 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI ACL 2024 Awards Announced: One of the Best Papers on Oracle Deciphering by HuaTech, GloVe Time Test Award
ACL 2024 Awards Announced: One of the Best Papers on Oracle Deciphering by HuaTech, GloVe Time Test AwardContributors have gained a lot from this ACL conference.


Authors: Julie Kallini, Isabel Papadimitriou, Richard Futrell, Kyle Mahowald, Christopher Potts Institutions: Stanford University, University of California, Irvine, University of Texas at Austin Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.06416

Author: Michael Hahn, Mark Rofin Institution: Saarland University Paper link: https://arxiv. org/abs/2402.09963

Author: Haisu Guan, Huanxin Yang, Xinyu Wang, Shengwei Han, etc. Institution: Huazhong University of Science and Technology , A Adelaide University, Anyang Normal College, South China University of Technology Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.00684

Author: Pietro Lesci, Clara Meister, Thomas Hofmann, Andreas Vlachos, Tiago Pimentel Institution: University of Cambridge , ETH Zurich Academy Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.04327
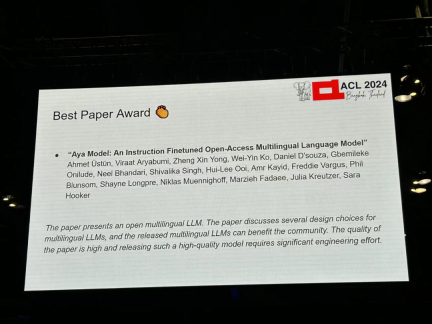
Author: Ahmet Üstün, Viraat Aryabumi, Zheng Xin Yong, Wei-Yin Ko, etc. Institution: Cohere, Brown University et al Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.07827

Authors: Liang Lu, Peirong Xie, David R. Mortensen -
Institution: CMU, University of Southern California Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.05930

Authors: Tharindu Madusanka, Ian Pratt-Hartmann, Riza Batista-Navarro

著者: Jeffrey Pennington、Richard Socher、Christopher D. Manning 機関: スタンフォード大学 論文リンク: https:/ / /aclanthology.org/D14-1162.pdf

著者: Lillian Lee 機関: コーネル大学 -
論文リンク: https://aclanthology .org /P99-1004.pdf


논문 1: 양자화 측면 튜닝: 양자화 대형 언어 모델의 빠르고 메모리 효율적인 튜닝 저자: Zhengxin Zhang, Dan Zhao, X 우펭 미아오, Gabriele Oliaro, Zhihao Zhang, Qing Li, Yong Jiang, Zhihao Jia 기관: CMU, Tsinghua University, Pengcheng Laboratory 등 -
논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.07159
문서 2: L-Eval: 장기 컨텍스트 언어 모델에 대한 표준화된 평가 실시 저자: Chenxin An, Shansan Gong, Ming Zhong, Xingjian Zhao, Mukai Li, Jun Zhang, Lingpeng Kong, Xipeng Qiu 기관: 푸단대학교, 홍콩대학교, 일리노이대학교 어바나 샴페인, 상하이 AI 연구소 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.11088
논문 3: 대규모 언어 모델 편향 제거를 위한 인과 기반 능동적 학습 논문 링크: https://openreview.net/forum?id=idp_1Q6F-lC
논문 4: CausalGym: 언어 작업에 대한 인과 해석 방법 벤치마킹 저자: Aryaman Arora, Dan Jurafsky, Christopher Potts 기관: Stanford University -
논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.12560
문서 5: 환각하지 말고 기권하세요: 다중 LLM 협업을 통해 LLM 지식 격차 식별 저자: Shangbin Feng, Weijia Shi, Yike Wang, Wenxuan Ding, Vidhisha Balachandran, Yulia Tsvetkov 기관: 워싱턴 대학교, 캘리포니아 대학교, 버클리, 홍콩 과학 기술 대학교, CMU 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.00367
논문 6: 음성 기초 모델 및 대규모 언어 모델을 사용한 음성 번역: 무엇이 있고 무엇이 빠졌나요? 저자: Marco Gaido, Sara Papi, Matteo Negri, Luisa Bentivogli -
조직: Bruno Kessler Foundation , Italy 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.12025
