_per_page;
$sql = "SELECT * FROM menuitem LIMIT " . $offset . "," . $items_per_page;
This query dynamically calculates the offset based on the requested page number, allowing you to display the appropriate page of results.
To display the pagination links, you can use a loop to generate links for all available pages:
for ($i = 1; $i ';
} else {
echo '<a href="%22/menuitem.php?page='" .>Page ' . $i . '</a><br>';
}
}
By following these steps, you can effectively implement pagination using MySQL LIMIT and OFFSET, providing a user-friendly and efficient way to display large data sets in a structured manner.
The above is the detailed content of How to Implement Pagination in MySQL: A Comprehensive Guide Using LIMIT and OFFSET?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PMLaravel simplifies handling temporary session data using its intuitive flash methods. This is perfect for displaying brief messages, alerts, or notifications within your application. Data persists only for the subsequent request by default: $request-
 cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AMThe PHP Client URL (cURL) extension is a powerful tool for developers, enabling seamless interaction with remote servers and REST APIs. By leveraging libcurl, a well-respected multi-protocol file transfer library, PHP cURL facilitates efficient execution of various network protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. This extension offers granular control over HTTP requests, supports multiple concurrent operations, and provides built-in security features.
 Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PMLaravel provides concise HTTP response simulation syntax, simplifying HTTP interaction testing. This approach significantly reduces code redundancy while making your test simulation more intuitive. The basic implementation provides a variety of response type shortcuts: use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http; Http::fake([ 'google.com' => 'Hello World', 'github.com' => ['foo' => 'bar'], 'forge.laravel.com' =>
 12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PMDo you want to provide real-time, instant solutions to your customers' most pressing problems? Live chat lets you have real-time conversations with customers and resolve their problems instantly. It allows you to provide faster service to your custom
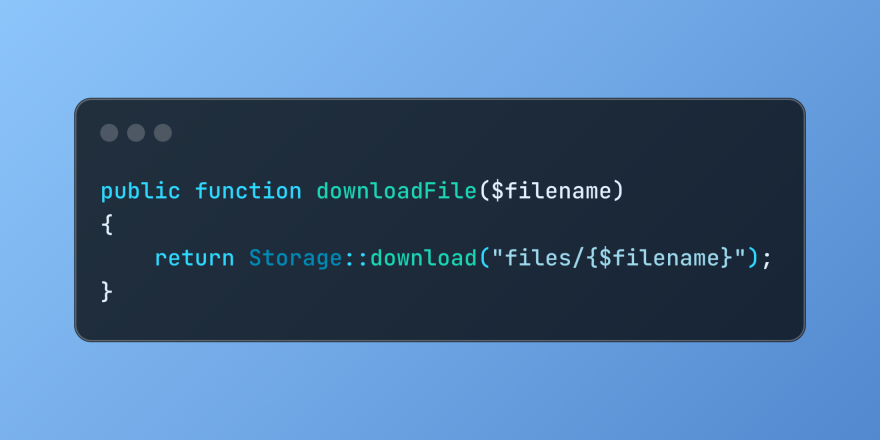 Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::downloadMar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::downloadMar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AMThe Storage::download method of the Laravel framework provides a concise API for safely handling file downloads while managing abstractions of file storage. Here is an example of using Storage::download() in the example controller:
 Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PMArticle discusses late static binding (LSB) in PHP, introduced in PHP 5.3, allowing runtime resolution of static method calls for more flexible inheritance.Main issue: LSB vs. traditional polymorphism; LSB's practical applications and potential perfo
 PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PMPHP logging is essential for monitoring and debugging web applications, as well as capturing critical events, errors, and runtime behavior. It provides valuable insights into system performance, helps identify issues, and supports faster troubleshoot
 How to Register and Use Laravel Service ProvidersMar 07, 2025 am 01:18 AM
How to Register and Use Laravel Service ProvidersMar 07, 2025 am 01:18 AMLaravel's service container and service providers are fundamental to its architecture. This article explores service containers, details service provider creation, registration, and demonstrates practical usage with examples. We'll begin with an ove


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.





