 System Tutorial
System Tutorial Windows Series
Windows Series Your Computer BIOS Is Full of Settings, But Which Should You Actually Change?
Your Computer BIOS Is Full of Settings, But Which Should You Actually Change?Your Computer BIOS Is Full of Settings, But Which Should You Actually Change?
Navigating the BIOS can feel overwhelming, with so many settings to consider. But there are a few simple tweaks you should make in the BIOS to boost the performance and stability of your system. We'll show you some of those tweaks, and explain when and why you might want to use them.
1 1. Password Protect Your BIOS
While we're careful to password-protect our user accounts, we often overlook securing the BIOS. This oversight can enable anyone to enter your computer's BIOS and alter system security settings, even if your user account is password-protected. By setting up a password for your BIOS, you can mitigate these risks and protect your data if the device gets stolen.
To set up this security feature, restart your computer and press the designated key(s) to access the BIOS setup utility. Then, locate the security settings section, where you can set up a password, usually labeled as "Supervisor Password," "Administrator Password," or "User Password." Save the changes and exit the BIOS.
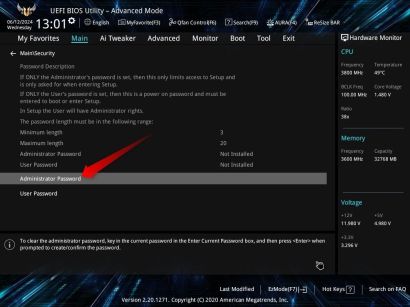
From now on, whenever you need to modify a BIOS setting, you'll need to confirm your identity by entering the password.
2 2. Change Fan Control Settings
If your PC overheats or struggles with heat dissipation (which is most noteably a problem with laptops), one effective solution is to increase the fan speed. Conversely, reducing the fan speed can prolong its lifespan. Since Windows lacks built-in options to control fan speed, users often turn to third-party software. If you don't want to go that route, you can adjust fan speed in BIOS.
Enter the BIOS setup, and locate the hardware monitoring section, which might be named "Hardware Monitor," "PC Health Status," "Fan Control," or similar. Within this section, go to the fan control settings. Here, choose from predefined fan profiles like "Silent," "Standard," "Turbo," or more. You can also manually control the fan curve.
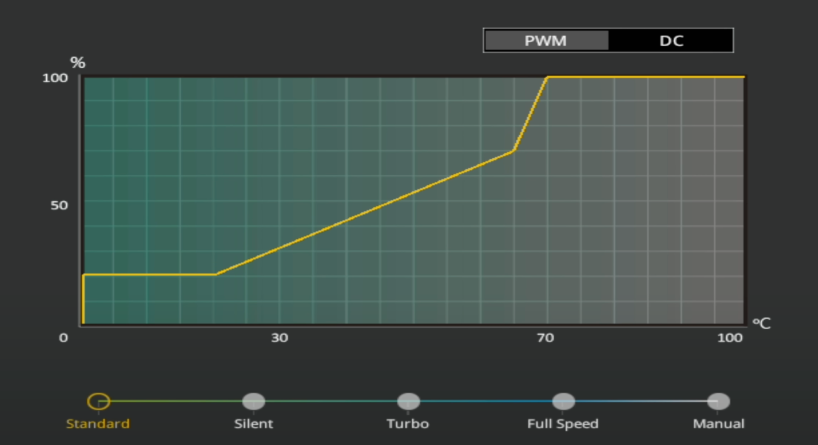
Not all manufacturers include fan control options in their BIOS settings, particularly on laptops. Desktop computers typically offer more flexibility in fan speed management.
3 3. Change the Boot Order
The boot order refers to the sequence in which a BIOS or UEFI searches for a bootable operating system during startup. If multiple storage devices are installed and your primary operating system resides on a lower-priority drive, your computer might expend unnecessary effort searching for a bootable OS on other drives.
To optimize boot time and minimize the risk of encountering boot errors, you should prioritize your primary operating system at the top of the boot order list in BIOS settings. To modify the boot order, open BIOS and go to the "Boot" section. If your primary OS drive isn't already at the top of the boot order, make sure to select it as the first boot option.