논문 7: NLP는 추출적이어야 합니까? 저자: Steven Bird : Charles Darwin University 문서 링크: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1hvF7_WQrou6CWZydhymYFTYHnd3ZIljV/view
문서 8: IRCoder: 중간 표현으로 Robus 만들기 t 다국어 코드 생성 erators 저자: Indraneil Paul, Goran Glavaš, Iryna Gurevych 기관: TU Darmstadt 등 -
논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.03894 -
논문 9: MultiLegalPile: 689GB 다국어 법률 자료 저자: Matthias Stürmer, Veton Matoshi 등 기관: 베른 대학교, 스탠포드 대학교 등 논문 링크: https:/ /arxiv.org/pdf/2306.02069
문서 10: PsySafe: 다중 에이전트 시스템 안전의 심리적 기반 공격, 방어 및 평가를 위한 포괄적인 프레임워크 저자: Zaibin Zhang, Yongting Zhang , Lijun Li , Hongzhi Gao, Lijun Wang, Huchuan Lu, Feng Zhao, Yu Qiao, Jing Shao 기관: 중국 대련 공과대학교 상하이 인공 지능 연구소 논문 링크: https://arxiv .org/pdf/2401.11880
논문 11: 감정적 지지 대화에 대한 선호 편향 완화 저자: 강동진 , 김성환 외 기관 : 연세대 등 논문 링크 : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.13211
논문 12 : 정치컴 합격하거나 Spinning Arrow? 대규모 언어 모델의 가치와 의견에 대한 보다 의미 있는 평가를 향하여 저자: Paul Röttger, Valentin Hofmann 등 기관: Bocconi University, Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence 등 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/ 2402.16786
문서 13: 동일한 작업, 더 많은 토큰: 입력 길이가 대규모 언어 모델의 추론 성능에 미치는 영향 저자: Mosh Levy, Alon Jacoby, Yoav Goldberg 기관: 파키스탄 Elan University, Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.14848
논문 14: 라마가 다국어의 잠재 언어에서 작동합니까? Transformers 저자: Chris Wendler, Veniamin Veselovsky 등 -
기관: EPFL - 문서 15: 유머에 대해 진지하게 생각하기: 재미없는 대형 언어 모델로 유머 데이터세트 만들기
- 기관: Columbia University, EPFL
- 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.00794
- 논문 16: Dia의 수준 추정 독선 다방어 아랍어 데이터 세트의 주석 간 일치 예측
- 기관: University of Edinburgh
- 문서 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf /2405.11282
- 논문 17: G-DlG: 그라데이션 기반 Dlverse 및 기계 번역을 위한 고품질 명령어 데이터 선택을 향하여
- 기관: ByteDance Research
- 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.12915
-
- 논문 19: SPZ: 알츠하이머병 탐지를 위한 구역 혼합을 사용한 의미론적 교란 기반 데이터 증강 방법
- 페이퍼 20: 탐욕만 있으면 됩니다: 토크나이저 추론 방법 평가
- 기관: Ben Guri, Negev Ann University, MIT
- 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.01289
- 기관: University of Notre Dame(미국)
- 저자: Chihiro Taquchi, David Chiang
- 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.09202
- 기관: Anthropic, Harvard University, University of Göttingen(독일), Center for Human-Compatible AI
- 저자: Nina Rimsky, Nick Gabrieli, Julian Schulz, Meg Tong, Evan J Hubinger, Alexander Matt Turner
- 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.06681
- 기관: Tsinghua University - Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University
- 저자: Nian Li, Chen Gao , Mingyu Li, Yong Li, Qingmin Liao
- 논문 링크: https: //arxiv.org/abs/2310.10436
- 기관 : 홍콩 중문 대학교, 화웨이 노아의 방주 연구소, 홍콩 과학 기술 대학교
- 저자: Wai-Chung Kwan, Xingshan Zeng, Yufei Wang, Yusen Sun, Liangyou Li, Lifeng Shang, Qun Liu, Kam- Fai Wong
- 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.19240
- 저자 : Jiasheng Si, Yibo Zhao, Yingjie Zhu, Haiyang Zhu, Wenpeng Lu, Deyu Zhou
- On Paper 26: On EFFICIENT and Statistics. , Apple Inc. for Large Language Models May Backfire!
