Jack Mallers, Founder and CEO of Bitcoin startup Strike, began his keynote at BTC Prague 2024 by emphasizing the theme of leveling up the understanding of Bitcoin.

At BTC Prague 2024, Jack Mallers, Founder and CEO of Bitcoin startup Strike, opened his keynote with a strong emphasis on the need to elevate the understanding of Bitcoin.
Mallers acknowledged the common questions about the differences between Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum and Solana, and the possibility of a “flippening” where another cryptocurrency might surpass Bitcoin. Countering this narrative, Mallers titled his talk “There Is No Second Best,” aiming to deeply explore the stark disparities between Bitcoin and all other cryptocurrencies.
Throughout his talk, Mallers highlighted the primary differentiator between Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies: the use of proof of work. According to Mallers, Bitcoin is the only major cryptocurrency that utilizes proof of work, a consensus mechanism critical for ensuring trust and security without relying on a trusted third party. Mallers attributed the importance of proof of work to Satoshi Nakamoto, who stated that it is the only solution to making peer-to-peer e-cash work without a trusted third party.
To understand Bitcoin, Mallers emphasized the need to understand proof of work. He proceeded to describe the digital age we live in, where virtual representations of reality are not reality itself but abstractions. Mallers used the analogy of a map and territory to explain that digital tools can map our world and offer new perspectives but ultimately remain tools, not substitutes for the world they represent.
Delving deeper into the concept of abstraction, Mallers explained that computers and digital technologies are essentially abstractions of our minds, reflecting back the significance we assign to circuits. He compared the execution of a computer program to an actor performing a script, underscoring that the hardware and computations are real, but the experiences created are abstract. Mallers went on to highlight that nothing in cyberspace physically exists; instead, digital objects are abstractions that can be manipulated.
To further illustrate the concept of abstract power in the digital age, Mallers used the example of Mark Zuckerberg. He explained that while Zuckerberg has no physical power over individuals, he wields significant abstract power through social media, influencing thoughts, actions, and relationships. Mallers contrasted abstract power with physical power, which is tangible and bound by the laws of physics, such as military force or physical assets like gold.
Shifting his focus to monetary systems, Mallers described the transition of the US dollar from the gold standard (a physical constraint) to a fiat standard (an abstracted reality). He highlighted how abstract power can be efficient and safe but lacks physical boundaries and ultimately requires trust. However, Mallers noted that breaches of trust have occurred throughout history, making abstract power potentially exploitative.
In his talk, Mallers also mentioned Adam Back, who notably created hash cash to address the problem of email spam by requiring proof of work, thereby imposing physical costs on virtual actions. Mallers emphasized that proof of work is what connects the physical world to the virtual realm, making it the only physically real thing on a digital screen. He explained that Satoshi Nakamoto used proof of work to create Bitcoin, ensuring that updating the Bitcoin ledger would require solving a hash cost function, thus protecting digital cash with physical power.
Mallers concluded his talk by detailing how proof of work is inclusive, decentralized, and verifiable, providing a safe and peaceful means of protecting Bitcoin. He contrasted this with proof of stake, which he argued is based on an abstracted reality, lacking the physical constraints that make Bitcoin secure.
In a compelling move, Mallers played a video of Vitalik Buterin, the creator of Ethereum, describing proof of stake as a system that allows for creating a simulated universe with its own laws of physics. Mallers used this statement to highlight his critique of proof of stake, arguing that it detaches the cryptocurrency from physical reality and subjects it to abstract power dynamics.
Countering the narrative of altcoins being superior to Bitcoin, Mallers argued that Ethereum and other altcoins, which do not use proof of work, are not bound to physical reality and are therefore susceptible to manipulation by entities like BlackRock. He asserted that Bitcoin’s proof of work ensures that it can be defended by honest actors using physical power, whereas proof of stake systems rely on trusting those with the most coins.
To further drive home his point, Mallers highlighted the pre-mining of Ethereum and the rule changes that concentrated power among a select few, contrasting it with Bitcoin’s equitable and fair nature. He argued that altcoins often alter their monetary policies and even have the capability to reverse transactions, ultimately undermining their credibility.
In closing, Mallers emphasized the importance of educating people about the distinctions between Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. He reiterated that understanding Bitcoin means understanding proof of work and declared that there is no second best in the world of cryptocurrencies.
News source:https://www.kdj.com/cryptocurrencies-news/articles/understanding-bitcoin-proof.html
The above is the detailed content of There Is No Second Best: Understanding Bitcoin\'s Proof of Work. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 FloppyPepe (FPPE) Price Could Explode As Bitcoin (BTC) Price Rallies Towards $450,000May 09, 2025 am 11:54 AM
FloppyPepe (FPPE) Price Could Explode As Bitcoin (BTC) Price Rallies Towards $450,000May 09, 2025 am 11:54 AMAccording to a leading finance CEO, the Bitcoin price could be set for a move to $450,000. This Bitcoin price projection comes after a resurgence of good performances, signaling that the bear market may end.
 Pi Network Confirms May 14 Launch—Qubetics and OKB Surge as Best Cryptos to Join for Long Term in 2025May 09, 2025 am 11:52 AM
Pi Network Confirms May 14 Launch—Qubetics and OKB Surge as Best Cryptos to Join for Long Term in 2025May 09, 2025 am 11:52 AMExplore why Qubetics, Pi Network, and OKB rank among the Best Cryptos to Join for Long Term. Get updated presale stats, features, and key real-world use cases.
 Sun Life Financial Inc. (TSX: SLF) (NYSE: SLF) Declares a Dividend of $0.88 Per ShareMay 09, 2025 am 11:50 AM
Sun Life Financial Inc. (TSX: SLF) (NYSE: SLF) Declares a Dividend of $0.88 Per ShareMay 09, 2025 am 11:50 AMTORONTO, May 8, 2025 /CNW/ - The Board of Directors (the "Board") of Sun Life Financial Inc. (the "Company") (TSX: SLF) (NYSE: SLF) today announced that a dividend of $0.88 per share on the common shares of the Company has been de
 Sun Life Announces Intended Renewal of Normal Course Issuer BidMay 09, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Sun Life Announces Intended Renewal of Normal Course Issuer BidMay 09, 2025 am 11:48 AMMay 7, 2025, the Company had purchased on the TSX, other Canadian stock exchanges and/or alternative Canadian trading platforms
 The Bitcoin price has hit $100k for the first time since February, trading at $101.3k at press time.May 09, 2025 am 11:46 AM
The Bitcoin price has hit $100k for the first time since February, trading at $101.3k at press time.May 09, 2025 am 11:46 AMBTC's strong correlation with the Global M2 money supply is playing out once again, with the largest cryptocurrency now poised for new all-time highs.
 Coinbase (COIN) Q1 CY2025 Highlights: Revenue Falls Short of Expectations, but Sales Rose 24.2% YoY to $2.03BMay 09, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Coinbase (COIN) Q1 CY2025 Highlights: Revenue Falls Short of Expectations, but Sales Rose 24.2% YoY to $2.03BMay 09, 2025 am 11:44 AMBlockchain infrastructure company Coinbase (NASDAQ: COIN) fell short of the market’s revenue expectations in Q1 CY2025, but sales rose 24.2% year
 Ripple Labs and the SEC Have Officially Reached a Settlement AgreementMay 09, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Ripple Labs and the SEC Have Officially Reached a Settlement AgreementMay 09, 2025 am 11:42 AMRipple Labs and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) have officially reached a deal that, if approved by a judge, will bring their years-long legal battle to a close.
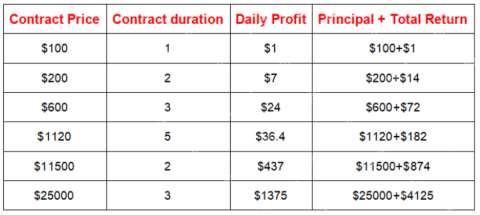 JA Mining Helps Global Users Share the Benefits of the Bitcoin Bull MarketMay 09, 2025 am 11:40 AM
JA Mining Helps Global Users Share the Benefits of the Bitcoin Bull MarketMay 09, 2025 am 11:40 AMBy lowering the threshold for mining and providing compliance protection, JA Mining helps global users share the benefits of the Bitcoin bull market.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.






