Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >Insert Greatest Common Divisors in Linked List
Insert Greatest Common Divisors in Linked List
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2024-09-10 16:30:02615browse
2807. Insert Greatest Common Divisors in Linked List
Difficulty: Medium
Topics: Linked List, Math, Number Theory
Given the head of a linked list head, in which each node contains an integer value.
Between every pair of adjacent nodes, insert a new node with a value equal to the greatest common divisor of them.
Return the linked list after insertion.
The greatest common divisor of two numbers is the largest positive integer that evenly divides both numbers.
Example 1:
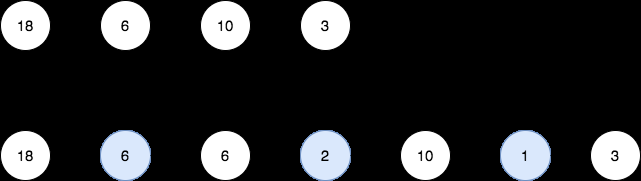
- Input: head = [18,6,10,3]
- Output: [18,6,6,2,10,1,3]
-
Explanation: The 1st diagram denotes the initial linked list and the 2nd diagram denotes the linked list after inserting the new nodes (nodes in blue are the inserted nodes).
- We insert the greatest common divisor of 18 and 6 = 6 between the 1st and the 2nd nodes.
- We insert the greatest common divisor of 6 and 10 = 2 between the 2nd and the 3rd nodes.
- We insert the greatest common divisor of 10 and 3 = 1 between the 3rd and the 4th nodes. There are no more adjacent nodes, so we return the linked list.
Example 2:

- Input: head = [7]
- Output: [7]
- Explanation: The 1st diagram denotes the initial linked list and the 2nd diagram denotes the linked list after inserting the new nodes. There are no pairs of adjacent nodes, so we return the initial linked list.
Example 3:
- Input: cost = [[2, 5, 1], [3, 4, 7], [8, 1, 2], [6, 2, 4], [3, 8, 8]]
- Output: 10
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 5000].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 1000
Hint:
- Each point on the left would either be connected to exactly point already connected to some left node, or a subset of the nodes on the right which are not connected to any node
- Use dynamic programming with bitmasking, where the state will be (number of points assigned in first group, bitmask of points assigned in second group).
Solution:
We need to insert nodes between every pair of adjacent nodes in a linked list. The value of the inserted node should be the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the two adjacent nodes' values. We'll traverse the linked list, calculate the GCD for every pair of adjacent nodes, and then insert the new node accordingly.
Here's how you can approach this:
- Define a ListNode Class: This class will represent each node in the linked list.
- Traverse the List: We'll iterate through the list to find each pair of adjacent nodes.
- Insert GCD Nodes: For each pair of adjacent nodes, we'll insert a new node whose value is the GCD of the two adjacent nodes.
- Return the modified list.
Let's implement this solution in PHP: 2807. Insert Greatest Common Divisors in Linked List
<?php
// Definition for a singly-linked list node.
class ListNode {
public $val = 0;
public $next = null;
public function __construct($val = 0, $next = null) {
$this->val = $val;
$this->next = $next;
}
}
/**
* Function to calculate the GCD of two numbers.
*
* @param $a
* @param $b
* @return mixed
*/
function gcd($a, $b) {
...
...
...
/**
* go to ./solution.php
*/
}
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @return ListNode
*/
function insertGreatestCommonDivisors($head) {
...
...
...
/**
* go to ./solution.php
*/
}
/**
* Function to print the linked list for testing purposes.
*
* @param $head
* @return void
*/
function printList($head) {
$current = $head;
while ($current != null) {
echo $current->val . " ";
$current = $current->next;
}
echo "\n";
}
// Example usage:
// Create the linked list: 18 -> 6 -> 10 -> 3
$head = new ListNode(18);
$head->next = new ListNode(6);
$head->next->next = new ListNode(10);
$head->next->next->next = new ListNode(3);
// Insert GCD nodes.
$modifiedHead = insertGreatestCommonDivisors($head);
// Print the modified linked list.
printList($modifiedHead);
// Output should be: 18 -> 6 -> 6 -> 2 -> 10 -> 1 -> 3
?>
<h3>
Explanation:
</h3>
<ol>
<li><p><strong>ListNode Class</strong>: This class represents the structure of a node in the linked list, with properties for the value ($val) and the next node ($next).</p></li>
<li><p><strong>GCD Calculation</strong>: The gcd function uses the Euclidean algorithm to compute the greatest common divisor of two integers.</p></li>
<li>
<p><strong>Main Logic (insertGreatestCommonDivisors)</strong>:</p>
<ul>
<li>We loop through the linked list until we reach the second-to-last node.</li>
<li>For each pair of adjacent nodes, we compute the GCD of their values.</li>
<li>We create a new node with this GCD value and insert it between the current node and the next node.</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li><p><strong>Edge Case</strong>: If the list has only one node, we return it as is without making any changes since there are no adjacent nodes.</p></li>
<li><p><strong>Testing</strong>: The function printList is a helper function used to output the values of the linked list for verification.</p></li>
</ol>
<h3>
Time Complexity:
</h3>
<ul>
<li>The time complexity of this solution is (O(n)), where (n) is the number of nodes in the linked list. Calculating the GCD for each adjacent pair takes constant time on average, and we perform a linear traversal of the list.</li>
</ul>
<h3>
Example:
</h3>
<p>For the input list [18, 6, 10, 3], the output is:<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">18 -> 6 -> 6 -> 2 -> 10 -> 1 -> 3
Contact Links
If you found this series helpful, please consider giving the repository a star on GitHub or sharing the post on your favorite social networks ?. Your support would mean a lot to me!
If you want more helpful content like this, feel free to follow me:
- GitHub
The above is the detailed content of Insert Greatest Common Divisors in Linked List. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