- Institusi: Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
- Pautan https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.12343
Kertas 28: IndicLLMSuite: Rangka Tindakan untuk Mencipta Set Data Pra-latihan dan Penalaan Halus untuk Bahasa-bahasa India Rahman Safi
- Institusi: Pusat Nilekani di AI4Bharat, Institut Teknologi India (Madras), Microsoft, dll.
- Pautan kertas: https://arxiv.org/pdf/ 2403 06350
- Institusi: Universiti Turin, aqua-tech, Pusat Pembangunan Amazon (Itali), dsb.
- Pautan kertas: https://assets.amazon.science/08/83/9b686f424c89b08e8fa0a6e1d020/multipico-multilingual-perspectivist🜎
- Pengarang: Chuanyang Jin, Yutong Wu, Jing Cao, jiannan Xiang, dll.
Universiti, MIT, University of California, San Diego, University of Virginia, Johns Hopkins University Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.08743 - paper 31: Peta tidak masih belum mati: Mendedahkan mod model bahasa sebenar dengan menyejukkan kemerosotan
Pengarang: Davis Yoshida , Kartik Goyal, Kevin Gimpel
Institusi: Toyota Institute of Technology Chicago, Georgia Institute of Technology - pautan: https://pautan Pautan : //arxiv.org/pdf/2311.08817
paper 32: Nounatlas: Mengisi jurang dalam Peranan Semantik Nominal Labeling - Pengawal: Roberto Navigli, Marco Lo Pinto, Pasquale Silvestri, dan lain -lain. .
- Pautan kertas: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.09085
- 4: Let's Go Real Talk: Model Dialog Pertuturan untuk Perbualan Bersemuka
- Pengarang: Se Jin Park, Chae Won Kim, Hyeongseop Rha, Minsu Kim, dll.
- Pautan kertas: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.07867
- Kertas 35 :Pembenaman Bahasa🜎
- Institusi: University of Illinois at Urbana - Champaign
- Pautan kertas: https://arxiv.org/pdf /2305.12798
저자: Dirk Groeneveld, Iz Beltagy 등 기관: Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence, University of Washington 등 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.00838 저자: Julen Etxaniz, Oscar Sainz, Naiara Perez, Itziar Aldabe, German Rigau, Eneko Agirre, Aitor Ormazabal, Mikel Artetxe, Aitor Soroa 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.20266 기관: Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence, University of California, Berkeley 등 -
