Home >Backend Development >Golang >Building Ollama Cloud - Scaling Local Inference to the Cloud
Building Ollama Cloud - Scaling Local Inference to the Cloud
- WBOYOriginal
- 2024-07-18 00:38:11861browse
Ollama is primarily a wrapper around llama.cpp, designed for local inference tasks. It's not typically your first choice if you're looking for cutting-edge performance or features, but it has its uses, especially in environments where external dependencies are a concern.
Local AI Development
When using Ollama for local AI development, the setup is straightforward but effective. Developers typically leverage Ollama to run inference tasks directly on their local machines. Here's a visual depiction of a typical local development setup using Ollama:

This configuration allows developers to test and iterate quickly without the complexities of remote server communications. It's ideal for initial prototyping and development phases where quick turnaround is critical.
From Local to Cloud
Transitioning from a local setup to a scalable cloud environment involves evolving from a simple 1:1 setup (one user request to one inference host) to a more complex many-to-many (multiple user requests to multiple inference hosts) configuration. This shift is necessary to maintain efficiency and responsiveness as demand increases.
Here's how this scaling looks when moving from local development to production:
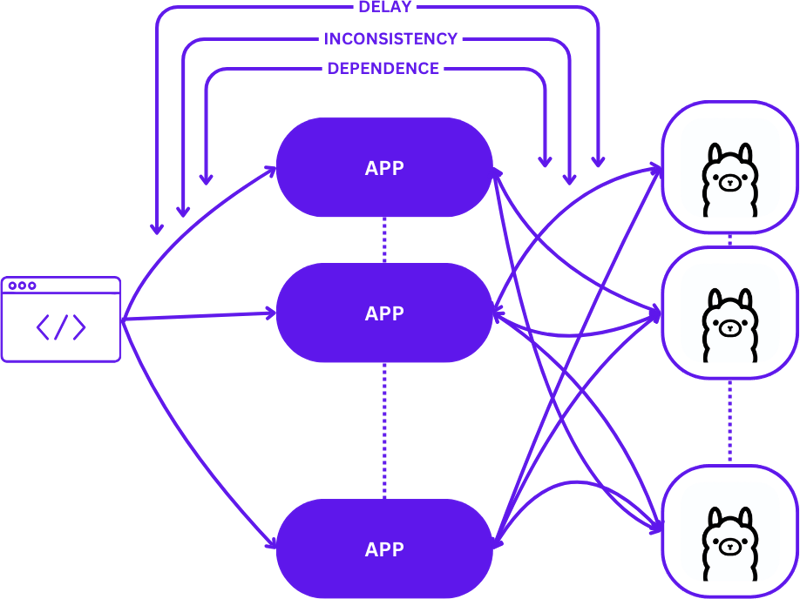
Adopting a straightforward approach during this transition can significantly increase the complexity of applications, especially as sessions need to maintain consistency across various states. Delays and inefficiencies may arise if requests are not optimally routed to the best available inference host.
Moreover, the complex nature of distributed applications makes them challenging to test locally, which can slow down the development process and increase the risk of failures in production environments.
Serverless
Serverless computing abstracts server management and infrastructure details, allowing developers to focus solely on code and business logic. By decoupling request handling and consistency maintenance from the application, serverless architecture simplifies scaling.
This approach allows the application to remain concentrated on delivering value, solving many common scaling challenges without burdening developers with infrastructure complexities.
WebAssembly
WebAssembly (Wasm) addresses the challenge of dependency management by enabling the compilation of applications into self-contained modules. This makes apps easier to orchestrate and test both locally and in the cloud, ensuring consistency across different environments.
Tau
Tau is a framework to build low-maintenance and highly scalable cloud computing platforms. It excels in simplicity and extendibility. Tau makes deployment straightforward and supports running a local cloud for development, allowing for end-to-end (E2E) testing of both the cloud infrastructure and the applications running on it.
This approach, referred to by Taubyte as "Local Coding Equals Global Production," ensures that what works locally will work globally, significantly easing the development and deployment processes.
Integrating Ollama into Tau with the Orbit Plugin System
Tau’s plugin system, known as Orbit, significantly simplifies turning services into manageable components by wrapping them into WebAssembly host modules. This approach allows Tau to take over the orchestration duties, streamlining the deployment and management process.
Exporting Functions in Ollama
To make Ollama functions accessible within Tau’s ecosystem, we utilize the Orbit system to export Ollama’s capabilities as callable endpoints. Here’s how you can export an endpoint in Go:
func (s *ollama) W_pull(ctx context.Context, module satellite.Module, modelNamePtr uint32, modelNameSize uint32, pullIdptr uint32) Error {
model, err := module.ReadString(modelNamePtr, modelNameSize)
if err != nil {
return ErrorReadMemory
}
id, updateFunc := s.getPullId(model)
if updateFunc != nil {
go func() {
err = server.PullModel(s.ctx, model, &server.RegistryOptions{}, updateFunc)
s.pullLock.Lock()
defer s.pullLock.Unlock()
s.pulls[id].err = err
}()
}
module.WriteUint64(pullIdptr, id)
return ErrorNone
}
For a straightforward example of exporting functions, you can refer to the hello_world example.
Once defined, these functions, now called via satellite.Export, enable the seamless integration of Ollama into Tau’s environment:
func main() {
server := new(context.TODO(), "/tmp/ollama-wasm")
server.init()
satellite.Export("ollama", server)
}
Writing Tests for the Ollama Plugin
Testing the plugin is streamlined and straightforward. Here's how you can write a serverless function test in Go:
//export pull
func pull() {
var id uint64
err := Pull("gemma:2b-instruct", &id)
if err != 0 {
panic("failed to call pull")
}
}
Using Tau's test suite and Go builder tools, you can build your plugin, deploy it in a test environment, and execute the serverless functions to verify functionality:
func TestPull(t *testing.T) {
ctx := context.Background()
// Create a testing suite to test the plugin
ts, err := suite.New(ctx)
assert.NilError(t, err)
// Use a Go builder to build plugins and wasm
gob := builder.New()
// Build the plugin from the directory
wd, _ := os.Getwd()
pluginPath, err := gob.Plugin(path.Join(wd, "."), "ollama")
assert.NilError(t, err)
// Attach plugin to the testing suite
err = ts.AttachPluginFromPath(pluginPath)
assert.NilError(t, err)
// Build a wasm file from serverless function
wasmPath, err := gob.Wasm(ctx, path.Join(wd, "fixtures", "pull.go"), path.Join(wd, "fixtures", "common.go"))
assert.NilError(t, err)
// Load the wasm module and call the function
module, err := ts.WasmModule(wasmPath)
assert.NilError(t, err)
// Call the "pull" function from our wasm module
_, err = module.Call(ctx, "pull")
assert.NilError(t, err)
}
Code
You can find the complete code here https://github.com/ollama-cloud/ollama-as-wasm-plugin/tree/main/Building Ollama Cloud - Scaling Local Inference to the Cloud
What's Next?
You can now build LLM applications with ease. Here are the steps to get started:
- Start locally using dream: Set up your local environment to develop and test your application.
- Create a project: Begin a new project with Tau to harness its full potential.
- Create your production cloud: Deploy your project in a production cloud environment.
- Drop the plugin binary in the /tb/plugins folder.
- Import your project into production
- Show off!
The above is the detailed content of Building Ollama Cloud - Scaling Local Inference to the Cloud. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

