 Backend Development
Backend Development PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial PART# Efficient File Transfer System Using HTTP for Large Datasets
PART# Efficient File Transfer System Using HTTP for Large Datasets
Let's break down the provided HTML, PHP, JavaScript, and CSS code for a chunked file upload dashboard part by part.
HTML Code:
Structure Overview:
-
Bootstrap for Layout: The code uses Bootstrap 4.5.2 to create a responsive layout with two main sections:
- Chunked Uploads Section: For uploading large files in chunks.
- Downloads Section: For listing and downloading previously uploaded files.
Key Elements:
- : This input allows multiple file selection.
- : Placeholder for displaying upload progress.
- : Placeholder to show selected files before uploading.
- : Button to initiate the upload process.
- : Button to fetch and display the list of downloadable files.
PHP Code (chunked-file-upload.php):
This file handles the server-side logic of uploading files in chunks.
Key Parts:
-
Receive Chunk and Metadata:
- $_FILES['fileChunk']: Receives the chunk of the file being uploaded.
- $_POST['chunkIndex']: The index of the current chunk.
- $_POST['totalChunks']: The total number of chunks for the file.
-
Chunk Storage:
- $chunkFilePath = $targetDir . "$fileName.part$chunkIndex": Each chunk is saved as a separate .part file until the final file is assembled.
-
Merging Chunks:
- if ($chunkIndex == $totalChunks - 1): When the last chunk is uploaded, the script merges all chunks into the final file.
-
Return Response:
- A JSON response is returned to the client with the upload status and file details.
Why use chunking?
- Large files are broken into smaller chunks to prevent timeouts and memory issues, making the upload process more reliable.
PHP Code (download.php):
Handles file downloads.
Key Parts:
- $_GET['file']: Retrieves the file name from the URL query string.
-
File Path Construction:
- $filePath = $targetDir . $fileName: Constructs the full path of the file.
-
File Download:
- readfile($filePath): Sends the file to the client as a downloadable stream.
Why use it?
- Enables users to download files directly from the server. The server sends proper headers to prompt the browser to download the file rather than displaying it.
PHP Code (get_files.php):
Lists all uploaded files available for download.
Key Parts:
- scandir($targetDir): Scans the directory for all uploaded files.
- array_diff(): Filters out . and .. from the list of files.
- echo json_encode(array_values($files)): Returns the file list as a JSON array.
Why use it?
- Provides a dynamic list of files available for download, which is updated on each request.
JavaScript Code (chunked-file-upload.js):
Handles the client-side logic of chunked file uploads and file downloads.
Key Parts:
-
Drag and Drop:
- preventDefaults(e): Prevents the browser from opening files when dropped.
- handleDrop(e): Handles dropped files and displays them.
-
Display File List:
- displayFileList(files): Shows the selected files with their sizes and statuses in the file list before upload.
-
Uploading Files in Chunks:
- for (let file of files): Loops through each selected file.
- const chunk = file.slice(start, end): Slices a portion of the file to upload as a chunk.
- uploadChunk(): Recursively uploads each chunk, updates the progress bar and status, and merges the chunks on the server.
-
Download Files:
- $.ajax({url: './src/get_files.php'}): Sends an AJAX request to get the list of uploaded files.
- downloadFile(fileName): Initiates the download by redirecting the user to download.php.
Why use chunked upload in JS?
- For large files, uploading in smaller chunks ensures the process continues even if one chunk fails. It improves reliability by allowing chunk-by-chunk retries.
CSS Code (chunked-file-upload.css):
Key Styles:
-
#drop-area:
- Dashed Border: Visually indicates the area where users can drop files.
- Highlight Effect: The border color changes when a file is dragged over.
-
Progress Bar:
- #progress-bar: The width dynamically updates to reflect the upload progress.
-
File List:
- #file-list .file-status: Adds spacing and styles to display the file name, size, and status.
Why style these elements?
- A user-friendly interface helps users understand what actions they can perform (drag-and-drop, file selection) and gives feedback on the status of their uploads/downloads.
Conclusion:
This system allows large files to be uploaded reliably in chunks and provides users with feedback through a progress bar and status updates. Additionally, the download section gives users the ability to download uploaded files. Combining Bootstrap, JavaScript, and PHP ensures that the system is both user-friendly and functional.
Connecting Links
If you found this series helpful, please consider giving the repository a star on GitHub or sharing the post on your favorite social networks ?. Your support would mean a lot to me!
If you want more helpful content like this, feel free to follow me:
- GitHub
Source Code
The above is the detailed content of PART# Efficient File Transfer System Using HTTP for Large Datasets. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PMLaravel simplifies handling temporary session data using its intuitive flash methods. This is perfect for displaying brief messages, alerts, or notifications within your application. Data persists only for the subsequent request by default: $request-
 cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AMThe PHP Client URL (cURL) extension is a powerful tool for developers, enabling seamless interaction with remote servers and REST APIs. By leveraging libcurl, a well-respected multi-protocol file transfer library, PHP cURL facilitates efficient execution of various network protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. This extension offers granular control over HTTP requests, supports multiple concurrent operations, and provides built-in security features.
 Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PMLaravel provides concise HTTP response simulation syntax, simplifying HTTP interaction testing. This approach significantly reduces code redundancy while making your test simulation more intuitive. The basic implementation provides a variety of response type shortcuts: use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http; Http::fake([ 'google.com' => 'Hello World', 'github.com' => ['foo' => 'bar'], 'forge.laravel.com' =>
 12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PMDo you want to provide real-time, instant solutions to your customers' most pressing problems? Live chat lets you have real-time conversations with customers and resolve their problems instantly. It allows you to provide faster service to your custom
 PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PMPHP logging is essential for monitoring and debugging web applications, as well as capturing critical events, errors, and runtime behavior. It provides valuable insights into system performance, helps identify issues, and supports faster troubleshoot
 Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PMArticle discusses late static binding (LSB) in PHP, introduced in PHP 5.3, allowing runtime resolution of static method calls for more flexible inheritance.Main issue: LSB vs. traditional polymorphism; LSB's practical applications and potential perfo
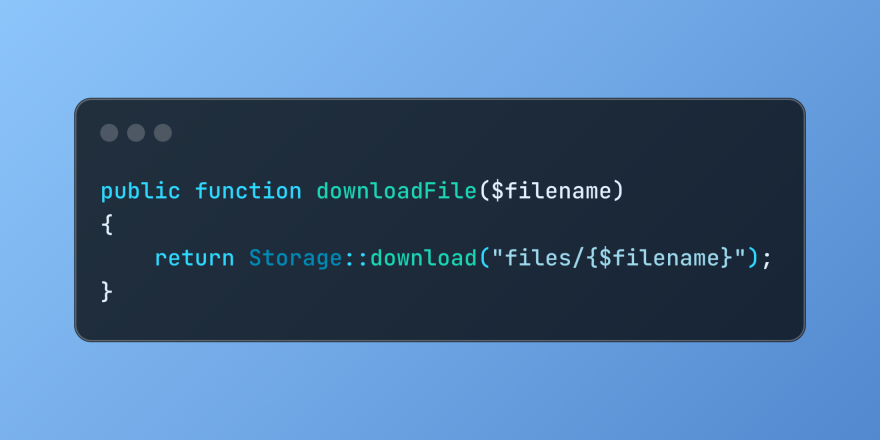 Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::downloadMar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::downloadMar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AMThe Storage::download method of the Laravel framework provides a concise API for safely handling file downloads while managing abstractions of file storage. Here is an example of using Storage::download() in the example controller:
 How to Register and Use Laravel Service ProvidersMar 07, 2025 am 01:18 AM
How to Register and Use Laravel Service ProvidersMar 07, 2025 am 01:18 AMLaravel's service container and service providers are fundamental to its architecture. This article explores service containers, details service provider creation, registration, and demonstrates practical usage with examples. We'll begin with an ove


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.





