Note: Because of how recent it is and its current status as a Working Draft, many of the features described in this article will change, and they will not be available in all browsers (some are!).
On September 13, 2024, the CSS Working Group released the first Public Working Draft for the CSS Values and Units Module Level 5. It is an extension of the previous level that includes some interesting additions.
Things that were unimaginable not so long ago are making their way into the specs: random values, using attributes as values in any property, being able to use the order in calculations... It looks promising.
Many of these features have a common denominator: they simplify the CSS code. Things that before would require multiple rules or hacky solutions will be possible with one or two lines of CSS. As I said, it looks promising. This is a list of the new changes (more details below):
- Changes to attr() function: so it can be used with any attribute and in any CSS property (not only on content).
- calc-size() function: use intrinsic values such as auto or min-content in calculations.
- New first-valid() function to avoid issues with custom properties with invalid values.
- New *-mix() family of functions with a new notation for ratios.
- New *-progress() family of functions to calculate the progress ratio between a range or within a media or container.
- Randomization with new random() and random-item() functions, to return random values from a range or list (finally!)
- New sibling-count() and sibling-index() functions that provide integer values to operate depending on the order and size.
- New toggle() function for styling nested elements easily cycling over a list of values.
- New functional notation for arguments with comma-separated lists of values, to avoid ambiguity with the comma separating the arguments.
- New URL modifiers to provide more control over url() requests.
- Extension of the position type to allow flow-relative values.
New Features and Updates
Changes to attr() function
Reading an attribute and using it in CSS is not new. That was already possible with attr(), but a common complaint was how limited the functionality was, only working with strings and in the content.
The attr() function will go through some updates, so any data attribute independent of its data type can be used in any property. It will be as simple as specifying the type and, if we want to, a fallback value just in case something doesn't go as expected.
This is a long-awaited update that will make a lot of developers happy.

Operations with intrinsic values using calc-size()
This module also introduces a new function able to safely operate with intrinsic values (auto, max-content, fit-content, etc.) This is a feature that will be especially helpful in transitions and animations.
It also adds new keywords (size) to provide more flexibility to the calculations, making it easier to work with the sizes.
Why have a whole new function when calc() is already there? As the document explains, there are backward compatibility and practical reasons why it was done this way (e.g., smooth interpolations in all cases, especially when operating in percentages.)

New first-valid() function
A new method is introduced: first-valid(). The idea is to pass a list of values to the function; they will be resolved, and the first valid one will be the one used. This will be especially useful when dealing with CSS custom properties (aka CSS variables).
One issue when operating with CSS variables is that, within a declaration, they are considered a valid value, even if the actual contained value isn't valid. Setting a fallback value won't help either, and a fallback declaration will be ignored, too.
With this method, we could simplify the code by consolidating all fallback declarations into a single one with first-valid().

New *-mix() family of functions
It also introduces a new function, mix(), that can be used to simplify the different *-mix functions. Do you want to mix colors? You could do something like color-mix(red 60%, blue) or a simpler mix(60%, red, blue) will do the trick too. And as we say colors, we could also mix lengths, transform functions, etc.
That notation is also extended to the other *-mix family of functions:
- calc-mix()
- color-mix()
- cross-fade()
- palette-mix()
If no easing function is specified in the progress parameter (the first one), linear will be applied by default.

New *-progress() family of functions
They represent the proportional progress of a given value from one starting value to another end value. The result is a number between 0 and 1 that can be used in operations, but it will be especially handy when combined with the *-mix family of functions previously described.
There are three functions in this family:
- progress(): generic, for any math function.
- media-progress(): for media features.
- content-progress(): for container queries.
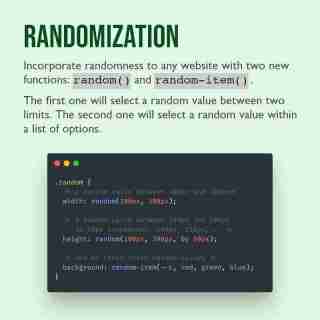
Randomization functions in CSS
Fun designs have some level of randomization, something that was missing in CSS. But this module introduces two new functions that return random values from a list (random-item()) or between a range (random()).
No more hacky tricks or dependencies on other languages to achieve this. The syntax is straightforward and powerful, too, with the possibility to calculate the random number by selector or element.
New sibling functions
Sometimes you may want to provide different styles depending on the order of the elements within a container. Unfortunately, counters cannot be used like that in CSS (I'll leave that rant for another day).
With the introduction of two new functions that return a number, making it possible to operate with them, this roadblock is removed:
- sibling-count(): returns the number of siblings.
- sibling-index(): returns the position/order of the element within the list of siblings.
No more need to set custom properties on each element or write individual selectors with nth-child.

New toggle() function
A convenient new way to define values in nested elements is introduced. The toggle() function sets values that the element and its descendants will cycle through, simplifying the code considerably. Forget about complex rules or redefinitions — everything will be in a single line of code.
For example, imagine that we have a list with four nested levels. We want the odd levels to have discs and the even levels to be squares. We could have some fun doing ul > li ul > li ul > li ul { ... } at different levels, or we can just do something like ul { list-style-type: disc, square; }. Boom! Done!
The only thing that is a bit concerning about this function is its name. Maybe it's just me, but the word "toggle" has "duality" connotations: on/off, yes/no — two values that switch/toggle between each other. The toggle() function can have as many parameters as you want, so it feels weird that it's named "toggle."

