Compiled by: Weird Thinking, BlockBeats
Translator’s Note: In March this year, 0G Labs completed a $35 million Pre-Seed investment led by Hack VC round of financing. 0G Labs aims to build the first modular AI chain to help developers launch AI dApps on a high-performance, programmable data availability layer. Through innovative system design, 0G Labs strives to achieve GB-level on-chain data transmission per second and support high-performance application scenarios such as AI model training.
In the fourth episode of the DealFlow podcast, BSCN Editor-in-Chief Jonny Huang, MH Ventures General Partner Kamran Iqbal, and Animoca Brands Head of Investment and Strategic Partnerships Mehdi Farooq jointly interviewed Michael, co-founder and CEO of 0G Labs Heinrich. Michael shared his personal background, from being a software engineer at Microsoft and SAP Labs to founding Garten, a Web2 company valued at over US$1 billion, to now working full-time on 0G, dedicated to building a modular AI technology stack on the blockchain. . The discussion covered the current status and vision of DA, the benefits of modularity, team management, and the bidirectional dependency of Web3 on AI. Looking to the future, he emphasized that AI will become mainstream and bring about huge social changes, and Web3 needs to keep up with this trend.
The following is the text of the interview:
Web2 Unicorn Head Starts Business Again
Jonny : Today we are going to delve into an important topic - data availability (DA), especially in the field of encrypted AI. Michael, your company has a strong voice in this area. Before going into the details, could you briefly introduce your professional background and how you got into this niche field.
Michael: I started out as a software engineer and technical product manager at Microsoft and SAP Labs, working on cutting-edge technologies on the Visual Studio team. Later, he turned to the business side and worked at Bain & Company for a few years. He then moved to Connecticut to work for Bridgewater Associates, responsible for portfolio construction. Reviewing approximately $60 billion in transactions every day, there are many risk indicators to understand. For example, we look at CDS rates to assess counterparty risk, etc. This experience gave me an in-depth understanding of traditional finance.
After that, I returned to Stanford for graduate school and founded my first Web2 company, Garten. At its peak, the company once expanded to 650 employees, with annual revenue reaching US$100 million and total financing of approximately US$130 million. It became a unicorn company with a valuation of over US$1 billion and a star project incubated by Y Combinator.
At the end of 2022, my classmate Thomas at Stanford contacted me. He mentioned that he invested in Conflux five years ago and thought that Ming Wu and Fan Long were the best engineers he had ever funded. The four of us should get together and see if we could create any sparks. After six months together, I came to the same conclusion. I thought to myself, "Wow, Ming and Fan are the best engineers and computer scientists I've ever worked with. We've got to start a business together." I became chairman of Garten and committed to 0G full time.

0 The four co-founders of G Labs, from left to right, are Fan Long, Thomas Yao, Michael Heinrich, and Ming Wu
DA’s current situation, challenges and ultimate goals
Jonny: This is one of the best founder introductions I have ever heard, and I guess your VC financing process It must be going well. Before I dive into the topic of data availability, I want to discuss the current state of DA. While there are some players that are well known, how do you assess the DA landscape as it stands?
Michael: DA now comes from multiple sources, depending on the blockchain. For example, before the Ethereum Danksharding upgrade, Ethereum’s DA was approximately 0.08 MB per second. Later, Celestia, EigenDA, and Avail entered the market, with throughput typically ranging from 1.2 to 10 MB per second. The problem is that this throughput is nowhere near enough for AI applications or any on-chain gaming applications. We need to talk about DA in gigabytes per second, not MB per second. For example, if you wanted to train an AI model on-chain, you would actually need 50 to 100 GB of data transfer per second to do that. This is an order of magnitude difference. We saw this opportunity and thought about how to create this breakthrough so that large-scale applications for Web2 can be built on-chain with the same performance and cost. This is a huge void that we see in the field. In addition, there are some issues that have not been fully considered. For example, we think of data availability as a combination of data publishing and data storage. Our core insight is to achieve breakthrough performance improvements by splitting data into these two channels to avoid broadcast bottlenecks in the system.
