Home >Java >javaTutorial >Multidimensional Array in Java
Multidimensional Array in Java
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2024-08-30 15:27:381260browse
A complete guide on Multidimensional Array in Java. An Array is a homogeneous data Multidimensional structure that is a collection of elements with a similar data type. They are stored in the contiguous memory location. In the array, the first element is stored in index 0; the second element is stored in index 1, and so on. Arrays can be of a single dimension or multi-dimension. In this document, we will look into multi-dimensional arrays in Java. A multi-dimensional array is an array of arrays that can hold more than one row and column. Now, let us see the syntax and implementation of a Multi-dimensional array in the following sections.
ADVERTISEMENT Popular Course in this category JAVA MASTERY - Specialization | 78 Course Series | 15 Mock TestsSyntax:
data_type[dimension 1][dimension 2][]…[dimension n] array_name= new data_type[size 1][size 2]…[size n]
- data_type: data type of array, Example: int, char, float, etc.
- dimension: the dimension of the array, Example: 1D, 2D, etc.
- array_name: Name of the array.
- size1, size2, …, sizeN: Sizes of the dimension.
Types of Multidimensional Array in Java
The most common Multidimensional Array in Java are:
- Two Dimensional Array or 2D Array.
- Three Dimensional Array or 3D Array.
1. Two Dimensional Array
2D arrays are commonly used in platform video games like Super Mario to represent terrain or screen. They can also be used for drawing Chess boards, representing structures like a spreadsheet, etc.
Code:
int[][] array1 = new int[2][2];//Two dimensional Integer Array with 2 rows and 2 columns
Example:
9 10
7 66
This is a 2D array with two rows and two columns.
2. Three Dimensional Array
Three Dimensional arrays are not commonly used in real-time applications. Therefore, two-dimensional arrays are given more preference in programming examples also.
Code:
int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //Three dimensional Array
Example:
6 8 66
66 65 47
46 89 98
How to Declare a Multidimensional Array in Java?
It is easy to understand the Multidimensional Array in Java if normal arrays are known. Multi-dimensional arrays can be declared as shown below:
First, let us see the declaration of 2D arrays:
- int[][] array1 = new int[2][2]; //Two dimensional Integer Array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
- String[][] array1 = new String[2][2]; //Two dimensional String Array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
- char[][] array1 = new char[2][2]; //Two dimensional char Array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
- boolean[][] array1 = new boolean[2][2]; //Two dimensional boolean Array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
- double[][] array1 = new double[2][2]; //Two dimensional double Array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
- float[][] array1 = new float[2][2]; //Two dimensional float Array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
- long[][] array1 = new long[2][2]; //Two dimensional long Array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
- short[][] array1 = new short[2][2]; //Two dimensional short Array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
- byte[][] array1 = new byte[2][2]; //Two dimensional byte Array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
Make sure that proper declaration is created while programming in Java.
Example #1
Code:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional 2D array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String args[]){
//2D array a is declared and initialized
int a[][]={{2,2,3},{8,4,5},{9,4,5}};
//Print the array elements
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}
Output:

Three Dimensional Array’s Declaration can be discussed.
- int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //Three dimensional Array
These arrays can be of any data types. Below are some of the three dimensional arrays with different data types.
- int [][][] IntArray; // declaring three dimensional array of Integers.
- byte[][][] ByteArray; // declaring three dimensional array of Bytes.
- short[][][] ShortArray; // declaring three dimensional array of Shorts.
- long[][][] LongArray; // declaring three dimensional array of Longs.
- float[][][] FloatArray; // declaring three dimensional array of Floats.
- double[][][] DoubleArray; // declaring three dimensional array of Doubles.
- boolean[][][] BooleanArray; // declaring three dimensional array of Booleans.
- char[][][] CharArray; // declaring three dimensional array of Chars.
- String[][][] StringArray; // declaring three dimensional array of Strings.
Example #2
Code:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3D array arr
int[][][] arr = { { { 1 , -9 , 3 } ,{ 2 , 7 , 4 } } , { { -45 , -5 , 6 , 75 } , { 88 } , { 29 , 30 } } };
// for..each loop to iterate through the elements of the 3d array arr
for (int[][] ar: arr) {
for (int[] a: ar) {
for(int finalarray: a) {
System.out.println(finalarray);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:

How to Initialize the Multidimensional Array in Java?
Multidimensional arrays can be initialized in multiple ways:
1. Declare and Create a Java Multidimensional Array
- int[][][] a= new int[3][5][4];
In a more traditional way, Initializing Array elements can be as follows.
- a[0][1][0] = 15; // Initializing Array elements at position [0][1][0]
- a[1][2][0] = 45; // Initializing Array elements at position [1][2][0]
- a[2][1][1] = 65; // Initializing Array elements at position [2][1][1]
2. Directly Specify the Elements
int[][][] a = { { { 11 , 23 , 30 }, { 5 ,65 , 70 } , { 0 , 80 , 10 } ,{ 10 , 12 , 450 } } ,{ { 33 , 2 , 4 } , {11, 66, 6}, {55, 11, 22}, {11, 57, 43} } };
In this case, even though the size of rows and columns are not mentioned, the java compiler is able to identify the size of rows and columns by counting the number of elements.
3. Nested For Loop
In the case of storing a large number of elements, Nested For Loop can be used as shown below:
int i, j, k;
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
a[i][j][k] = i + j + k;} } }
4. Assigning Values to One Row
int a= new int[3][2][4]; a[0][2][1]= 33; a[0][1][2]= 73; a[0][1][1]= 88;
A three-dimensional array of size 3 levels * 2 rows * 4 columns is created, but values are assigned to some positions only. Since none of the other elements does have any value assigned, default values will be assigned.
Operations on Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional Array in Java can perform several operations.
Example #1
Let Us See the Matrix Addition of Two Arrays.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String args[])
{
int row, col, c, d;
//input the number of rows and columns
Scanner <u>in</u> = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows of matrix");
row = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the number of columns of matrix");
col = in.nextInt();
//initialization of two matrices and sum matrix
int firstmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int secondmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int summat[][] = new int[row][col];
//adding elements to first matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the first matrix");
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
firstmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//adding elements to second matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the second matrix");
for (c = 0 ; c < row ; c++)
for (d = 0 ; d < col ; d++)
secondmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//sum of the two matrices
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
summat[c][d] = firstmat[c][d] + secondmat[c][d];
System.out.println("Sum of the two given matrices is:");
//printing the sum matrix
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
{
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
System.out.print(summat[c][d]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:

If subtraction needs to be performed, replace ‘+’ with ‘-‘ in the code.
Example #2
Let us see how Matrix Multiplication Works.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to perform matrix multiplication
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
static int N = 4;
// multiply matrices a and b, and then stores the result in c
static void mul(int a[][],
int b[][], int c[][])
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
c[i][j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++)
c[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j]; //multiply a and b matrices
}
}
}
//main method
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int a[][] = { {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2},
{9, 7, 2, 3}};
int b[][] = {{ 9, 7, 2, 3}, {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2}};
// Store the result in c
int c[][] = new int[N][N] ;
int i, j;
mul(a, b, c); //calling the mul method
System.out.println("Multiplication result matrix" + " is ");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
System.out.print( c[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
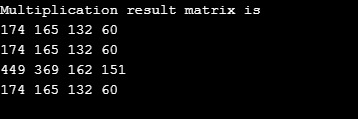
Output:
Conclusion
Arrays are homogenous data structures that can store similar types of elements. It can be of single-dimensional or multidimensional. In this document, multidimensional arrays are discussed with explaining the syntax structure, initialization, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Multidimensional Array in Java. Here we discuss 2 types of the multidimensional array in java, how to declare, how to initialize and operation in it. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
- Multidimensional Array in C
- 2D Arrays in Java
- 2D Arrays in C#
- Multidimensional Array in PHP
The above is the detailed content of Multidimensional Array in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

