YoloCS: Effectively reduce the space complexity of feature maps

Paper address: YOLOCS: Object Detection based on Dense Channel Compression for Feature Spatial Solidification (arxiv.org)
01 Total Description
In today’s sharing, the researchers examined the correlation between channel features and convolution kernels during feature purification and gradient backpropagation, focusing on the forward and backward directions within the network. spread. Therefore, the researchers proposed a feature space solidification method called dense channel compression. Based on the core concepts of the method, two innovative modules for backbone and head networks are introduced: dense channel compression (DCFS) for feature space solidification and asymmetric multi-level compression decoupled head (ADH). When integrated into the YOLOv5 model, these two modules demonstrated extraordinary performance, resulting in an improved model known as YOLOCS.


Evaluated on the MSCOCO data set, the AP of the large, medium and small YOLOCS models are 50.1%, 47.6% and 42.5% respectively . While maintaining a similar inference speed to the YOLOv5 model, the large, medium, and small YOLOCS models achieved 1.1%, 2.3%, and 5.2% advantages over YOLOv5's AP respectively.
02 Background
In recent years, target detection technology has received widespread attention in the field of computer vision. Among them, the target detection technology based on the single shot multi-box algorithm (Single Shot Multi Box Detector, referred to as SSD) and the target detection technology based on the convolutional neural network (Convolutional Neural Networks, referred to as CNN) are the two most commonly used target detection technologies. However, due to the low accuracy of the single-shot multi-frame algorithm and the high computational complexity of target detection technology based on convolutional neural networks, finding an efficient and high-precision target detection technology has become a hot spot in current research. one.

Dense Channel Compression (DCC) is a new convolutional neural network compression technology that compresses the feature map of the convolutional neural network. Perform spatial solidification to achieve compression and acceleration of network parameters. However, the application of DCC technology in the field of target detection has not been fully studied. Dense Channel Compression (DCC) technology aims to improve computational efficiency by reducing the number of network parameters. Specifically, DCC reduces the number of parameters of the convolutional layer by performing channel compression on the output feature map of the convolutional layer. This compression technique can be achieved by removing redundant and unnecessary channels, or using methods such as low-rank decomposition. Although DCC technology is effective in image classification tasks

Therefore, a target detection technology based on Dense Channel Compression is proposed, named YOLOCS (YOLO with Dense Channel Compression). YOLOCS technology combines DCC technology with the YOLO (You Only Look Once) algorithm to achieve efficient and high-precision processing of target detection. Specifically, YOLOCS technology uses DCC technology to spatially solidify the feature map, thereby achieving precise positioning of the target position; at the same time, YOLOCS technology uses the single-shot multi-frame algorithm characteristics of the YOLO algorithm to achieve target classification. Quick calculation.
03 New Framework
- Dense Channel Compression for Feature Spatial Solidification Structure (DCFS)

In the proposed method (above (c)), the researchers not only solved the balance problem between network width and depth, but also solved the problem of network width and depth through 3 × 3 volumes. The product compresses features from different depth layers, reducing the number of channels by half before outputting and fusing features. This approach enables researchers to refine feature outputs from different layers to a greater extent, thereby enhancing feature diversity and effectiveness during the fusion stage.
In addition, the compressed features from each layer are carried with larger convolution kernel weights (3×3), effectively expanding the receptive field of the output features. This approach is called feature space solidified dense channel compression. The rationale behind dense channel compression for feature space solidification relies on utilizing larger convolution kernels to facilitate channel compression. This technique has two key advantages: First, it expands the receptive field of feature perception during forward propagation, thereby ensuring that region-related feature details are incorporated to minimize feature loss throughout the compression stage. Second, the enhancement of error details during error backpropagation allows for more accurate weight adjustment.
To further illustrate these two advantages, convolution with two different kernel types (1×1 and 3×3) is used to compress the two channels, as shown below:

#The network structure of DCFS is shown in the figure below. A three-layer bottleneck structure is adopted to gradually compress the channel during the network forward propagation process. Half-channel 3×3 convolution is applied to all branches, followed by batch normalization (BN) and activation function layers. Subsequently, a 1 × 1 convolutional layer is used to compress the output feature channels to match the input feature channels.

- ##Asymmetric Multi-level Channel Compression Decoupled Head (ADH)
In order to solve the decoupling head problem in the YOLOX model, the researchers conducted a series of studies and experiments. The results reveal a logical correlation between the utilization of decoupled head structures and the associated loss functions. Specifically, for different tasks, the structure of the decoupling head should be adjusted according to the complexity of the loss calculation. In addition, when the decoupled head structure is applied to various tasks, directly compressing the feature channels of the previous layer (as shown below) into task channels may result in significant feature loss due to differences in final output dimensions. This, in turn, can adversely affect the overall performance of the model.

# Additionally, when considering the proposed dense channel compression method for feature space solidification, the number of channels in the final layer is directly reduced to match the output Channels may cause feature loss during forward propagation, thus degrading network performance. At the same time, in the context of backpropagation, this structure may lead to suboptimal error backpropagation, hindering the achievement of gradient stability. To address these challenges, a new decoupling head is introduced, called an asymmetric multi-stage compression decoupling head (see Figure (b) below).

#Specifically, the researchers deepened the network path dedicated to the target scoring task and used 3 convolutions to expand the perception of this task field and number of parameters. At the same time, the features of each convolutional layer are compressed along the channel dimension. This method not only effectively alleviates the training difficulty related to the target scoring task and improves model performance, but also greatly reduces the parameters and GFLOPs of the decoupled head module, thereby significantly improving the inference speed. Furthermore, 1 convolutional layer is used to separate the classification and bounding box tasks. This is because for matched positive samples, the losses associated with both tasks are relatively small, thus avoiding over-extension. This approach significantly reduces parameters and GFLOPs in the decoupling header, ultimately increasing inference speed.
04 Experiment VisualizationAblation Experiment on MS-COCO val2017

Comparison of YOLOCS, YOLOX and YOLOv5- r6.1[7] in terms of AP on MS-COCO 2017 test-dev


The above is the detailed content of YoloCS: Effectively reduce the space complexity of feature maps. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Personal Hacking Will Be A Pretty Fierce BearMay 11, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Personal Hacking Will Be A Pretty Fierce BearMay 11, 2025 am 11:09 AMCyberattacks are evolving. Gone are the days of generic phishing emails. The future of cybercrime is hyper-personalized, leveraging readily available online data and AI to craft highly targeted attacks. Imagine a scammer who knows your job, your f
 Pope Leo XIV Reveals How AI Influenced His Name ChoiceMay 11, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Pope Leo XIV Reveals How AI Influenced His Name ChoiceMay 11, 2025 am 11:07 AMIn his inaugural address to the College of Cardinals, Chicago-born Robert Francis Prevost, the newly elected Pope Leo XIV, discussed the influence of his namesake, Pope Leo XIII, whose papacy (1878-1903) coincided with the dawn of the automobile and
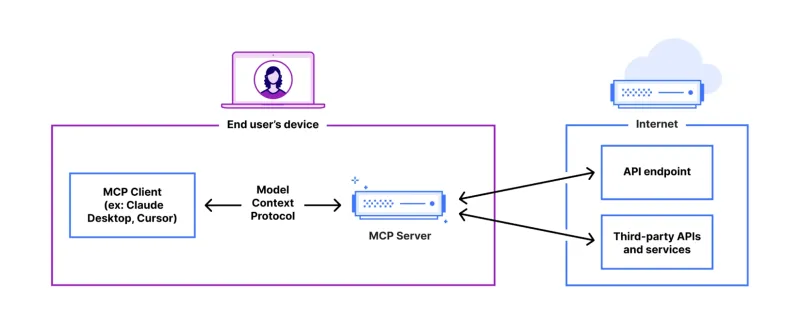 FastAPI-MCP Tutorial for Beginners and Experts - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:56 AM
FastAPI-MCP Tutorial for Beginners and Experts - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:56 AMThis tutorial demonstrates how to integrate your Large Language Model (LLM) with external tools using the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and FastAPI. We'll build a simple web application using FastAPI and convert it into an MCP server, enabling your L
 Dia-1.6B TTS : Best Text-to-Dialogue Generation Model - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:27 AM
Dia-1.6B TTS : Best Text-to-Dialogue Generation Model - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:27 AMExplore Dia-1.6B: A groundbreaking text-to-speech model developed by two undergraduates with zero funding! This 1.6 billion parameter model generates remarkably realistic speech, including nonverbal cues like laughter and sneezes. This article guide
 3 Ways AI Can Make Mentorship More Meaningful Than EverMay 10, 2025 am 11:17 AM
3 Ways AI Can Make Mentorship More Meaningful Than EverMay 10, 2025 am 11:17 AMI wholeheartedly agree. My success is inextricably linked to the guidance of my mentors. Their insights, particularly regarding business management, formed the bedrock of my beliefs and practices. This experience underscores my commitment to mentor
 AI Unearths New Potential In The Mining IndustryMay 10, 2025 am 11:16 AM
AI Unearths New Potential In The Mining IndustryMay 10, 2025 am 11:16 AMAI Enhanced Mining Equipment The mining operation environment is harsh and dangerous. Artificial intelligence systems help improve overall efficiency and security by removing humans from the most dangerous environments and enhancing human capabilities. Artificial intelligence is increasingly used to power autonomous trucks, drills and loaders used in mining operations. These AI-powered vehicles can operate accurately in hazardous environments, thereby increasing safety and productivity. Some companies have developed autonomous mining vehicles for large-scale mining operations. Equipment operating in challenging environments requires ongoing maintenance. However, maintenance can keep critical devices offline and consume resources. More precise maintenance means increased uptime for expensive and necessary equipment and significant cost savings. AI-driven
 Why AI Agents Will Trigger The Biggest Workplace Revolution In 25 YearsMay 10, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Why AI Agents Will Trigger The Biggest Workplace Revolution In 25 YearsMay 10, 2025 am 11:15 AMMarc Benioff, Salesforce CEO, predicts a monumental workplace revolution driven by AI agents, a transformation already underway within Salesforce and its client base. He envisions a shift from traditional markets to a vastly larger market focused on
 AI HR Is Going To Rock Our Worlds As AI Adoption SoarsMay 10, 2025 am 11:14 AM
AI HR Is Going To Rock Our Worlds As AI Adoption SoarsMay 10, 2025 am 11:14 AMThe Rise of AI in HR: Navigating a Workforce with Robot Colleagues The integration of AI into human resources (HR) is no longer a futuristic concept; it's rapidly becoming the new reality. This shift impacts both HR professionals and employees, dem


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools