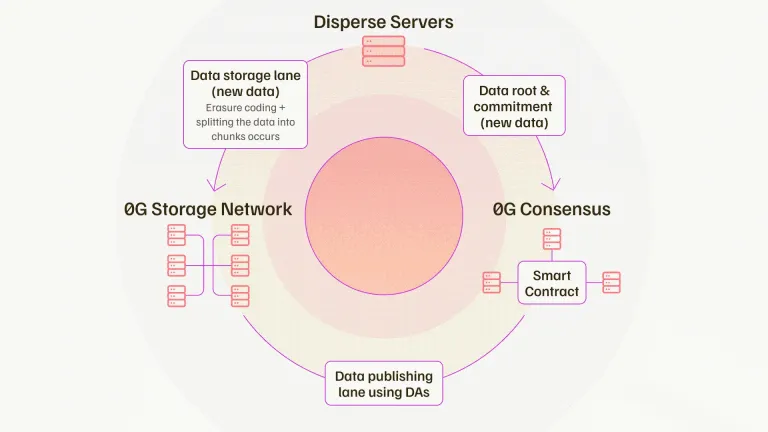
An additional storage network allows you to do many things, such as model storage, training data storage for specific use cases, and even programmability. You can do complete state management, deciding where to store data, how long to store it, and how much security is required. Therefore, real-world use cases that are really needed in various fields are now possible.
The current status of DA is that we have made significant progress from 0.08 MB per second to 1.4 MB, which has indeed reduced transaction costs, in some cases even by 99%. But this is not enough for the real needs of the future world. High-performance AI applications, on-chain games, high-frequency DeFi, all of these applications require higher throughput.
Mehdi: I have two fundamental questions. The first is about storage. You mentioned L2's transaction history and even the history of the AI model. In terms of storage, how long do we need to store the data? This is my first question. The second question is, there are already decentralized storage networks like Arweave and Filecoin, do you think they can help improve throughput? I don't mean data publishing, but storage.
Michael: How long data is stored depends on its purpose. If disaster recovery is considered, data should be stored permanently so that the state can be reconstructed. For optimistic rollups, where there is a fraud-proof window, at least 7 days of storage is required to allow the state to be reconstructed if needed. For other types of rollups, the storage time may be shorter. The specifics vary, but that's generally the case.
As for other storage platforms, we chose to build the storage system in-house because Arweave and Filecoin are more designed for log-type storage, that is, long-term cold storage. Therefore they are not designed for very fast data writing and reading, which is critical for AI applications and structured data applications that require key-value stores or transactional data types. In this way, fast processing can be achieved, and a decentralized Google Docs application can even be built.
Jonny: You are very clear on why DA is needed and why existing decentralized storage solutions are not suitable for this specific scenario. Can you discuss the ultimate goal of data availability?
Michael: The ultimate goal is easy to define. What we want to achieve is performance and cost comparable to Web2, making it possible to build anything on the chain, especially AI application. It's straightforward, just like AWS has compute and storage, S3 is a key component. Data availability, although it has different characteristics, is also a critical component. Our ultimate goal is to build a modular AI technology stack where the data availability part includes not only data publishing but also storage components, consolidated by a consensus network. We let the consensus network handle data availability sampling, and once consensus is reached, we can prove it on the underlying Layer 1 (like Ethereum). Our ultimate goal is to build an on-chain system that can run any high-performance application and even support on-chain training of AI models.
Kamran: Can you elaborate a little more on your target market? Besides artificial intelligence and those building AI applications on the blockchain, which projects do you hope to use 0G?
Michael: You have already mentioned an application field. We are working hard to build the largest decentralized AI community and hope to have a large number of projects built on top of us. Whether Pond is building a large graph model, Fraction AI or PublicAI is doing decentralized data annotation or cleaning, or even execution layer projects like Allora, Talus Network or Ritual, we are working hard to build the largest community for AI builders . This is a basic requirement for us.
But really, any high-performance application can be built on top of us. Taking on-chain games as an example, 5,000 users require 16MB of data availability per second to achieve a complete on-chain game state without compression. No DA layer currently can do this, maybe Solana can, but that’s not the same as the Ethereum ecosystem and support is limited. So, such applications are also very interesting for us, especially if they are combined with on-chain AI agents (such as NPCs). There is a lot of potential for cross-application in this area.
High-frequency DeFi is another example. Future fully homomorphic encryption (FHE), data markets, and high-frequency deep-end applications all require very large data throughput and require a DA layer that can truly support high performance. Therefore, any high-performance DA app or Layer2 can be built on top of us.
Advantages of Modularity: Flexible Choice
Mehdi: You are working hard to improve scalability, throughput, and solve the problem of state expansion caused by storage components. Why not just launch a complete Layer1? If you have the ability to achieve a technological breakthrough, why take a modular approach instead of creating a Layer1 with its own virtual machine? What is the logic behind adopting a modular stack?
Michael: Fundamentally speaking, our bottom layer is Layer 1, but we firmly believe that modularization is the way to build applications in the future. And we are modular and do not rule out providing an execution environment specifically optimized for AI applications in the future. We're not quite sure of the roadmap for this yet, but it's possible.
The core of modularity is choice. You can choose the settlement layer, execution environment and DA layer. Depending on the use case, developers can choose the best solution. Just like in Web2, TCP/IP succeeded because it was modular in nature and developers were free to use different aspects of it as they chose. Therefore, we hope to give developers more choices so that they can build the most suitable environment according to their application types.
Mehdi : If you were to choose a virtual machine right now, which virtual machine on the market would be the best fit for the application you are considering or working toward?
Michael: I take a very practical view on this. If it were to attract more Web2 developers to Web3, it would be some type of WASM virtual machine that could build applications in the most common programming languages like JavaScript or Python. These languages are not necessarily the best choices for on-chain development.
Move VM is designed very well in terms of objects and throughput. If you're after high performance, this is an option worth paying attention to. If you think about a battle-tested virtual machine, it's E VM because of the large number of Solidity developers. So the choice depends on the specific usage scenario.
Prioritization and Community Building
Jonny: I want to hear what the biggest obstacles you guys faced, or was it all smooth sailing? I can't imagine that your career is so huge and it can't always be so smooth.
Michael: Yes, I think any startup will not be smooth sailing and there will always be some challenges. The biggest challenge from my perspective is making sure we can keep up because we have to perform multiple tasks very well and have to make some trade-offs to get to market quickly.
For example, we originally wanted to launch with a customized consensus mechanism, but that would extend the launch time by four to five months. So we decided to use an off-the-shelf consensus mechanism in the first phase to do a strong proof of concept and achieve part of the end goal, such as 50 GB per second per consensus layer. A horizontally scalable consensus layer is then introduced in the second phase to achieve unlimited DA throughput. Just like turning on a switch to spin up another AWS server, we can add additional consensus layers, thereby increasing overall DA throughput.
Another challenge is ensuring we attract top talent to the company. Our team is strong, including Informatics Olympiad gold medalists and top computer science Ph.D.s, so we need our marketing team and new developers to match that.
Jonny : It sounds like the biggest hurdle you guys are facing right now is prioritization, right? Accept that you can't do everything in a short period of time and that some trade-offs have to be made. What do you think about competition? I'm guessing Celestia or EigenDA don't pose a serious threat to your specific use case.
Michael: In Web3, competition largely depends on the community. We've built a strong community around high-performance and AI builders, whereas Celestia and EigenDA probably have more general-purpose communities. EigenDA is probably more concerned about bringing economic security and building AVS on EigenLayer, while Celestia is more concerned about which Layer2 wants to reduce their transaction costs and doesn't have many high-throughput applications. For example, building high-frequency DeFi on Celestia is very challenging because you need multi-terabytes per second throughput, which would completely clog the Celestia network.
From this perspective, we really don’t feel threatened. We are building a very strong community, and even if others come along, we already have the network effect of developers and market share, and hopefully more funding will follow. So, the best defense is our network effects.
The two-way dependence of Web3 and AI
Jonny: You chose artificial intelligence as your main focus, but why does Web3 need to host artificial intelligence within its ecosystem? Conversely, why does artificial intelligence need Web3? This is a two-way question, and the answer to both questions is not necessarily yes.
Michael: Of course, Web3 without AI is possible. But I think in the next 5 to 10 years, every company will be an AI company because AI will be as transformative as the Internet was. Do we really want to miss this opportunity in Web3? I don't think so. According to McKinsey, AI will unlock trillions of dollars in economic value and 70% of jobs can be automated by AI. So why not take advantage of it? Web3 without AI is possible, but with AI, the future will be better. We believe that in the next 5 to 10 years, the majority of participants on the blockchain will be AI agents who perform tasks and transactions for you. It’s going to be a very exciting world where we’ll have a lot of automated services powered by AI that are tailored to the user.
In turn, I think AI absolutely needs Web3. Our mission is to make AI a public good. This is fundamentally a question of incentives. How do you ensure that AI models don’t cheat and that they make decisions that are best for humans? Alignment can be broken down into incentive, verification and security components, each of which is well suited to be implemented in a blockchain environment. Blockchain can help with financialization and incentives through tokens, creating an environment where AI is financially disinclined to cheat. All transaction history is also on the blockchain. To make a bold statement here, I think fundamentally, everything from the training data to the data cleaning components to the data ingestion and collection components should be on-chain so that there is complete traceability of who provided the data and then What decisions did the AI model make?
Looking ahead 5 to 10 years, if AI systems are managing logistical, administrative, and manufacturing systems, I would want to know the version of the model, its decisions, and oversee the model beyond human intelligence to ensure it is consistent with Alignment of human interests. And by putting AI into a black box that can cheat and not make decisions in the best interest of humanity, I'm not sure we can trust a few companies to consistently ensure the security and integrity of such a system, especially given the future impact of AI models. Possible superpowers in 5 to 10 years.
Kamran: We all know that the crypto space is full of narratives, and you are so focused on the AI space, do you think this will be a hindrance for you in the long run? As you said, your technology stack will be far superior to what we see now. Do you think the narrative around AI, and the naming itself, will hinder your development in the future?
Michael: We don’t think so. We firmly believe that in the future, every company will be an AI company. There is hardly a company that doesn’t use AI in some form in its applications or platforms. From this perspective, every time GPT launches a new version, such as one with trillions of parameters, it opens new features that were not available before and reaches a higher performance level. I think the heat is here to stay because this is a completely new paradigm. For the first time, we've been able to tell computers what to do using human language. In some cases, you gain the ability to transcend the average person and automate processes that were previously unachievable. For example, some companies have almost completely automated their sales development and customer support. With the release of GPT-5, GPT-6, etc., AI models will become smarter. We need to make sure we keep up with this trend in Web3 and build our own open source version.
AI agents will run parts of society in the future, and ensuring they are governed by blockchain in an appropriate manner is critical. Within 10 to 20 years, AI will definitely become mainstream and bring about huge social changes. Just look at Tesla's fully autonomous driving mode and you will know that the future is becoming a reality day by day. Robots will also enter our lives and provide us with a lot of support. We are basically living in a science fiction movie.
The above is the detailed content of Conversation with 0G Labs: DA's road to the end and the new era of on-chain AI. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Qubetics ($TICS): The Revolutionizing AI CryptoMar 23, 2025 am 10:08 AM
Qubetics ($TICS): The Revolutionizing AI CryptoMar 23, 2025 am 10:08 AMCryptocurrency has always been a realm where the cutting edge of technology meets bold ambition, and it's only getting more exciting in the future. As artificial intelligence continues to grow in influence, there are a handful of digital assets that
![Bitcoin [BTC] was on a downtrend after losing the $92,000-support level in the final week of February](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/246/273/174209101774967.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40) Bitcoin [BTC] was on a downtrend after losing the $92,000-support level in the final week of FebruaryMar 16, 2025 am 10:10 AM
Bitcoin [BTC] was on a downtrend after losing the $92,000-support level in the final week of FebruaryMar 16, 2025 am 10:10 AMTechnical indicators such as the OBV showed that selling pressure has been dominant, meaning more losses may be likely ahead.
 Bitcoin historical price list 2015-2025 Bitcoin price trend charts in the past decadeMar 12, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
Bitcoin historical price list 2015-2025 Bitcoin price trend charts in the past decadeMar 12, 2025 pm 06:54 PMThis article reviews the ten-year price trend of Bitcoin from 2015 to 2025 in detail. Data shows that Bitcoin price fluctuates dramatically, experiencing huge changes from $200 to over $100,000. During this period, the price of Bitcoin was affected by a variety of factors, including halving of block rewards, market sentiment, regulatory policies, and global macroeconomic situation. The article analyzes the rise and fall of Bitcoin prices year by year, and focuses on interpreting the price changes in key years, providing a reference for investors to understand the history of Bitcoin prices and predict future trends. Keywords: Bitcoin price, Bitcoin trend, Bitcoin decade, digital currency, cryptocurrency
 Top 10 Free Virtual Currency Exchanges Rankings The latest top ten virtual currency APP trading platformsMar 11, 2025 am 10:18 AM
Top 10 Free Virtual Currency Exchanges Rankings The latest top ten virtual currency APP trading platformsMar 11, 2025 am 10:18 AMThe top ten free virtual currency exchanges are ranked: 1. OKX; 2. Binance; 3. Gate.io; 4. Huobi Global; 5. Kraken; 6. Coinbase; 7. KuCoin; 8. Crypto.com; 9. MEXC Global; 10. Bitfinex. These platforms each have their own advantages.
 Ethereum historical price trend chart 2015-2024 Ethereum k-line chart ten years trend trendMar 12, 2025 pm 06:57 PM
Ethereum historical price trend chart 2015-2024 Ethereum k-line chart ten years trend trendMar 12, 2025 pm 06:57 PMThis article reviews the price trend of Ethereum since its listing in 2015, from the initial $0.31, it experienced a surge in 2017 to nearly $1,400, as well as a market plunge in 2018 and 2022, and then hit a record high of $4,891.70 in 2021, as well as a rebound and stability in 2023. The article data covers the significant changes in Ethereum prices over each year and predicts price trends for 2024-2025, providing investors with a comprehensive historical reference and future outlook for Ethereum prices. Understand the history of Ethereum price fluctuations and seize investment opportunities!
 Top 10 digital currency app platforms rankings Virtual currency exchange latest rankings in 2025Mar 13, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
Top 10 digital currency app platforms rankings Virtual currency exchange latest rankings in 2025Mar 13, 2025 pm 06:45 PMTop 10 digital currency app platforms: 1. OKX, 2. Binance, 3. Gate.io, 4. Kraken, 5. Coinbase, 6. Huobi, 7. KuCoin, 8. Crypto.com, 9. Bitfinex, 10. Gemini; these platforms are ranked according to factors such as transaction volume, security and user experience. When choosing, the platform's security, liquidity, transaction fees, currency selection, user interface and customer support should be considered.
 Cyber criminals were able to steal cryptocurrency worth 1.5 billion US dollarsMar 16, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Cyber criminals were able to steal cryptocurrency worth 1.5 billion US dollarsMar 16, 2025 am 11:12 AMSince then, the provider has been investigating how this could have happened and how it will (hopefully) not happen again in the future.
 BTFD Coin: The Presale That's Breaking RecordsMar 14, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
BTFD Coin: The Presale That's Breaking RecordsMar 14, 2025 pm 03:15 PMEver wonder which meme coin could turn your small investment into life-changing gains? With the meme coin market heating up in 2025, investors are diving into fresh opportunities, hoping to catch the next big wave before prices skyrocket.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft







