 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Efficiently and accurately predict DDI, the explanatory drug AI model of Fuzhou University and Yuanxing Intelligent Drug Team was published in Nature sub-journal
Efficiently and accurately predict DDI, the explanatory drug AI model of Fuzhou University and Yuanxing Intelligent Drug Team was published in Nature sub-journal
Unexpected drug interactions (DDIs) are an important issue in drug research and clinical application because they are highly likely to cause serious adverse drug effects. reaction or drug withdrawal.
While many deep learning models have achieved good results in DDI prediction, model interpretability to reveal the underlying causes of DDI has not been widely explored.
Researchers from Fuzhou University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University and Yuanxing Intelligent Medicine proposed MeTDDI - a deep learning framework with local-global self-attention and joint attention for learning based on DDI prediction plot of subject.
Regarding interpretability, researchers conducted an extensive evaluation on 73 drugs (13,786 DDIs), and MeTDDI can accurately explain the structural mechanisms of 5,602 DDIs involving 58 drugs. Furthermore, MeTDDI shows potential to explain complex DDI mechanisms and reduce DDI risk.
MeTDDI provides a new perspective for exploring DDI mechanisms, which will facilitate drug discovery and polypharmacy, thereby providing safer treatments for patients.
The study was titled "Learning motif-based graphs for drug–drug interaction prediction via local–global self-attention" and was published in "Nature Machine Intelligence" on August 27, 2024.

Due to aging and multimorbidity, drug combinations or polypharmacy are widely used and may have consequences for public health and the economy. Despite the therapeutic benefits of polypharmacy, there is a risk of unintended drug-drug interactions (DDIs), which may lead to serious adverse drug reactions (ADRs) or even discontinuation.
Thus, predicting DDIs in advance will bring huge benefits to drug research and clinical settings, thereby improving drug safety and protecting patient health. DDI assessment through in vitro and in vivo experiments is useful but is costly, time-consuming, and laborious, hindering the practicality of large-scale DDI screening.
Today, deep learning models have emerged as a promising alternative for high-throughput accurate DDI prediction as well as root cause explanation.
In the latest study, the research team of Fuzhou University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, and Yuanxing Intelligent Medicine focused on the prediction of metabolism-mediated drug interactions (MMDDI) and proposed a deep molecular structure-based Learning framework MeTDDI for predicting MMDDI.
This method is mainly used to solve three challenges in DDI prediction: (1) learning intra- and intermolecular substructural interactions, (2) predicting DDI-related drug metabolism, (3) widely providing and evaluating the model Interpretability.
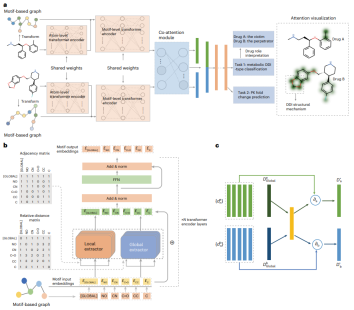
Benefiting from local-global self-attention and joint attention structures, MeTDDI can effectively learn intra- and intermolecular substructure interactions within/between graphs based on motifs , thereby performing DDI reasoning.
Evaluation results show that it achieves competitive performance compared to baselines in both classification and regression tasks. MeTDDI can also accurately identify the mechanistic role of a drug (perpetrator or victim) in DDI and quantify the impact of the perpetrator on the victim PK, which is very beneficial for both drug research and clinical applications.

Regarding model interpretability, MeTDDI demonstrates the ability to identify key mechanistic substructures relevant to DDI.
First, the key substructures visualized by MeTDDI roughly match those reported in the literature from the analysis of 73 representative compounds (with 13,786 DDI pairs).

Second, the researchers evaluated the model interpretability of MeTDDI and two state-of-the-art models, namely CIGIN and CGIB. The results show that MeTDDI also exhibits excellent performance in terms of model interpretability.
Additionally, MeTDDI can highlight metabolic sites of chemicals associated with enzyme inhibition.
Advantages of MeTDDI
Traditional methods only explain the mechanism of DDI by testing the metabolic enzyme inhibition of the perpetrator in vitro, without fully considering the victim. This is problematic because the potency of enzyme inhibition by the perpetrator can vary depending on the chemical identity of the victim.
被害者は、代謝酵素 (特に CYP) と加害者の結合または相互作用パターンを変更し、その結果、さまざまな酵素阻害メカニズムが生じる可能性があります。これは、インビトロで単独で使用すると代謝酵素の強力な阻害剤であるエチニルエストラジオールやゲストデンなどの一部の化学物質が、それらの犠牲者と組み合わせると効果が低くなる理由を説明する可能性があります。これは、エチニルエストラジオールを用いた研究でなぜ 2 つの反応しか観察されなかったのかを説明する可能性があり、これが in vitro で CYP3A4 を不活化するメカニズムであると考えられています。
さらに、パロキセチンとイトラコナゾールのケーススタディでは、MeTDDI が化学物質のモチーフの変化を正確に予測し、生物学的実験の結果と一致していることが示されており、研究者が薬物の構造を変更して MMDDI のリスクを軽減するのに役立つ可能性が実証されています。
要約すると、MeTDDI は DDI 予測機能を強化し、DDI メカニズムを理解して探索するための新しい視点を提供します。これにより、医薬品開発とポリファーマシーが促進され、それによって患者により安全な治療が提供されます。

図: MeTDDI を使用した DDI 軽減の 2 つのケーススタディ。 (出典:論文) MeTDDI の改善方向
MeTDDI には多くの利点がありますが、同時にいくつかの制限もあります。
まず、困難なシナリオでは正確な予測が困難です。これは、DDI メカニズムの多様性と複雑さ、および薬物構造のみに依存することの限界に起因している可能性があります。
MMDDI では両方の薬物が同じ代謝酵素上で相互作用する必要があるため、酵素の特徴をモデルに組み込んで学習を改善できます。ただし、一部の代謝酵素 (CYP など) は薬物と酵素の相互作用部位に非常に高い柔軟性を示すため、酵素特性のモデル化は依然として課題です。
第二に、MeTDDI でトレーニングされたデータセットは FDA の医薬品ラベルに基づいています。これは集団の統計的観察であり、個々の患者の特徴を反映していない可能性があります。したがって、モデルを開発し、将来的により正確な予測を行うために、利用可能な場合は個々の患者データを考慮する必要があります。第三に、MeTDDI は 3 つ以上の薬物の相互作用を同時に予測することが難しい可能性があります。
ただし、ポリファーマシーを確保するための一般的な方法は、考えられるすべての薬物ペア間のペアごとの DDI を検索することです。MeTDDI を直接展開して、すべての薬物ペアを列挙することで複数の薬物間の DDI を予測できます。
最後に、DDI の基礎となる新たに発見された部分構造については、分子ドッキングなどの代替技術を補完的なアプローチとして採用して、MeTDDI 可視化機能の信頼性を高めることができます。そして研究者らは、分子ドッキングはMeTDDIを補完する貴重なツールであると述べている。
論文リンク: https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-024-00888-6
The above is the detailed content of Efficiently and accurately predict DDI, the explanatory drug AI model of Fuzhou University and Yuanxing Intelligent Drug Team was published in Nature sub-journal. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 From Friction To Flow: How AI Is Reshaping Legal WorkMay 09, 2025 am 11:29 AM
From Friction To Flow: How AI Is Reshaping Legal WorkMay 09, 2025 am 11:29 AMThe legal tech revolution is gaining momentum, pushing legal professionals to actively embrace AI solutions. Passive resistance is no longer a viable option for those aiming to stay competitive. Why is Technology Adoption Crucial? Legal professional
 This Is What AI Thinks Of You And Knows About YouMay 09, 2025 am 11:24 AM
This Is What AI Thinks Of You And Knows About YouMay 09, 2025 am 11:24 AMMany assume interactions with AI are anonymous, a stark contrast to human communication. However, AI actively profiles users during every chat. Every prompt, every word, is analyzed and categorized. Let's explore this critical aspect of the AI revo
 7 Steps To Building A Thriving, AI-Ready Corporate CultureMay 09, 2025 am 11:23 AM
7 Steps To Building A Thriving, AI-Ready Corporate CultureMay 09, 2025 am 11:23 AMA successful artificial intelligence strategy cannot be separated from strong corporate culture support. As Peter Drucker said, business operations depend on people, and so does the success of artificial intelligence. For organizations that actively embrace artificial intelligence, building a corporate culture that adapts to AI is crucial, and it even determines the success or failure of AI strategies. West Monroe recently released a practical guide to building a thriving AI-friendly corporate culture, and here are some key points: 1. Clarify the success model of AI: First of all, we must have a clear vision of how AI can empower business. An ideal AI operation culture can achieve a natural integration of work processes between humans and AI systems. AI is good at certain tasks, while humans are good at creativity and judgment
 Netflix New Scroll, Meta AI's Game Changers, Neuralink Valued At $8.5 BillionMay 09, 2025 am 11:22 AM
Netflix New Scroll, Meta AI's Game Changers, Neuralink Valued At $8.5 BillionMay 09, 2025 am 11:22 AMMeta upgrades AI assistant application, and the era of wearable AI is coming! The app, designed to compete with ChatGPT, offers standard AI features such as text, voice interaction, image generation and web search, but has now added geolocation capabilities for the first time. This means that Meta AI knows where you are and what you are viewing when answering your question. It uses your interests, location, profile and activity information to provide the latest situational information that was not possible before. The app also supports real-time translation, which completely changed the AI experience on Ray-Ban glasses and greatly improved its usefulness. The imposition of tariffs on foreign films is a naked exercise of power over the media and culture. If implemented, this will accelerate toward AI and virtual production
 Take These Steps Today To Protect Yourself Against AI CybercrimeMay 09, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Take These Steps Today To Protect Yourself Against AI CybercrimeMay 09, 2025 am 11:19 AMArtificial intelligence is revolutionizing the field of cybercrime, which forces us to learn new defensive skills. Cyber criminals are increasingly using powerful artificial intelligence technologies such as deep forgery and intelligent cyberattacks to fraud and destruction at an unprecedented scale. It is reported that 87% of global businesses have been targeted for AI cybercrime over the past year. So, how can we avoid becoming victims of this wave of smart crimes? Let’s explore how to identify risks and take protective measures at the individual and organizational level. How cybercriminals use artificial intelligence As technology advances, criminals are constantly looking for new ways to attack individuals, businesses and governments. The widespread use of artificial intelligence may be the latest aspect, but its potential harm is unprecedented. In particular, artificial intelligence
 A Symbiotic Dance: Navigating Loops Of Artificial And Natural PerceptionMay 09, 2025 am 11:13 AM
A Symbiotic Dance: Navigating Loops Of Artificial And Natural PerceptionMay 09, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe intricate relationship between artificial intelligence (AI) and human intelligence (NI) is best understood as a feedback loop. Humans create AI, training it on data generated by human activity to enhance or replicate human capabilities. This AI
 AI's Biggest Secret — Creators Don't Understand It, Experts SplitMay 09, 2025 am 11:09 AM
AI's Biggest Secret — Creators Don't Understand It, Experts SplitMay 09, 2025 am 11:09 AMAnthropic's recent statement, highlighting the lack of understanding surrounding cutting-edge AI models, has sparked a heated debate among experts. Is this opacity a genuine technological crisis, or simply a temporary hurdle on the path to more soph
 Bulbul-V2 by Sarvam AI: India's Best TTS ModelMay 09, 2025 am 10:52 AM
Bulbul-V2 by Sarvam AI: India's Best TTS ModelMay 09, 2025 am 10:52 AMIndia is a diverse country with a rich tapestry of languages, making seamless communication across regions a persistent challenge. However, Sarvam’s Bulbul-V2 is helping to bridge this gap with its advanced text-to-speech (TTS) t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version





