Home >Java >javaTutorial >Static Method in Java
Static Method in Java
- 王林Original
- 2024-08-30 16:17:02900browse
Static Method in Java is a method that is part of a class but is not considered an instance of the class; rather, the static method in java can easily be created and implemented without any invocation of instances. The static method can access any data member of the class and can make any manipulation to the data members or can put any value as an input despite for the fact that the member variable to be accessed should have the scope of the variable in the class and method to be static only.
Start Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Syntax:
Representation of the static method in Java is as follows:
public static void syntax_ex (String_name) {
Body of the program for execution.
}
- public: The access modifier of the class is public.
- static: The scope of the method is made to be static which means that all the member variables and the return type will be within the scope of static.
- void: This keyword in the syntax flow represents that there is no return type handled in the current method.
- syntax_ex: Name of the class, which represents that the static method is the part of the currently defined class followed by the string name.
- Body of the program for execution: It includes the entire core logic or the business logic if required to be in static mode.
How Static Method works in Java?
- Static method and instance method are the two methods in Java which create a bit of confusion among the programmers, but this is just a mere misconception. Both static method and instance method have a huge difference in them. Let’s see how the static method works in Java. The static method in java is a method which resides in the class and can be accessed even if no object is created or say there is no instantiation done. The class name followed by the method name and passing the argument is enough for accessing any instance of the class.
- It can be represented as ClassName.methodName(arguments). Further, these methods are composed with a single goal that the method should be sharable to all the member variables and the objects everyone present in the class with the scope defined with the modifier static. These methods don’t have any capability to override; rather, they can be overloaded using the static binding of the compiler at the time of compilation whenever the programmers require that a common code snippet is required to be shared among all the instances and the objects or the member variables of the class then static method comes as a savior as it creates a kind of shared provisioning for all the members, objects and variables by creating a common static scope for reference.
- All the static fields of a class are accessible using the static field as part of the static method of a class. Also, static methods are related and are supportable with the memory allocation feature as well. It stores the part of the static method fields and variables with some permanently generated heap in the memory, which is used for associated values. The memory allocation doesn’t support the objects as static method heap creation, or the method itself does not support instantiation. But then the very next question which comes into mind is how the static method works by sharing and creating scope for all the members as part of the class.
- The answer lies in the fact that the local variables passed as an argument to the method, which in turn is called by the class, gets stored in the stack itself. Since they all are part of the class and belong to the class this way, they get easily accessible by other member variables or method without the creation of any object.
Examples of Static Method in Java
Given below are the examples of Static Method in Java:
Example #1
This program demonstrates the static class with its specific members, which tries to rectify the marks in the subjects mentioned; basically, it shows that without creating any object or without any instantiation, it is able to create and access the fields or member variables of the class which is within static scope.
Code:
public class E_Static_Method_Ex {
int roll_no;
String stdnt_name;
static String subject = "Maths";
public void rectify()
{
subject = "English";
}
E_Static_Method_Ex(int roll, String name) {
roll = roll_no;
name = stdnt_name;
}
void represent()
{
System.out.println(roll_no+""+stdnt_name+""+subject);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String mrks = E_Static_Method_Ex.subject;
System.out.println(mrks);
}
}
Output:
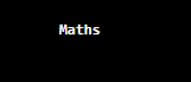
Example #2
This program demonstrates a very significant point which needs to be kept in mind while executing any static method code, which is like the arguments passed and declared in the class should be defined within the scope of static or should have initialized with the static keyword so that accessing the field or the member variable becomes easy and there remains no compilation error as represented in the given program.
Code:
public class Restrcn_Static_Class {
int bi = 30;
String name = "Welcome Everyone!";
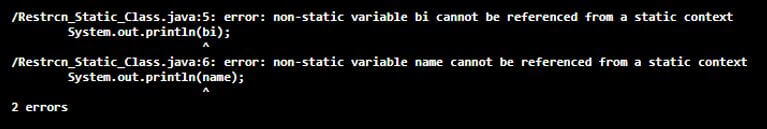
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(bi);
System.out.println(name);
}
}
Output:
Example #3
This program demonstrates the static variable that becomes accessible for the static class if the fields are declared and defined with static as a modifier; otherwise, the scope of static won’t get satisfied, and it will throw compilation error like the earlier example.
Code:
public class Static_Var_1 {
static int cnt=0;
Static_Var_1(){
cnt++;
System.out.println(cnt);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Static_Var_1 d1=new Static_Var_1();
Static_Var_1 dd2=new Static_Var_1();
Static_Var_1 dd3=new Static_Var_1();
Static_Var_1 dd4=new Static_Var_1();
Static_Var_1 dd6=new Static_Var_1();
}
}
Output:

Conclusion
Static Method in Java is a useful method in a class and has a clear difference when compared with the instance method as static method gives programmers flexibility by making them free from object creation, i.e. from the method of object instantiation. It helps in making the entire static class dynamic and versatile in nature, unlike the instantiation method.
The above is the detailed content of Static Method in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

