Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Efficient and accurate, Zhengzhou University team develops new AI tool to identify drug-target interactions
Efficient and accurate, Zhengzhou University team develops new AI tool to identify drug-target interactions
Accurate identification of drug-target interactions (DTIs) is one of the key steps in the drug discovery and drug repositioning process.
Currently, many computational-based models have been proposed for predicting DTI, and some significant progress has been achieved.
However, these methods rarely focus on how to fuse multi-view similarity networks related to drugs and targets in an appropriate manner. Furthermore, how to fully incorporate known interaction relationships to accurately represent drugs and targets has not been well studied. Therefore, improving the accuracy of DTI prediction models remains necessary.
In the latest research, teams from Zhengzhou University and University of Electronic Science and Technology of China proposed a new method, MIDTI. This method adopts a multi-view similarity network fusion strategy and a deep interactive attention mechanism to predict drug-target interactions.
The results show that MIDTI performs significantly better than other baseline methods on the DTI prediction task. The results of the ablation experiment also confirm the effectiveness of the attention mechanism and the deep interactive attention mechanism in the multi-view similarity network fusion strategy.
The study is titled "Drug–target interaction predictions with multi-view similarity network fusion strategy and deep interactive attention mechanism" and was published in "Bioinformatics" on June 6, 2024.

occupies a core position in the process of new drug development and reuse. Traditional wet experiment methods are costly and time-consuming, prompting researchers to turn to computationally assisted drug screening methods. Speed up the process.
Computational DTI prediction methods
are mainly divided into:
- Structure-based methods: Rely on drug molecules and target structures and binding sites, but are limited by structural information of certain targets such as membrane proteins lack of.
- Ligand-based method: Build a model based on known active small molecules, but it does not work well when the number of target binding ligands is limited.
- Machine learning-based method: Predict potential DTI by extracting drug chemical structure and target gene sequence features for binary classification.
Limitations of machine learning methods
Current methods only learn representations based on the structure of the drug and target itself, ignoring the interaction between DTI pairs.
Heterogeneous network construction
The relationships between biological entities contain rich semantic information. Building a network that integrates heterogeneous information helps the system understand DTI.
MIDTI method
The Zhengzhou University team proposed MIDTI, a new method for predicting DTI, based on:
- Multi-view similarity network fusion strategy
- Deep interactive attention mechanism
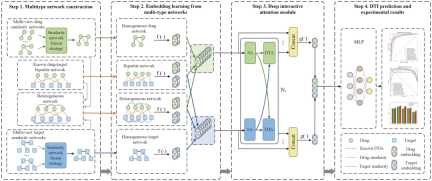
MIDTI as a whole Framework
Illustration: The overall framework of MIDTI (Source: paper)
Steps:
- Building a similarity network: MIDTI builds a drug similarity network based on drug association information and adopts a fusion strategy Obtain an integrated drug similarity network; similarly build an integrated target similarity network.
- Learning embeddings: MIDTI adopts GCN to learn drug and target embeddings from integrated drug similarity networks, integrated target similarity networks, drug-target bipartite networks, and drug-target heterogeneous networks.
- Discriminative embedding: MIDTI utilizes an interactive attention mechanism to learn discriminative embeddings based on known DTI relationships.
-
Predict DTI: The learned drug-target pair representations are fed into the MLP to predict DTI.
Illustration: Four steps of multi-perspective drug similarity network fusion strategy. (Source: paper)
To evaluate the performance of MIDTI, researchers used a variety of evaluation metrics, including accuracy (ACC), area under the curve (AUC), area under the precision-recall curve (AUPR), F1 score and Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC). The researchers compared MIDTI with ten other competing methods, including random forests, graph convolutional networks, graph attention networks, MMGCN, GraphCDA, and DTINet, among others.
MIDTI achieved scores of 0.9340, 0.9787, and 0.9701 on the ACC, AUC, and AUPR metrics, respectively, which are 2.55%, 2.31%, and 2.30% higher than the highest scores of MMGCN and GraphCDA. This indicates that MIDTI is one of the most competitive methods in predicting drug-target interactions. In experiments with different positive and negative sample ratios, MIDTI also showed excellent performance.
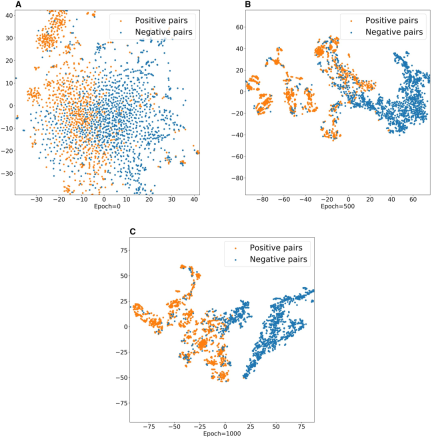
The study also shows the visualization results of the drug-target embeddings learned by MIDTI, using the t-SNE tool to map the embeddings into two-dimensional space. As the number of training rounds increases, positive examples and negative examples are gradually distinguished, which proves that the embeddings learned by MIDTI have good discriminability and interpretability, thereby improving the accuracy of DTI predictions.
The core contribution of MIDTI is:
- It proposes a new multi-view similar network fusion strategy that can integrate different similar networks in an unsupervised manner;
- Using a deep interactive attention mechanism, based on known DTI information learns discriminative representations of drugs and targets;
- A large number of experiments prove that MIDTI outperforms other advanced methods in DTI prediction tasks.
In short, MIDTI is an efficient and accurate drug-target interaction prediction method. Its innovation lies in the use of multi-view information and deep attention mechanisms to enhance prediction capabilities.
The researchers said that the next work will be carried out in the following two aspects. First, embedding learning is performed using other relevant data sources of drugs and targets. Second, MIDTI can be applied to other link prediction problems, such as miRNA-disease association prediction.
Related reports: https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/40/6/btae346/7688335
The above is the detailed content of Efficient and accurate, Zhengzhou University team develops new AI tool to identify drug-target interactions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:30 PM
2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:30 PM机器学习是一个不断发展的学科,一直在创造新的想法和技术。本文罗列了2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术。 本文罗列了2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术。2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术是一个教计算机从数据中学习的过程,无需明确的编程。机器学习是一个不断发展的学科,一直在创造新的想法和技术。为了保持领先,数据科学家应该关注其中一些网站,以跟上最新的发展。这将有助于了解机器学习中的技术如何在实践中使用,并为自己的业务或工作领域中的可能应用提供想法。2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术:1. 深度神经网
 人工智能自动获取知识和技能,实现自我完善的过程是什么Aug 24, 2022 am 11:57 AM
人工智能自动获取知识和技能,实现自我完善的过程是什么Aug 24, 2022 am 11:57 AM实现自我完善的过程是“机器学习”。机器学习是人工智能核心,是使计算机具有智能的根本途径;它使计算机能模拟人的学习行为,自动地通过学习来获取知识和技能,不断改善性能,实现自我完善。机器学习主要研究三方面问题:1、学习机理,人类获取知识、技能和抽象概念的天赋能力;2、学习方法,对生物学习机理进行简化的基础上,用计算的方法进行再现;3、学习系统,能够在一定程度上实现机器学习的系统。
 超参数优化比较之网格搜索、随机搜索和贝叶斯优化Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:05 PM
超参数优化比较之网格搜索、随机搜索和贝叶斯优化Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:05 PM本文将详细介绍用来提高机器学习效果的最常见的超参数优化方法。 译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟简介通常,在尝试改进机器学习模型时,人们首先想到的解决方案是添加更多的训练数据。额外的数据通常是有帮助(在某些情况下除外)的,但生成高质量的数据可能非常昂贵。通过使用现有数据获得最佳模型性能,超参数优化可以节省我们的时间和资源。顾名思义,超参数优化是为机器学习模型确定最佳超参数组合以满足优化函数(即,给定研究中的数据集,最大化模型的性能)的过程。换句话说,每个模型都会提供多个有关选项的调整“按钮
 得益于OpenAI技术,微软必应的搜索流量超过谷歌Mar 31, 2023 pm 10:38 PM
得益于OpenAI技术,微软必应的搜索流量超过谷歌Mar 31, 2023 pm 10:38 PM截至3月20日的数据显示,自微软2月7日推出其人工智能版本以来,必应搜索引擎的页面访问量增加了15.8%,而Alphabet旗下的谷歌搜索引擎则下降了近1%。 3月23日消息,外媒报道称,分析公司Similarweb的数据显示,在整合了OpenAI的技术后,微软旗下的必应在页面访问量方面实现了更多的增长。截至3月20日的数据显示,自微软2月7日推出其人工智能版本以来,必应搜索引擎的页面访问量增加了15.8%,而Alphabet旗下的谷歌搜索引擎则下降了近1%。这些数据是微软在与谷歌争夺生
 荣耀的人工智能助手叫什么名字Sep 06, 2022 pm 03:31 PM
荣耀的人工智能助手叫什么名字Sep 06, 2022 pm 03:31 PM荣耀的人工智能助手叫“YOYO”,也即悠悠;YOYO除了能够实现语音操控等基本功能之外,还拥有智慧视觉、智慧识屏、情景智能、智慧搜索等功能,可以在系统设置页面中的智慧助手里进行相关的设置。
 人工智能在教育领域的应用主要有哪些Dec 14, 2020 pm 05:08 PM
人工智能在教育领域的应用主要有哪些Dec 14, 2020 pm 05:08 PM人工智能在教育领域的应用主要有个性化学习、虚拟导师、教育机器人和场景式教育。人工智能在教育领域的应用目前还处于早期探索阶段,但是潜力却是巨大的。
 30行Python代码就可以调用ChatGPT API总结论文的主要内容Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:05 PM
30行Python代码就可以调用ChatGPT API总结论文的主要内容Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:05 PM阅读论文可以说是我们的日常工作之一,论文的数量太多,我们如何快速阅读归纳呢?自从ChatGPT出现以后,有很多阅读论文的服务可以使用。其实使用ChatGPT API非常简单,我们只用30行python代码就可以在本地搭建一个自己的应用。 阅读论文可以说是我们的日常工作之一,论文的数量太多,我们如何快速阅读归纳呢?自从ChatGPT出现以后,有很多阅读论文的服务可以使用。其实使用ChatGPT API非常简单,我们只用30行python代码就可以在本地搭建一个自己的应用。使用 Python 和 C
 人工智能在生活中的应用有哪些Jul 20, 2022 pm 04:47 PM
人工智能在生活中的应用有哪些Jul 20, 2022 pm 04:47 PM人工智能在生活中的应用有:1、虚拟个人助理,使用者可通过声控、文字输入的方式,来完成一些日常生活的小事;2、语音评测,利用云计算技术,将自动口语评测服务放在云端,并开放API接口供客户远程使用;3、无人汽车,主要依靠车内的以计算机系统为主的智能驾驶仪来实现无人驾驶的目标;4、天气预测,通过手机GPRS系统,定位到用户所处的位置,在利用算法,对覆盖全国的雷达图进行数据分析并预测。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.