Home >Backend Development >C#.Net Tutorial >Recursive Function in C#
Recursive Function in C#
- WBOYOriginal
- 2024-09-03 15:14:33514browse
In Recursive Function in C#, Recursion means to denotes the same meaning as in the English language, precisely known as repeating itself. So, the recursive nature of a function denotes doing the same work repeatedly. And, yes if the program is not handled correctly, it would definitely run the program in a continuous loop. We have to make sure we specify proper conditions in executing these recursive functions, else the function would be calling itself, again and again, leading to a continuous execution of the program. Here let’s go ahead and look at how we can create these functions in C#.
Syntax of Recursive functions in C#
The syntax here is the same as the basic function syntax in C#. Let’s have a look here.

There is no special syntax here, but we can observe that a function is calling itself in providing the return result. And we must be very careful in passing those parameter values into that recursive function as obviously we don’t want a running code which doesn’t stop.
In the above syntax, there is nothing like, we have to call the function only in return statements. Rather, we can even assign the recursive function return value to a variable and return that variable too.
Execution of Factorization
Here let us take our default problem statement, Factorization, for generating our recursive function.
Code:
using System;
class First {
static void Main() {
int result;
result = fact(7);
Console.WriteLine("Factorial is : " + result);
}
public static int fact(int num)
{
if(num==0)
{
return 1;
}
return num*fact(num-1);
}
}
Let us have a look at the step by step process.
- First, we have created our own parameterized function to take an input value from main function, for which we want to calculate the factorial.
- Then, we made an if condition to check if the given number is zero. If the number is zero, then we are returning 1 as our default value.
- Else, we are multiplying the present number with the function taking in the number minus 1 as its parameter.
- So, this multiplication repeats itself until we get to number 0. As by default, we have written our return output for zero as 1, the final result would be multiplied by 1.
Output:
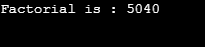
Now, in the code, I am going to replace our function parameter from num minus 1 to, num. In this case, the function would be calling itself again and again and the process would be repeating.
Code:
using System;
class First {
static void Main() {
int result;
result = fact(7);
Console.WriteLine("Factorial is : " + result);
}
public static int fact(int num)
{
if(num==0)
{
return 1;
}
return num*fact(num);
}
}
Output:

Through the above output, we can clearly see the stack overflow exception, where the function is repeatedly calling itself. Only the highlighted part is changed with respect to the first program.
In the same way, we can make the number as a user inputted value like below:
Code:
using System;
class First {
static void Main() {
int result,c;
string a;
Console.Write("Enter value for number :");
a = Console.ReadLine();
c = Convert.ToInt32(a);
result = fact(c);
Console.WriteLine("Factorial is : " + result);
}
public static int fact(int num)
{
if(num==0)
{
return 1;
}
return num*fact(num-1);
}
}
Output:

What if we give zero as the input? Yes, one would be returned.
Output:

Now, what if we give a negative number?
Output:
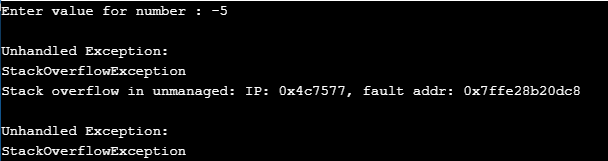
This gave me a Stack overflow exception too, as our factorial recursion function is decreasing its value of the parameter on every execution. So, the negative numbers would be going on reduced to -6, -7, -8 and so on. That is the reason we go to this exception.
As an exercise, can you try creating a recursive function for negative numbers?
Hint: We can take a pre-condition of number less than zero and add one to our recursive function parameter until zero comes.
Examples of Recursive Function in C#
There are few good examples that can be quoted with respect to the recursive functions:
We do have a few other places where we can use these recursive functions.
- Print numbers from a given start point and endpoint continuously. (Program below)
- Add numbers starting from a given start point and stop at the endpoint or when a particular sum is reached.
- Print numbers that are divided by any particular number in any particular range.
- We want to print out any of the numbers of continuous lines or dots after writing a sentence and many more.
As you can observe recursive function is similar to the functionality of a loop, but where we are calling the same function repeatedly.
Let us see how we can write a recursive function in adding numbers continuously until the program finds the second number that is given as input.
Code:
using System;
class First {
static void Main() {
int result,c,d;
string a,b;
Console.Write("Enter value for 1st number :");
a = Console.ReadLine();
c = Convert.ToInt32(a);
Console.Write("Enter value for 2nd number :");
b = Console.ReadLine();
d = Convert.ToInt32(b);
result = add(c,d);
Console.WriteLine("Add is : " + result);
}
public static int add(int num1,int num2)
{
int sum ;
sum=num1;
if (num1 < num2 )
{
num1++;
sum=sum+add(num1,num2);
return sum;
}
return sum;
}
}
Here, what we did is:
- We have taken two numbers num1 and num2 through user inputs
- Add function, adds the numbers starting from num1 till it gets the num2.
For example, if I take num1 = 5 and num2 = 8, then the output sum we get is 5+6+7+8, which is 26.
Output:

And what if, I give num1 less than num2?
Output:

It gives some as the num1 value as first, we assigned the sum value to num1 value and returning sum if the if statement is not applicable.
As an exercise can you write a recursive function to print “I like coding” until it follows a certain condition?
Hint: We can follow the same procedure of adding which is done in the above program.
Conclusion
So, here we have successfully got the execution of recursive functions, how these functions are called and a few examples of them. We also learned how a simple difference in the calling of a function can make the program run out of its bounds and create an exception.
The above is the detailed content of Recursive Function in C#. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