New functional notation for arguments
One thing you may have noticed is how some of the new functions (e.g., random() or toggle()) can take arguments that are comma-separated lists of values.
How can we distinguish one argument from the next in those cases? That is why there's a proposal for "comma upgrading" for functional notations. This means we can use a semicolon (;) instead of a comma (,) to separate parameters unambiguously.
For example, imagine that you want to have a random font-family on your page and specify different options:
- Times, serif
- Arial, sans-serif
- Roboto, sans-serif
All those arguments are comma-separated lists of values. If we used a comma to separate the arguments, it would be a huge mess. But with the new notation, it is easy to identify where one argument ends and the next one begins:
.random-font {
font-family: random-item(Times, serif; Arial, sans-serif; Roboto, sans-serif);
}

Extension to the position type
CSS already has logical properties for margin, padding, and border — values that are relative to the text writing direction and may change from one language to another.
This is now introduced for the position type (not to be confused with the position property). Properties that indicate position (e.g., background-position, object-position, etc.) can specify values that will be relative to the text flow and direction.
The new values that can be used are:
- x-start
- x-end
- y-start
- y-end
- block-start
- block-end
- inline-start
- inline-end

Conclusion
It is still at an early stage, and things will change, but some of the new features and functionality included in the CSS Values and Units Module Level 5 look incredibly promising.
Some are long-awaited, too! Especially the possibility of using any attribute with any property. I recall seeing that option in the specs a long time ago. Hopefully, this is the push it needs to make it a reality.
Don't forget to check the CSS Values and Units Module Level 5 Working Draft for more details and information. If you have any questions or comments, log a ticket at their GitHub repo.
Happy (CSS) experimenting and coding!
The above is the detailed content of New Values and Functions in CSS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 CSS Inclusion: Choosing the Right Method for Your ProjectMay 16, 2025 am 12:02 AM
CSS Inclusion: Choosing the Right Method for Your ProjectMay 16, 2025 am 12:02 AMThebestmethodforincludingCSSdependsonprojectsizeandcomplexity:1)Forlargerprojects,useexternalCSSforbettermaintainabilityandperformance.2)Forsmallerprojects,internalCSSissuitabletoavoidextraHTTPrequests.Alwaysconsidermaintainabilityandperformancewhenc
 This Isn't Supposed to Happen: Troubleshooting the ImpossibleMay 15, 2025 am 10:32 AM
This Isn't Supposed to Happen: Troubleshooting the ImpossibleMay 15, 2025 am 10:32 AMWhat it looks like to troubleshoot one of those impossible issues that turns out to be something totally else you never thought of.
 @keyframes vs CSS Transitions: What is the difference?May 14, 2025 am 12:01 AM
@keyframes vs CSS Transitions: What is the difference?May 14, 2025 am 12:01 AM@keyframesandCSSTransitionsdifferincomplexity:@keyframesallowsfordetailedanimationsequences,whileCSSTransitionshandlesimplestatechanges.UseCSSTransitionsforhovereffectslikebuttoncolorchanges,and@keyframesforintricateanimationslikerotatingspinners.
 Using Pages CMS for Static Site Content ManagementMay 13, 2025 am 09:24 AM
Using Pages CMS for Static Site Content ManagementMay 13, 2025 am 09:24 AMI know, I know: there are a ton of content management system options available, and while I've tested several, none have really been the one, y'know? Weird pricing models, difficult customization, some even end up becoming a whole &
 The Ultimate Guide to Linking CSS Files in HTMLMay 13, 2025 am 12:02 AM
The Ultimate Guide to Linking CSS Files in HTMLMay 13, 2025 am 12:02 AMLinking CSS files to HTML can be achieved by using elements in part of HTML. 1) Use tags to link local CSS files. 2) Multiple CSS files can be implemented by adding multiple tags. 3) External CSS files use absolute URL links, such as. 4) Ensure the correct use of file paths and CSS file loading order, and optimize performance can use CSS preprocessor to merge files.
 CSS Flexbox vs Grid: a comprehensive reviewMay 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
CSS Flexbox vs Grid: a comprehensive reviewMay 12, 2025 am 12:01 AMChoosing Flexbox or Grid depends on the layout requirements: 1) Flexbox is suitable for one-dimensional layouts, such as navigation bar; 2) Grid is suitable for two-dimensional layouts, such as magazine layouts. The two can be used in the project to improve the layout effect.
 How to Include CSS Files: Methods and Best PracticesMay 11, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How to Include CSS Files: Methods and Best PracticesMay 11, 2025 am 12:02 AMThe best way to include CSS files is to use tags to introduce external CSS files in the HTML part. 1. Use tags to introduce external CSS files, such as. 2. For small adjustments, inline CSS can be used, but should be used with caution. 3. Large projects can use CSS preprocessors such as Sass or Less to import other CSS files through @import. 4. For performance, CSS files should be merged and CDN should be used, and compressed using tools such as CSSNano.
 Flexbox vs Grid: should I learn them both?May 10, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Flexbox vs Grid: should I learn them both?May 10, 2025 am 12:01 AMYes,youshouldlearnbothFlexboxandGrid.1)Flexboxisidealforone-dimensional,flexiblelayoutslikenavigationmenus.2)Gridexcelsintwo-dimensional,complexdesignssuchasmagazinelayouts.3)Combiningbothenhanceslayoutflexibilityandresponsiveness,allowingforstructur


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools







