Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Nature sub-journal, with an accuracy rate of 96%, AI predicts protein-ligand interactions from sequences
Nature sub-journal, with an accuracy rate of 96%, AI predicts protein-ligand interactions from sequencesNature sub-journal, with an accuracy rate of 96%, AI predicts protein-ligand interactions from sequences

In drug development, it is crucial to determine the binding affinity and functional effect of small molecule ligands on proteins. Current computational methods can predict these protein-ligand interaction properties, but without high-resolution protein structures, accuracy is often lost and functional effects cannot be predicted.
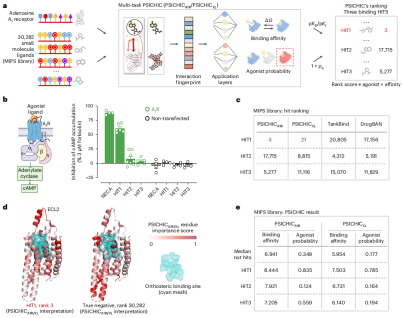
Researchers at Monash University and Griffith University have developed PSICHIC (PhySIcoCHhemICal Graph Neural Network), a framework that combines physicochemical constraints directly from sequences Data decoding interaction fingerprints. This enables PSICHIC to decode the mechanisms behind protein-ligand interactions, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy and interpretability.
Trained on the same protein-ligand pairs without structural data, PSICHIC performed on par with, or even exceeded, leading structure-based methods in binding affinity predictions.
PSICHIC’s interpretable fingerprint identifies protein residues and ligand atoms involved in the interaction and helps reveal the selectivity determinants of protein-ligand interactions.
The study was titled "Physicochemical graph neural network for learning protein–ligand interaction fingerprints from sequence data" and was published in "Nature Machine Intelligence" on June 17, 2024.

In the drug discovery process, it is critical to understand the binding affinity and functional effects of small molecule ligands on proteins, as the selective interaction of the ligand with a specific protein determines The expected effect of the drug.
However, although current computational methods are capable of predicting protein-ligand interaction properties, in the absence of high-resolution protein structures, the prediction accuracy often decreases, and there are also difficulties in predicting functional effects.
Although sequence-based methods have more advantages in cost and resources (for example, they do not require expensive experimental structure determination processes), these methods often face the problem of excessive degrees of freedom in pattern matching, which can easily lead to overfitting and limited generalization. ization capabilities, thereby creating a performance gap with structure- or composite-based methods.
Physical Chemistry Graph Neural Network
A research team from Monash University and Griffith University developed PSICHIC (Physical Chemistry Graph Neural Network), a method to directly decode protein-ligands from sequence data following physical and chemical principles. Body interaction fingerprint method. Unlike previous sequence-based models, PSICHIC uniquely incorporates physicochemical constraints to achieve state-of-the-art accuracy and interpretability.
As a 2D sequence-based method, PSICHIC generates and imposes these constraints on a 2D plot by applying a clustering algorithm, allowing PSICHIC to primarily adapt to the rational underlying patterns that determine protein-ligand interactions during training.
(Source: Paper)
Performance Validation and Comparison
After training on the same protein-ligand pairs without structural data, PSICHIC outperforms in binding affinity predictions State-of-the-art structure-based and composite-based methods rival or even surpass them.
Experimental results on PDBBind v2016 and PDBBind v2020 datasets show that PSICHIC outperforms other sequence-based methods, such as TransCPI, MolTrans, and DrugBAN, on multiple indicators.

Performance statistical summary of protein-ligand binding affinity predictions on PDBBind v2016 and PDBBind v2020 benchmarks. (Source: paper)
Specifically:
- PSICHIC shows lower prediction error and higher correlation index, especially in terms of prediction accuracy and generalization ability.
- PSICHIC achieves up to 96% accuracy in functional effect prediction.
Also:
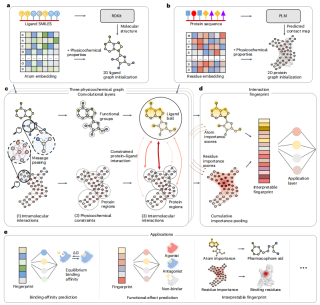
- PSICHIC excels in the identification of binding sites and key ligand functional groups.
- In the analysis of multiple protein-ligand complex structures (such as PDB 6K1S and 6OXV), PSICHIC was able to accurately locate important binding residues and ligand functional groups, verifying its direct decoding of protein-ligands in sequence data. The ability of body interaction patterns.
- This ability is particularly reflected in its ability to predict protein-ligand binding sites and key residues from sequence data.
Illustration: Virtual screening using interactive fingerprints. (Source: Paper)
Interestingly, PSICHIC’s interpretable fingerprints show that it obtains the ability to decode the underlying mechanism of protein-ligand interactions from sequence data alone, identifying binding site protein residues and involved ligands atomic capabilities, even when trained only on sequence data with binding affinity labels and no interaction information.

- Protein-ligand interaction fingerprint describes the specific interaction characteristics between ligands and protein residues.
- PSICHIC provides a unique approach to obtaining interpretable interaction fingerprints using only sequence data.
- PSICHIC incorporates constraints and demonstrates emerging capabilities to reveal protein-ligand interaction mechanisms and efficiently predict interaction properties.
- PSICHIC eliminates the need for 3D data, paving the way for robust learning on large-scale sequence databases.
Future Outlook
- Expand PSICHIC analysis to protein complexes, such as GPCRs complexed with heterotrimeric G proteins.
- Exploring complex interactions such as allosteric regulation helps understand how allosteric ligands regulate orthosteric ligands within protein targets.
- PSICHIC has proven its robustness and effectiveness in various application fields and has broad potential for future development.
The above is the detailed content of Nature sub-journal, with an accuracy rate of 96%, AI predicts protein-ligand interactions from sequences. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Personal Hacking Will Be A Pretty Fierce BearMay 11, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Personal Hacking Will Be A Pretty Fierce BearMay 11, 2025 am 11:09 AMCyberattacks are evolving. Gone are the days of generic phishing emails. The future of cybercrime is hyper-personalized, leveraging readily available online data and AI to craft highly targeted attacks. Imagine a scammer who knows your job, your f
 Pope Leo XIV Reveals How AI Influenced His Name ChoiceMay 11, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Pope Leo XIV Reveals How AI Influenced His Name ChoiceMay 11, 2025 am 11:07 AMIn his inaugural address to the College of Cardinals, Chicago-born Robert Francis Prevost, the newly elected Pope Leo XIV, discussed the influence of his namesake, Pope Leo XIII, whose papacy (1878-1903) coincided with the dawn of the automobile and
 FastAPI-MCP Tutorial for Beginners and Experts - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:56 AM
FastAPI-MCP Tutorial for Beginners and Experts - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:56 AMThis tutorial demonstrates how to integrate your Large Language Model (LLM) with external tools using the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and FastAPI. We'll build a simple web application using FastAPI and convert it into an MCP server, enabling your L
 Dia-1.6B TTS : Best Text-to-Dialogue Generation Model - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:27 AM
Dia-1.6B TTS : Best Text-to-Dialogue Generation Model - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:27 AMExplore Dia-1.6B: A groundbreaking text-to-speech model developed by two undergraduates with zero funding! This 1.6 billion parameter model generates remarkably realistic speech, including nonverbal cues like laughter and sneezes. This article guide
 3 Ways AI Can Make Mentorship More Meaningful Than EverMay 10, 2025 am 11:17 AM
3 Ways AI Can Make Mentorship More Meaningful Than EverMay 10, 2025 am 11:17 AMI wholeheartedly agree. My success is inextricably linked to the guidance of my mentors. Their insights, particularly regarding business management, formed the bedrock of my beliefs and practices. This experience underscores my commitment to mentor
 AI Unearths New Potential In The Mining IndustryMay 10, 2025 am 11:16 AM
AI Unearths New Potential In The Mining IndustryMay 10, 2025 am 11:16 AMAI Enhanced Mining Equipment The mining operation environment is harsh and dangerous. Artificial intelligence systems help improve overall efficiency and security by removing humans from the most dangerous environments and enhancing human capabilities. Artificial intelligence is increasingly used to power autonomous trucks, drills and loaders used in mining operations. These AI-powered vehicles can operate accurately in hazardous environments, thereby increasing safety and productivity. Some companies have developed autonomous mining vehicles for large-scale mining operations. Equipment operating in challenging environments requires ongoing maintenance. However, maintenance can keep critical devices offline and consume resources. More precise maintenance means increased uptime for expensive and necessary equipment and significant cost savings. AI-driven
 Why AI Agents Will Trigger The Biggest Workplace Revolution In 25 YearsMay 10, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Why AI Agents Will Trigger The Biggest Workplace Revolution In 25 YearsMay 10, 2025 am 11:15 AMMarc Benioff, Salesforce CEO, predicts a monumental workplace revolution driven by AI agents, a transformation already underway within Salesforce and its client base. He envisions a shift from traditional markets to a vastly larger market focused on
 AI HR Is Going To Rock Our Worlds As AI Adoption SoarsMay 10, 2025 am 11:14 AM
AI HR Is Going To Rock Our Worlds As AI Adoption SoarsMay 10, 2025 am 11:14 AMThe Rise of AI in HR: Navigating a Workforce with Robot Colleagues The integration of AI into human resources (HR) is no longer a futuristic concept; it's rapidly becoming the new reality. This shift impacts both HR professionals and employees, dem


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function