? Welcome, all new subscribers and returning component coders! I'm kicking off a new 10 part tutorial series. While my other tutorials have used Modulo.js to build specific, fun little apps like pokemon dance parties, retro extruded text editors, or video game galleries, this tutorial series will build up on basic principals, starting from square one: What is a Web Component?
The Next Step After HTML and CSS
Have you just learned the basics of HTML and CSS, and are curious about going taking the next step, and want to build bigger and more complete web applications? Or, are you already a web developer or JavaScript pro, and just want to build quick and light web apps without too much bloat, tooling, or excess dependencies?
If so, Web Components are for you! They let you create reusable portions of code. By taking this tutorial, you'll learn how to fix repetitive, difficult-to-maintain HTML and CSS. It also uses only minimal tools and libraries, meaning you won't need Node.js, NPM, or a massive node_modules. It also lets you hone your skills in modern frontend web development: In the future tutorials in this series, you'll learn concepts like slots, shadowDOM, props, templating, state management, and more! These are concepts that are transferable to use other popular frameworks, and Modulo's simple, declarative approach could be a more inviting way to learn the core concepts without getting bogged down in complex setup.
Introducing the Modulo Framework
What is Modulo? Modulo is a free software / open source, small-but-mighty web framework written in JavaScript. It has no dependencies, and uses HTML syntax so it can set itself up on page load, with no need for Node.js or compilation. You can use it in a plain HTML "static site" (e.g. when you assemble HTML, CSS, and other static assets in a directory to launch on a static web host), or any other existing web app. This tutorial is about using Modulo as a tool to build Web Components.
Introducing Part 1
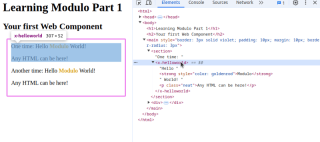
In Part 1, we'll learn how to build a simple "Hello World" component. In future parts, we'll learn how to add in Style, Props, State, reactive forms, slots, APIs, and so much more, but for now, we'll start with the basics: Going beyond basic HTML and CSS by creating and re-using a Web Component with Modulo.
Step 1: Including Modulo
Before we can use Modulo, we'll have to include the framework. The entire framework is contained in "Modulo.js", a file containing 2000-lines of JavaScript. This means that starting a Modulo project requires literally no dependencies beyond your browser and editor. So, just open up a blank HTML file and get going with the following very simple starter code:
<template modulo>
<!-- our stuff will go here eventually... -->
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/mdu.js"></script>
Step 2: Defining your first component
Now that we have included it, we can start writing Modulo definitions and use the framework in general. We define our first component by creating a Modulo
<component name="HelloWorld">
<template>
Hello <strong>Modulo</strong> World!
</template>
</component>
This "Template" thus becomes the "template" for our component: Every time our component shows up on the page, it will render the given template inside of it.
Step 3: Using your first component
Once defined, you can use a component by referring to it's name as though it were a plain HTML tag:
<x-helloworld></x-helloworld>
This will cause the following to show on the screen:
Hello Modulo World!
Note that once registered, components can go anywhere that plain HTML tags can go, and can be styled with CSS the same way as well. In other words, creating a component is like creating a brand-new type of HTML tag that can be used anywhere, just like the original HTML tags of
The above is the detailed content of Writing your first web component (Learn Modulo.js - Part f. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment







