Home >Java >javaTutorial >Metadata in Java
Metadata in Java
- PHPzOriginal
- 2024-08-30 16:23:13999browse
Metadata in Java, defined as the data about the data, is called “Metadata”. Metadata is also said to be documentation about the information required by the users. This is one of the essential aspects in the case of data warehousing.
ADVERTISEMENT Popular Course in this category JAVA MASTERY - Specialization | 78 Course Series | 15 Mock TestsReal-Time Examples: A library catalog, the table of content, data items about person data (person weight, a person walking, etc.), etc.
Metadata Consisting of the following things:
- The description and location of the system and its components.
- It also has the Names, definitions, content, and structures of data and end-user views.
- Identification of authoritative data.
- Integration and transformation rules are used to populate data.
- Subscription information of subscribers.
- Used to analyze data usage and performance.
Why is Metadata Necessary?
It gives the Java developers information about the contents like table data, library catalog, etc., and structures.
Types of Metadata
There are 3 types of metadata:
- Operational Metadata
- Extraction and Transformation Metadata
- End-User Metadata
1. Operational Metadata: Operational metadata has all the information of the operational data sources. While selecting information from the source system for Datawarehouse, we will divide the records, combine the factors of documents from various sources, and deal with multiple coding schemes and field lengths. While we deliver the information to end-users, then we must be able to get back to source data sets.
2. Extraction and Transformation Metadata: Extraction and Transformation Metadata include data about removing data from the source systems. Those extraction methods, frequencies, and business rules for data extraction belong to Extraction and Transformation Metadata.
3. End-User Metadata: The end-user metadata is the navigational map of the data house. It enables the end-users to find the data from the data warehouse.
How does Metadata work in Java?
Java Metadata works based on data provided to it. It gives information of data about the data.
Syntax:
class Metadata{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
//load required database class
//creating database metadata class
DatabaseMetaData metaData=con.getMetaData();
//display the metadata of the table content
System.out.println(metaData.getDriverName());
System.out.println(metaData.getDriverVersion());
System.out.println(metaData.getUserName());
System.out.println(metaData.getDatabaseProductName());
System.out.println(metaData.getDatabaseProductVersion());
con.close();
}catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e);}
}
}
Note: Before getting into the example, you must need MySQL database and mysql-connector jar.
Examples to Implement Metadata in Java
Below are examples of Metadata in Java:
Example #1 – Result Set Metadata
Code:
import java.sql.*;//importing sql package
public class A {//Creating class
//main method for run the application
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
//loading my sql driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//get the connection by providing database, user name and password
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "root", "root");
//select the all from employee table
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("select * from employee");
//executing the query
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//Create result meta data for get the meta data of table
ResultSetMetaData resultSetMetaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
//Displaying meta data of employee table
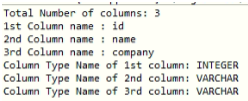
System.out.println("Total Number of columns: " + resultSetMetaData.getColumnCount());
System.out.println("1st Column name : " + resultSetMetaData.getColumnName(1));
System.out.println("2nd Column name : " + resultSetMetaData.getColumnName(2));
System.out.println("3rd Column name : " + resultSetMetaData.getColumnName(3));
System.out.println("Column Type Name of 1st column: " + resultSetMetaData.getColumnTypeName(1));
System.out.println("Column Type Name of 2nd column: " + resultSetMetaData.getColumnTypeName(2));
System.out.println("Column Type Name of 3rd column: " + resultSetMetaData.getColumnTypeName(3));
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Output:
Example #2 – Database Metadata
Code:
import java.sql.*;//importing sql package
public class A {//Creating class
//main method for run the application
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
//loading my sql driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//get the connection by providing database, user name and password
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test","root", "root");
//select the all from employee table
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("select * from employee");
//executing the query
preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//Create databse result set meta data for get the meta data of databse of mysql
DatabaseMetaData databaseMetaData=connection.getMetaData();
//Displaying meta data of mysql table
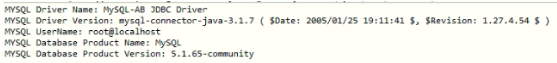
System.out.println("MYSQL Driver Name: "+databaseMetaData.getDriverName());
System.out.println("MYSQL Driver Version: "+databaseMetaData.getDriverVersion());
System.out.println("MYSQL UserName: "+databaseMetaData.getUserName());
System.out.println("MYSQL Database Product Name:"+databaseMetaData.getDatabaseProductName());
System.out.println("MYSQL Database Product Version: "+databaseMetaData.getDatabaseProductVersion());
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Output:
Example #3 – Database Metadata for Extracting Table Names
Code:
import java.sql.*;//importing sql package
public class A {// Creating class
// main method for run the application
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
// loading my sql driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// get the connection by providing database, user name and password
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "root", "root");
// Create databse result set meta data for get the meta data of
// databse of mysql
DatabaseMetaData dbmd = connection.getMetaData();
String table[] = { "VIEW" };
ResultSet resultSet = dbmd.getTables(null, null, null, table);
// iterating number table names from database of mysql
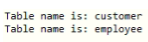
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("Table name is: "+resultSet.getString(3));
}
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
Metadata in Java is used to know the data about data. It means, for example, table field names, field data type, field data type length, database table names, number of databases that existed in the specific database, etc.
The above is the detailed content of Metadata in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