저자 : Luca Soldaini, Rodney Kinney 등 링크 : https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.00159 기관: 뉴욕 주립대학교 Stony Brook, Allen 인공 지능 연구소 등 -
저자: Harsh Trivedi, Tushar Khot 등 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.18901 -
저자: Yi Zeng, Hongpeng Lin, Jingwen Zhang, Diyi Yang 등 . 기관: 버지니아 공대, 중국 인민 대학교, 캘리포니아 대학교, 데이비스, 스탠포드 대학교 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.06373 -
저자: Fahim Faisal, Orevaoghene Ahia, Aarohi Srivastava, Kabir Ahuja 등 기관: 조지 메이슨 대학교, 워싱턴 대학교, 노트르담 대학교, RC Athena 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.11009 저자: Tarek Naous, Michael J. Ryan, Alan Ritter, Wei Xu 기관: Georgia Institute of Technology 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.14456
The above is the detailed content of ACL 2024 Awards Announced: One of the Best Papers on Oracle Deciphering by HuaTech, GloVe Time Test Award. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
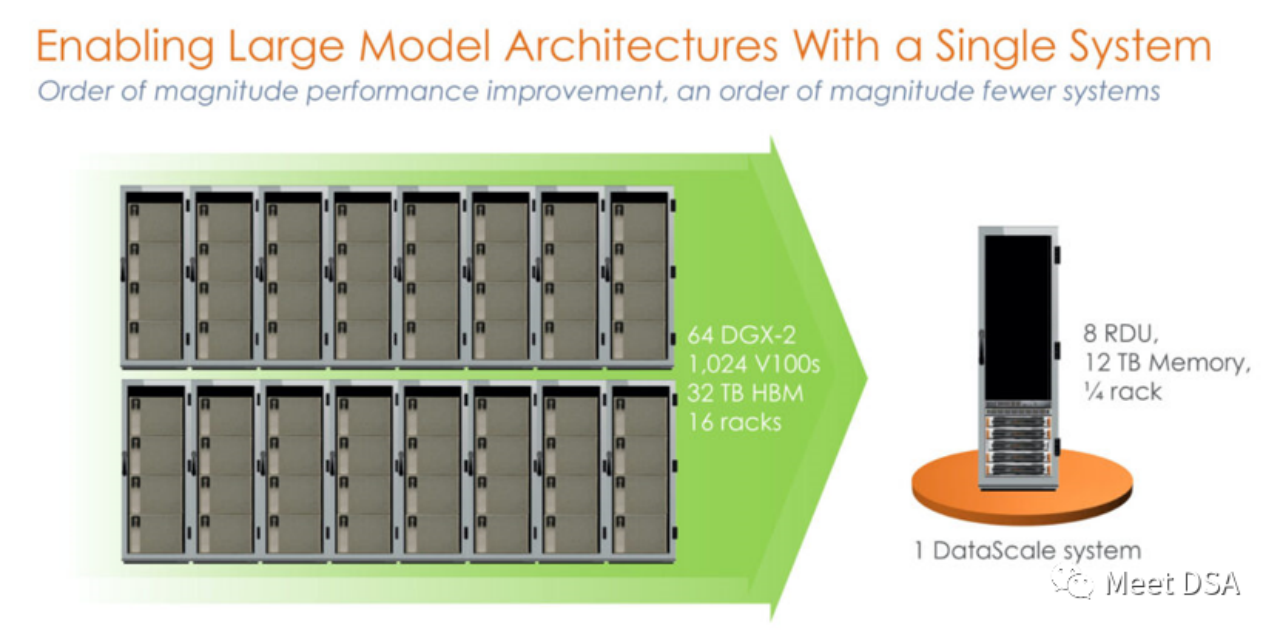 DSA如何弯道超车NVIDIA GPU?Sep 20, 2023 pm 06:09 PM
DSA如何弯道超车NVIDIA GPU?Sep 20, 2023 pm 06:09 PM你可能听过以下犀利的观点:1.跟着NVIDIA的技术路线,可能永远也追不上NVIDIA的脚步。2.DSA或许有机会追赶上NVIDIA,但目前的状况是DSA濒临消亡,看不到任何希望另一方面,我们都知道现在大模型正处于风口位置,业界很多人想做大模型芯片,也有很多人想投大模型芯片。但是,大模型芯片的设计关键在哪,大带宽大内存的重要性好像大家都知道,但做出来的芯片跟NVIDIA相比,又有何不同?带着问题,本文尝试给大家一点启发。纯粹以观点为主的文章往往显得形式主义,我们可以通过一个架构的例子来说明Sam
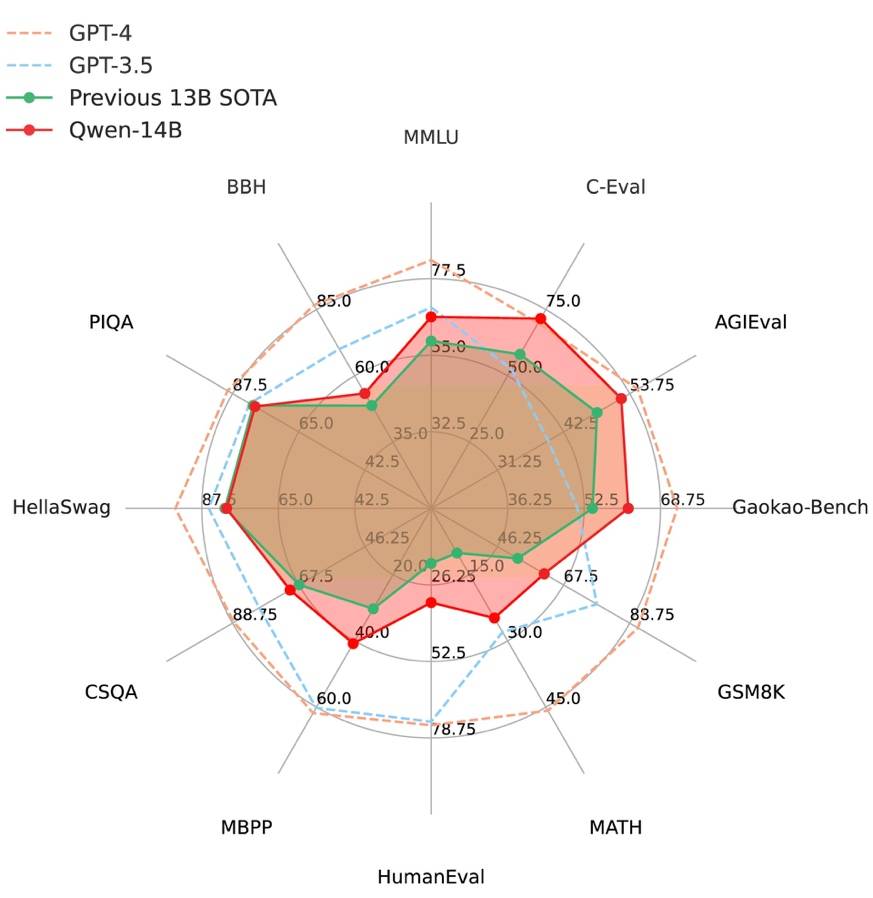 阿里云通义千问14B模型开源!性能超越Llama2等同等尺寸模型Sep 25, 2023 pm 10:25 PM
阿里云通义千问14B模型开源!性能超越Llama2等同等尺寸模型Sep 25, 2023 pm 10:25 PM2021年9月25日,阿里云发布了开源项目通义千问140亿参数模型Qwen-14B以及其对话模型Qwen-14B-Chat,并且可以免费商用。Qwen-14B在多个权威评测中表现出色,超过了同等规模的模型,甚至有些指标接近Llama2-70B。此前,阿里云还开源了70亿参数模型Qwen-7B,仅一个多月的时间下载量就突破了100万,成为开源社区的热门项目Qwen-14B是一款支持多种语言的高性能开源模型,相比同类模型使用了更多的高质量数据,整体训练数据超过3万亿Token,使得模型具备更强大的推
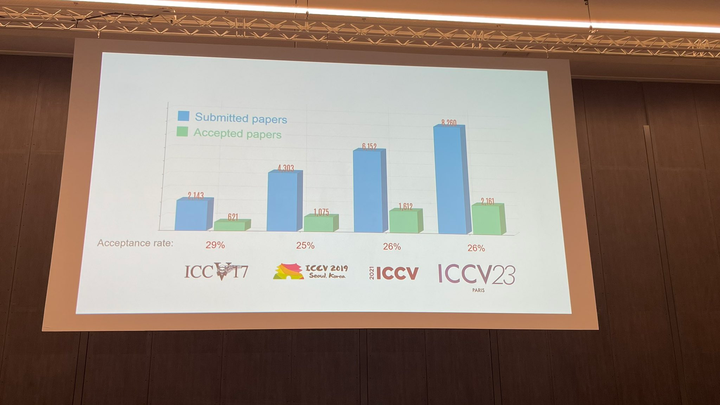 ICCV 2023揭晓:ControlNet、SAM等热门论文斩获奖项Oct 04, 2023 pm 09:37 PM
ICCV 2023揭晓:ControlNet、SAM等热门论文斩获奖项Oct 04, 2023 pm 09:37 PM在法国巴黎举行了国际计算机视觉大会ICCV(InternationalConferenceonComputerVision)本周开幕作为全球计算机视觉领域顶级的学术会议,ICCV每两年召开一次。ICCV的热度一直以来都与CVPR不相上下,屡创新高在今天的开幕式上,ICCV官方公布了今年的论文数据:本届ICCV共有8068篇投稿,其中有2160篇被接收,录用率为26.8%,略高于上一届ICCV2021的录用率25.9%在论文主题方面,官方也公布了相关数据:多视角和传感器的3D技术热度最高在今天的开
 复旦大学团队发布中文智慧法律系统DISC-LawLLM,构建司法评测基准,开源30万微调数据Sep 29, 2023 pm 01:17 PM
复旦大学团队发布中文智慧法律系统DISC-LawLLM,构建司法评测基准,开源30万微调数据Sep 29, 2023 pm 01:17 PM随着智慧司法的兴起,智能化方法驱动的智能法律系统有望惠及不同群体。例如,为法律专业人员减轻文书工作,为普通民众提供法律咨询服务,为法学学生提供学习和考试辅导。由于法律知识的独特性和司法任务的多样性,此前的智慧司法研究方面主要着眼于为特定任务设计自动化算法,难以满足对司法领域提供支撑性服务的需求,离应用落地有不小的距离。而大型语言模型(LLMs)在不同的传统任务上展示出强大的能力,为智能法律系统的进一步发展带来希望。近日,复旦大学数据智能与社会计算实验室(FudanDISC)发布大语言模型驱动的中
 百度文心一言全面向全社会开放,率先迈出重要一步Aug 31, 2023 pm 01:33 PM
百度文心一言全面向全社会开放,率先迈出重要一步Aug 31, 2023 pm 01:33 PM8月31日,文心一言首次向全社会全面开放。用户可以在应用商店下载“文心一言APP”或登录“文心一言官网”(https://yiyan.baidu.com)进行体验据报道,百度计划推出一系列经过全新重构的AI原生应用,以便让用户充分体验生成式AI的理解、生成、逻辑和记忆等四大核心能力今年3月16日,文心一言开启邀测。作为全球大厂中首个发布的生成式AI产品,文心一言的基础模型文心大模型早在2019年就在国内率先发布,近期升级的文心大模型3.5也持续在十余个国内外权威测评中位居第一。李彦宏表示,当文心
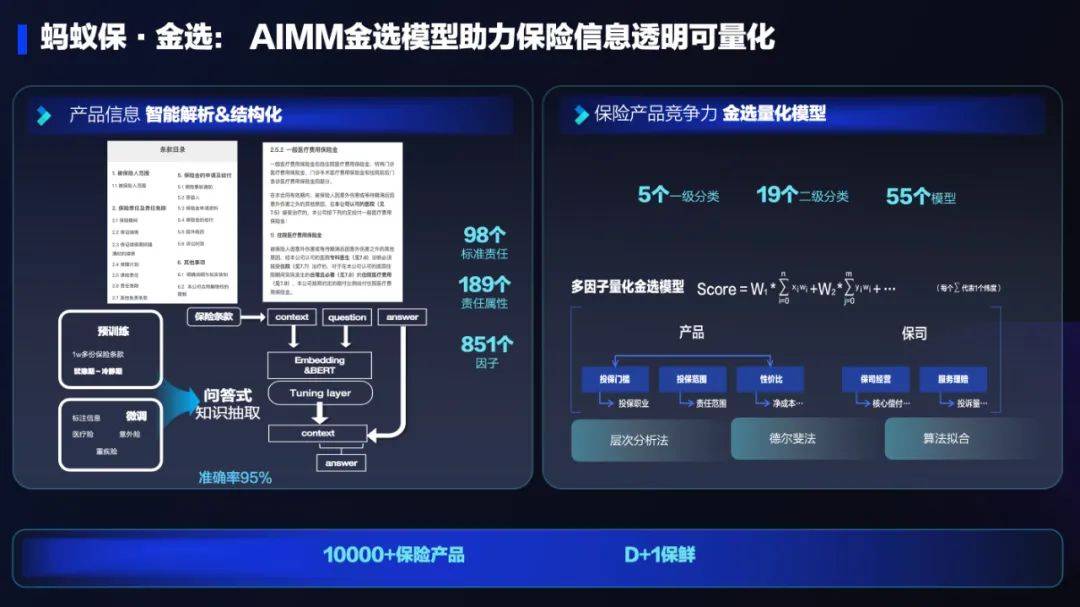 AI技术在蚂蚁集团保险业务中的应用:革新保险服务,带来全新体验Sep 20, 2023 pm 10:45 PM
AI技术在蚂蚁集团保险业务中的应用:革新保险服务,带来全新体验Sep 20, 2023 pm 10:45 PM保险行业对于社会民生和国民经济的重要性不言而喻。作为风险管理工具,保险为人民群众提供保障和福利,推动经济的稳定和可持续发展。在新的时代背景下,保险行业面临着新的机遇和挑战,需要不断创新和转型,以适应社会需求的变化和经济结构的调整近年来,中国的保险科技蓬勃发展。通过创新的商业模式和先进的技术手段,积极推动保险行业实现数字化和智能化转型。保险科技的目标是提升保险服务的便利性、个性化和智能化水平,以前所未有的速度改变传统保险业的面貌。这一发展趋势为保险行业注入了新的活力,使保险产品更贴近人民群众的实际
 致敬TempleOS,有开发者创建了启动Llama 2的操作系统,网友:8G内存老电脑就能跑Oct 07, 2023 pm 10:09 PM
致敬TempleOS,有开发者创建了启动Llama 2的操作系统,网友:8G内存老电脑就能跑Oct 07, 2023 pm 10:09 PM不得不说,Llama2的「二创」项目越来越硬核、有趣了。自Meta发布开源大模型Llama2以来,围绕着该模型的「二创」项目便多了起来。此前7月,特斯拉前AI总监、重回OpenAI的AndrejKarpathy利用周末时间,做了一个关于Llama2的有趣项目llama2.c,让用户在PyTorch中训练一个babyLlama2模型,然后使用近500行纯C、无任何依赖性的文件进行推理。今天,在Karpathyllama2.c项目的基础上,又有开发者创建了一个启动Llama2的演示操作系统,以及一个
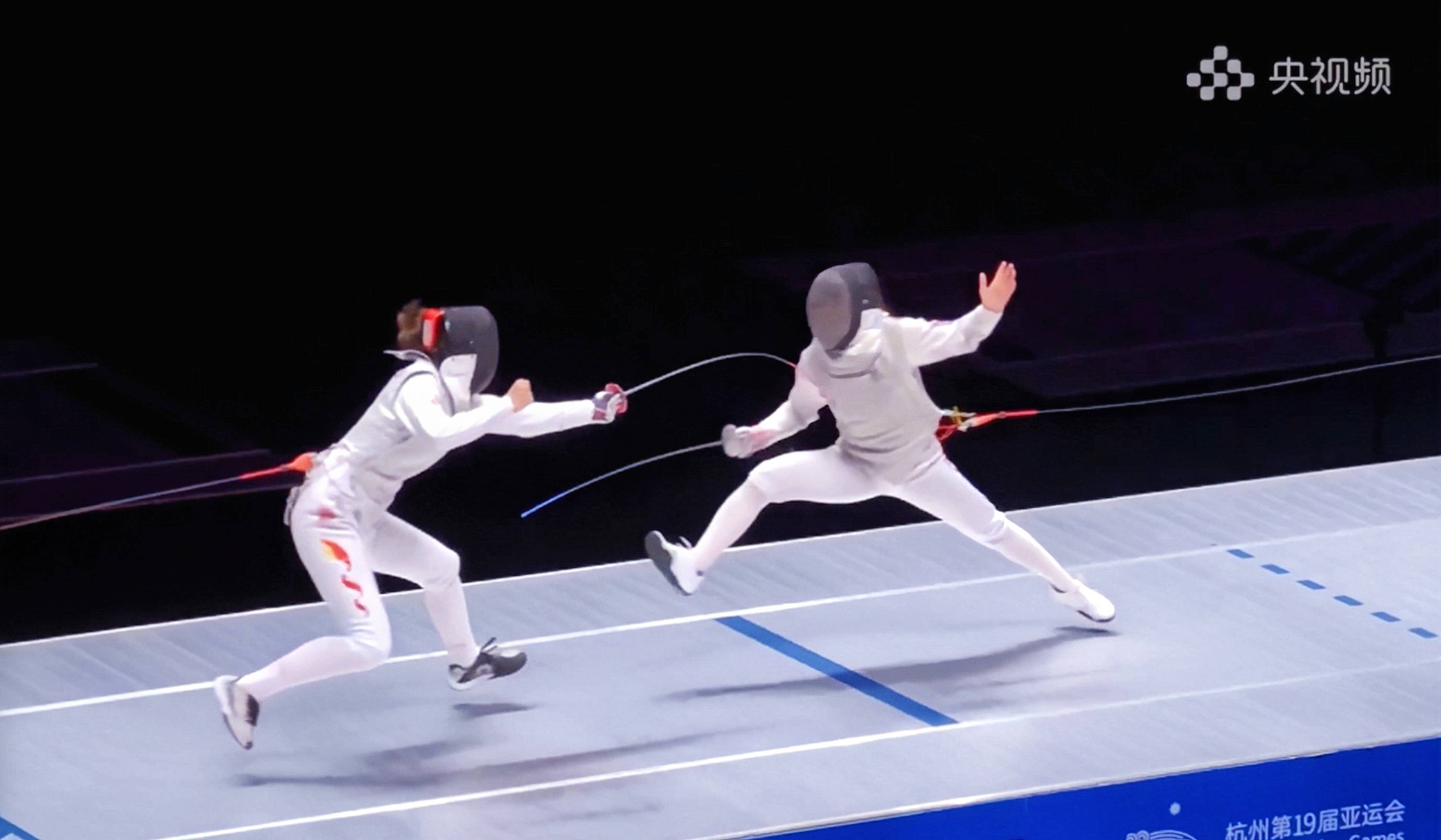 快手黑科技“子弹时间”赋能亚运转播,打造智慧观赛新体验Oct 11, 2023 am 11:21 AM
快手黑科技“子弹时间”赋能亚运转播,打造智慧观赛新体验Oct 11, 2023 am 11:21 AM杭州第19届亚运会不仅是国际顶级体育盛会,更是一场精彩绝伦的中国科技盛宴。本届亚运会中,快手StreamLake与杭州电信深度合作,联合打造智慧观赛新体验,在击剑赛事的转播中,全面应用了快手StreamLake六自由度技术,其中“子弹时间”也是首次应用于击剑项目国际顶级赛事。中国电信杭州分公司智能亚运专班组长芮杰表示,依托快手StreamLake自研的4K3D虚拟运镜视频技术和中国电信5G/全光网,通过赛场内部署的4K专业摄像机阵列实时采集的高清竞赛视频,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment





