 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI New standard for AI imaging, only 1% of original data can achieve the best performance, general medical basic model published in Nature sub-journal
New standard for AI imaging, only 1% of original data can achieve the best performance, general medical basic model published in Nature sub-journalNew standard for AI imaging, only 1% of original data can achieve the best performance, general medical basic model published in Nature sub-journal

Editor | Cabbage Leaf
The large-scale pre-trained base model has achieved great success in non-medical fields. However, training these models often requires large, comprehensive datasets, in contrast to the smaller and more specialized datasets common in biomedical imaging.
Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Digital Medicine MEVIS in Germany proposed a multi-task learning strategy that separates the number of training tasks from memory requirements.
They trained a universal biomedical pre-trained model (UMedPT) on a multi-task database including tomography, microscopy and X-ray images and employed various labeling strategies such as classification, segmentation and object detection. The UMedPT base model outperforms ImageNet pre-trained and previous STOA models.
In external independent validation, imaging features extracted using UMedPT were proven to set a new standard for cross-center transferability.
The study was titled "Overcoming data scarcity in biomedical imaging with a foundational multi-task model" and was published in "Nature Computational Science" on July 19, 2024.

Deep learning is gradually revolutionizing biomedical image analysis due to its ability to learn and extract useful image representations.
The general method is to pre-train the model on a large-scale natural image dataset (such as ImageNet or LAION), and then fine-tune it for specific tasks or directly use the pre-trained features. But fine-tuning requires more computing resources.
At the same time, the field of biomedical imaging requires a large amount of annotated data for effective deep learning pre-training, but such data is often scarce.
Multi-task learning (MTL) provides a solution to data scarcity by training a model to solve multiple tasks simultaneously. It leverages many small and medium-sized datasets in biomedical imaging to pre-train image representations suitable for all tasks and is suitable for data-scarce domains.
MTL has been applied to biomedical image analysis in a variety of ways, including training from multiple small and medium-sized datasets for different tasks, and using multiple label types on a single image, demonstrating that shared features can improve task performance.
In the latest research, in order to combine multiple datasets with different label types for large-scale pre-training, researchers from the MEVIS Institute introduced a multi-task training strategy and corresponding model architecture, specifically through learning Versatile representations across different modalities, diseases, and label types to address data scarcity in biomedical imaging.

To cope with the memory constraints encountered in large-scale multi-task learning, this method adopts a gradient accumulation-based training loop, whose expansion is almost unlimited by the number of training tasks.
On this basis, the researchers trained a fully supervised biomedical imaging base model called UMedPT using 17 tasks and their original annotations.
The image below shows the architecture of the team’s neural network, which consists of shared blocks including an encoder, segmentation decoder, and localization decoder, as well as task-specific heads. Shared blocks are trained to be applicable to all pre-training tasks, helping to extract common features, while task-specific supervisors handle label-specific loss calculations and predictions.
The set tasks include three supervised label types: object detection, segmentation and classification. For example, classification tasks can model binary biomarkers, segmentation tasks can extract spatial information, and object detection tasks can be used to train biomarkers based on cell numbers.
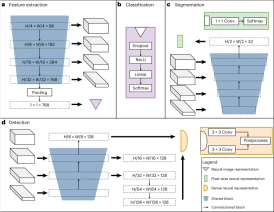
Illustration: UMedPT’s architecture. (Source: Paper)
UMedPT consistently matches or outperforms pretrained ImageNet networks on both in-domain and out-of-domain tasks, while maintaining strong performance using less training data when directly applying image representation (freezing) and fine-tuning settings.
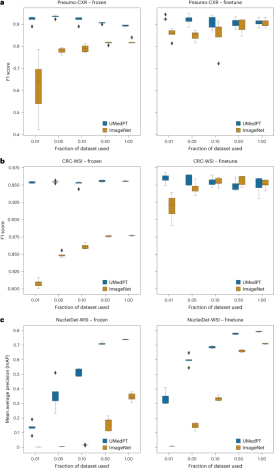
Illustration: Results of tasks within the domain. (Source: paper)
For classification tasks associated with pre-trained databases, UMedPT is able to achieve the best performance of the ImageNet baseline on all configurations using only 1% of the original training data. This model achieves higher performance using frozen encoders compared to the model using fine-tuning.
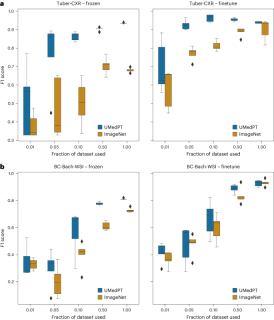
Illustration: Results for out-of-domain tasks (source: paper)
For out-of-domain tasks, UMedPT is able to match the performance of ImageNet using only 50% or less data, even with fine-tuning applied.
Additionally, the researchers compared the performance of UMedPT with results reported in the literature. When using the frozen encoder configuration, UMedPT exceeded the external reference results in most tasks. In this setting, it also outperforms the average area under the curve (AUC) in the MedMNIST database 16 .
It is worth noting that the tasks for which the frozen application of UMedPT did not outperform the reference results were outside the domain (BC-Bach-WSI for breast cancer classification and CNS-MRI for CNS tumor diagnosis). With fine-tuning, pre-training with UMedPT outperforms external reference results in all tasks.

Illustration: The amount of data required by UMedPT to achieve state-of-the-art performance on tasks in different imaging domains. (Source: Paper)
As a foundation for future developments in data-scarce fields, UMedPT opens up the prospect of deep learning applications in medical fields where collecting large amounts of data is particularly challenging, such as rare diseases and pediatric imaging.
Paper link:https://www.nature.com/articles/s43588-024-00662-z
Related content:https://www.nature.com/articles/s43588-024-00658- 9
The above is the detailed content of New standard for AI imaging, only 1% of original data can achieve the best performance, general medical basic model published in Nature sub-journal. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Cooking Up Innovation: How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Food ServiceApr 12, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Cooking Up Innovation: How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Food ServiceApr 12, 2025 pm 12:09 PMAI Augmenting Food Preparation While still in nascent use, AI systems are being increasingly used in food preparation. AI-driven robots are used in kitchens to automate food preparation tasks, such as flipping burgers, making pizzas, or assembling sa
 Comprehensive Guide on Python Namespaces & Variable ScopesApr 12, 2025 pm 12:00 PM
Comprehensive Guide on Python Namespaces & Variable ScopesApr 12, 2025 pm 12:00 PMIntroduction Understanding the namespaces, scopes, and behavior of variables in Python functions is crucial for writing efficiently and avoiding runtime errors or exceptions. In this article, we’ll delve into various asp
 A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AMIntroduction Imagine walking through an art gallery, surrounded by vivid paintings and sculptures. Now, what if you could ask each piece a question and get a meaningful answer? You might ask, “What story are you telling?
 MediaTek Boosts Premium Lineup With Kompanio Ultra And Dimensity 9400Apr 12, 2025 am 11:52 AM
MediaTek Boosts Premium Lineup With Kompanio Ultra And Dimensity 9400Apr 12, 2025 am 11:52 AMContinuing the product cadence, this month MediaTek has made a series of announcements, including the new Kompanio Ultra and Dimensity 9400 . These products fill in the more traditional parts of MediaTek’s business, which include chips for smartphone
 This Week In AI: Walmart Sets Fashion Trends Before They Ever HappenApr 12, 2025 am 11:51 AM
This Week In AI: Walmart Sets Fashion Trends Before They Ever HappenApr 12, 2025 am 11:51 AM#1 Google launched Agent2Agent The Story: It’s Monday morning. As an AI-powered recruiter you work smarter, not harder. You log into your company’s dashboard on your phone. It tells you three critical roles have been sourced, vetted, and scheduled fo
 Generative AI Meets PsychobabbleApr 12, 2025 am 11:50 AM
Generative AI Meets PsychobabbleApr 12, 2025 am 11:50 AMI would guess that you must be. We all seem to know that psychobabble consists of assorted chatter that mixes various psychological terminology and often ends up being either incomprehensible or completely nonsensical. All you need to do to spew fo
 The Prototype: Scientists Turn Paper Into PlasticApr 12, 2025 am 11:49 AM
The Prototype: Scientists Turn Paper Into PlasticApr 12, 2025 am 11:49 AMOnly 9.5% of plastics manufactured in 2022 were made from recycled materials, according to a new study published this week. Meanwhile, plastic continues to pile up in landfills–and ecosystems–around the world. But help is on the way. A team of engin
 The Rise Of The AI Analyst: Why This Could Be The Most Important Job In The AI RevolutionApr 12, 2025 am 11:41 AM
The Rise Of The AI Analyst: Why This Could Be The Most Important Job In The AI RevolutionApr 12, 2025 am 11:41 AMMy recent conversation with Andy MacMillan, CEO of leading enterprise analytics platform Alteryx, highlighted this critical yet underappreciated role in the AI revolution. As MacMillan explains, the gap between raw business data and AI-ready informat


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.