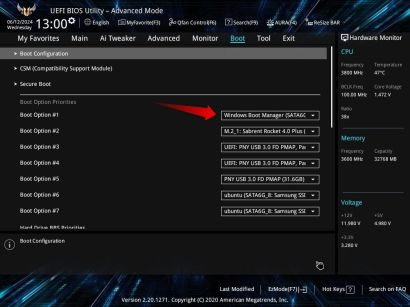
After you've made these adjustments, save the changes, exit BIOS, and restart your computer. You may experience a noticeable improvement in boot time.
Even if you don't get a performance improvement, changing your boot order to include a Windows recovery USB or other utility programs is an important part of troubleshooting a malfunctioning PC.
4 4. Overclock Your RAM
Although you can adjust other parameters, overclocking RAM primarily involves increasing data transfer rates and refining timings to enhance overall device performance, especially for tasks that require substantial memory usage. These adjustments reduce latency, which makes applications more responsive and snappy.
To overclock your RAM, open the BIOS and navigate to the memory or overclocking section. Manual RAM overclocking lets you adjust memory frequency, timings, and voltage settings. However, it demands caution, as improper configuration can cause system instability or even damage your hardware, though that is very unlikely.
To mitigate these risks, you can use pre-configured profiles such as XMP (for Intel systems) or DOCP or AMP (for AMD systems), which provide safe overclocking options. The preset overclocking options available through XMP, DOCP, or AMP are usually pretty stable, but there are no guarantees that every specific setting will work with every hardware configuration.
5 5. Disable the Unused Integrated Peripherals
Turning off unused integrated peripherals through the BIOS can yield several benefits. For instance, disabling onboard audio when using a dedicated sound card can prevent conflicts between audio devices and improve audio performance. This doesn't just apply to sound cards—dedicated and integrated hardware trying to do the same thing usually increases the chances of bugs occurring.
Likewise, deactivating other peripherals, such as unused RAID controllers and ports, can reduce power consumption and potentially improve system stability.
To implement these adjustments, navigate to the BIOS and locate the section labeled "Integrated Peripherals," "Onboard Devices," or "Advanced." Within this section, turn off the peripherals that are not in use. However, don't turn off integrated peripherals unless you're certain you have a dedicated alternative installed in your system. Otherwise, you may encounter problems with any programs that require that hardware to work. More importantly, disabling something essential will lead to system instability.
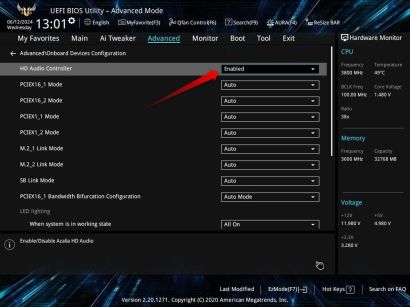
6 6. Optimize CPU Performance
Most manufacturers, particularly in desktop computers, offer BIOS settings that can improve CPU performance. Features like Hyper-Threading, which enables CPU cores to handle two threads simultaneously, boost performance in multi-threaded applications such as video editing and rendering.
Similarly, Turbo Boost (for Intel CPUs) and Precision Boost (for AMD CPUs) raise the CPU's clock speed beyond its base frequencies, ensuring it can meet processing demands as they escalate. Some manufacturers offer additional features to maximize CPU performance when processing demands increase.
However, these features typically increase power consumption. Disabling them, if unnecessary, can help reduce power usage. Conversely, you can enable them if you want better performance. To turn these features on or off, access the BIOS settings and navigate to the "Advanced," "CPU Configuration," "Performance," or a similar tab.

Adjust the settings according to your requirements. Once configured, remember to save the changes and exit the BIOS.
These settings can boost your system's performance and stability. But remember, tweaking the BIOS can be risky if you're not experienced. Making the wrong changes could even make your device unbootable. Only adjust settings you're familiar with and are sure will not cause any problems for your system.
If in doubt, it's best to leave them alone or seek advice from someone who knows their way around BIOS settings.
The above is the detailed content of Your Computer BIOS Is Full of Settings, But Which Should You Actually Change?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Fedora 42 Joins the Windows Subsystem for LinuxMay 09, 2025 am 03:01 AM
Fedora 42 Joins the Windows Subsystem for LinuxMay 09, 2025 am 03:01 AMPushing the boundaries of Linux: exploring unusual applications. Purely for fun, of course. Posts 7 Technically, you can create a WSL image for any compatible Linux distribution. However, officially supported images offer a significantly smoother e
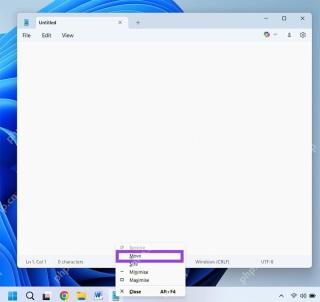 How to Move a Window When You Can't Click on the Title BarMay 09, 2025 am 01:03 AM
How to Move a Window When You Can't Click on the Title BarMay 09, 2025 am 01:03 AMWhen applications unexpectedly extend beyond your screen's edges, accessing their title bars becomes impossible. This is especially common with dual monitors but can occur on single displays as well. This guide offers solutions for regaining control
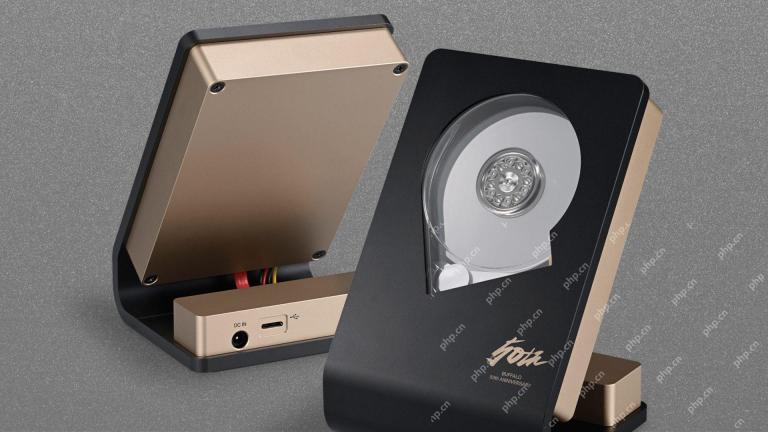 This Limited-Edition 'Skeleton” HDD Shows You How It Writes BytesMay 08, 2025 pm 09:04 PM
This Limited-Edition 'Skeleton” HDD Shows You How It Writes BytesMay 08, 2025 pm 09:04 PMThe HD-SKL, a limited-edition hard drive, is a modern take on Buffalo's 1998 Skeleton Hard Disk. The original, a 4.3GB drive with a clear acrylic case, was produced in a limited run of 500 units. While Buffalo cites its 1978 Melco 3533 turntable as
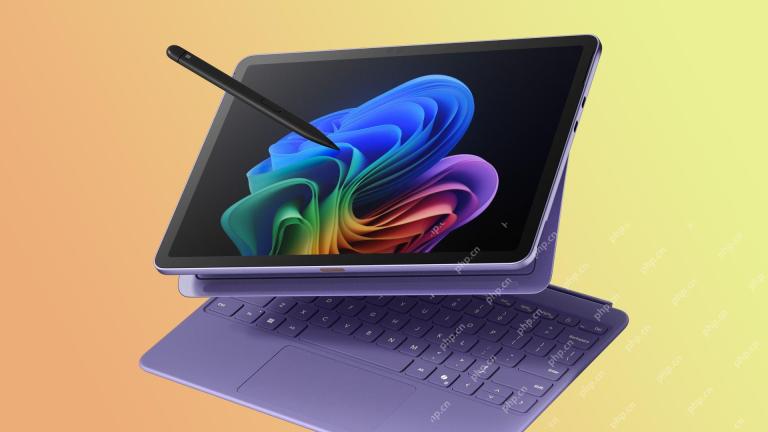 The New Surface Pro Doesn't Feel ProMay 08, 2025 am 06:01 AM
The New Surface Pro Doesn't Feel ProMay 08, 2025 am 06:01 AMThe new Surface Pro: A step back? Microsoft's latest Surface Pro offers connectivity via two USB-C ports, supporting charging, USB 3.2 data transfer, and DisplayPort 1.4a (up to two 4K monitors at 60Hz). However, the device ships without a power ad
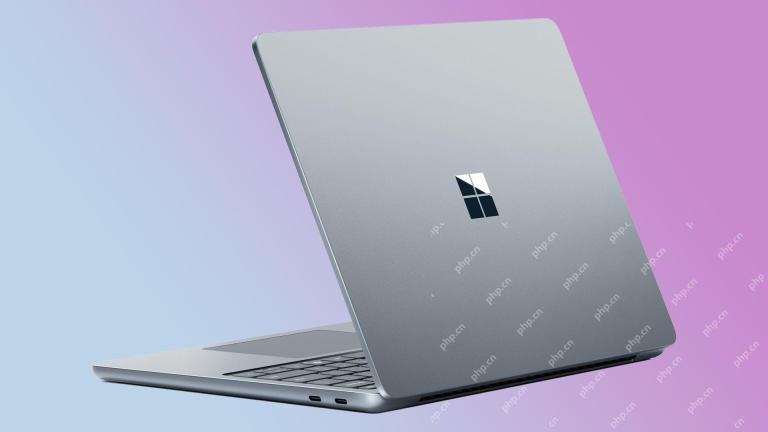 Microsoft Challenges the MacBook Air With New Surface LaptopMay 08, 2025 am 03:02 AM
Microsoft Challenges the MacBook Air With New Surface LaptopMay 08, 2025 am 03:02 AMMicrosoft's latest Surface Laptop aims to rival the MacBook Air, but with some notable compromises. The absence of a Surface Connect port marks a significant departure from previous models, reflecting the growing prevalence of Thunderbolt and USB do
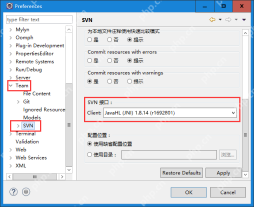 Solve the problem that the svn plugin in eclipse always prompts for password inputMay 07, 2025 pm 05:03 PM
Solve the problem that the svn plugin in eclipse always prompts for password inputMay 07, 2025 pm 05:03 PM1. Background Recently, when using the svn plug-in to manage remote warehouse code in eclipse, prompts to enter passwords are always prompted to enter passwords, which is particularly annoying. After hard work, I finally solved the problem and shared it with you~ 2. Analysis of the password mechanism of the svn plug-in and the cause of the problem. When we use the svn plug-in for the first time and enter the password, a file that saves the password will be generated, and then the svn plug-in will read the username and password information by default every time. When eclipse is started, the configuration information will be automatically read into the program cache. After the password of svn is modified, it is impossible to log in again, and there is no prompt to re-enter the password. At this time, we can delete the relevant configuration files and let the svn plugin prompt us to re-enter the password. However, ec
 How to restore the win8 system details stepsMay 07, 2025 pm 05:00 PM
How to restore the win8 system details stepsMay 07, 2025 pm 05:00 PMThe steps to start system restore in Windows 8 are: 1. Press the Windows key X to open the shortcut menu; 2. Select "Control Panel", enter "System and Security", and click "System"; 3. Select "System Protection", and click "System Restore"; 4. Enter the administrator password and select the restore point. When selecting the appropriate restore point, it is recommended to select the restore point before the problem occurs, or remember a specific date when the system is running well. During the system restore process, if you encounter "The system restore cannot be completed", you can try another restore point or use the "sfc/scannow" command to repair the system files. After restoring, you need to check the system operation status, reinstall or configure the software, and re-back up the data, and create new restore points regularly.
 'Modern Operating System Original Book 3rd Edition'May 07, 2025 pm 04:57 PM
'Modern Operating System Original Book 3rd Edition'May 07, 2025 pm 04:57 PM"Modern Operating Systems (English Edition 3rd Edition)" is a classic work written by Professor Tanenbaum. With his profound experience in the design of three operating systems, the book perfectly integrates theory and practice. The third edition of the book explores a number of topics in depth, such as process, threading, storage management, file systems, I/O deadlock, interface design, multimedia, performance trade-offs, and introduces the latest trends in operating system design. The book not only explains the principles and practices of modern operating systems in detail, but also pays special attention to Linux operating systems, Windows Vista operating systems, embedded operating systems, real-time operating systems and multimedia operating systems. Covering Windows Vista and the latest Linux/Unix operations


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.






