Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinationsCan fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Large language models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning.

Align the model or perform instruction tuning to let the model learn how to make full use of this knowledge and how to respond more naturally to the user's questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input created by human annotators or other LLMs, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and incorporates it into the parameters.
How does the model integrate this new additional knowledge?
At a mechanistic level, we don’t really know how this interaction occurs of. According to some, exposure to this new knowledge may cause the model to hallucinate. This is because the model is trained to generate facts that are not based on its pre-existing knowledge (or may conflict with the model's prior knowledge). There is also knowledge of what looks the model is likely to encounter (e.g., entities that appear less frequently in the pre-training corpus).

#So a recently published study focused on analyzing what happens when a model learns new knowledge through fine-tuning. The authors examine in detail what happens to a fine-tuned model and how it reacts after acquiring new knowledge.
They try to classify the examples at the knowledge level after fine-tuning. The knowledge inherent in a new example may not be completely consistent with the knowledge of the model. Examples can be known or unknown. Even if it is known, it may be highly known, it may be known, or it may be less known knowledge.

Then the author used a model (PaLM 2-M) to fine-tune it. Each nudge example is made up of factual knowledge (subjects, relations, objects). This is to allow the model to query this knowledge with specific questions, specific triples (e.g., "Where is Paris?"), and ground truth answers (e.g., "France"). In other words, they provide the model with some new knowledge, and then reconstruct these triples into questions (question-answer pairs) to test its knowledge. They group all these examples into the categories discussed above and then evaluate the answers.
Test results after fine-tuning the model: A high proportion of unknown facts leads to performance degradation (which is not compensated by longer fine-tuning time).
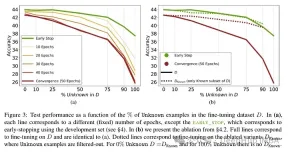
Unknown facts have almost a neutral effect at lower epoch numbers, but at more The number of epochs will hurt performance. So unknown examples appear to be harmful, but their negative impact is mainly reflected in the later stages of training. The graph below shows training accuracy as a function of fine-tuning duration for known and unknown subsets of the dataset example. It can be seen that the model learns unknown examples at a later stage.
Lastly, since Unknown examples are the ones that are likely to introduce new factual knowledge, their significantly slow fitting rate suggests that LLMs struggle to acquire new factual knowledge through fine-tuning , instead they learn to expose their preexisting knowledge using the Known examples. The relationship between examples is quantified and whether it is linear. The results show that there is a strong linear relationship between unknown examples hurting performance and known examples improving performance, almost as strong (the correlation coefficients in this linear regression are very close).
这种微调不仅对特定情况下的性能有影响,而且对模型知识有广泛的影响。作者使用分布外(OOD)的测试集表明,未知样本对OOD性能是有害的。根据作者的说法,这与幻觉的发生也有关系:
Overall, our insights transfer across relations. This essentially shows that fine-tuning on Unknown examples such as “Where is [E1] located?”, can encourage hallucinations on seemingly unrelated questions, such as “Who founded [E2]?”.
另外一个有趣的结果是,最好的结果不是用众所周知的例子获得的,而是用可能已知的例子。换句话说,这些例子允许模型更好地利用其先验知识(过于众所周知的事实不会对模型产生有用的影响)。
相比之下,未知和不太清楚的事实会损害模型的表现,而这种下降源于幻觉的增加。
This work highlights the risk in using supervised fine-tuning to update LLMs’ knowledge, as we present empirical evidence that acquiring new knowledge through finetuning is correlated with hallucinations w.r.t preexisting knowledge.
根据作者的说法,这种未知的知识可能会损害性能(这使得微调几乎毫无用处)。而用“我不知道”标记这种未知知识可以帮助减少这种伤害。
Acquiring new knowledge via supervised fine-tuning is correlated with hallucinations w.r.t. pre-existing knowledge. LLMs struggle to integrate new knowledge through fine-tuning and mostly learn to use their pre-existing knowledge.
综上所述,如果在微调过程中出现未知知识,则会对模型造成损害。这种性能下降与幻觉的增加有关。相比之下,可能已知的例子反而有有益的影响。这表明该模型难以整合新知识。也就是说在模型所学到的知识和它如何使用新知识之间存在冲突。这可能与对齐和指令调优有关(但是这篇论文没有研究这一点)。
所以如果想要使用具有特定领域知识的模型,论文建议最好使用RAG。并且带有“我不知道”标记的结果可以找到其他策略来克服这些微调的局限性。
这项研究是非常有意思,它表明微调的因素以及如何解决新旧知识之间的冲突仍然不清楚。这就是为什么我们要测试微调前和后结果的原因。
The above is the detailed content of Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AM
The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe term "AI-ready workforce" is frequently used, but what does it truly mean in the supply chain industry? According to Abe Eshkenazi, CEO of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), it signifies professionals capable of critic
 How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe decentralized AI revolution is quietly gaining momentum. This Friday in Austin, Texas, the Bittensor Endgame Summit marks a pivotal moment, transitioning decentralized AI (DeAI) from theory to practical application. Unlike the glitzy commercial
 Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AMEnterprise AI faces data integration challenges The application of enterprise AI faces a major challenge: building systems that can maintain accuracy and practicality by continuously learning business data. NeMo microservices solve this problem by creating what Nvidia describes as "data flywheel", allowing AI systems to remain relevant through continuous exposure to enterprise information and user interaction. This newly launched toolkit contains five key microservices: NeMo Customizer handles fine-tuning of large language models with higher training throughput. NeMo Evaluator provides simplified evaluation of AI models for custom benchmarks. NeMo Guardrails implements security controls to maintain compliance and appropriateness
 AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI: The Future of Art and Design Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the field of art and design in unprecedented ways, and its impact is no longer limited to amateurs, but more profoundly affecting professionals. Artwork and design schemes generated by AI are rapidly replacing traditional material images and designers in many transactional design activities such as advertising, social media image generation and web design. However, professional artists and designers also find the practical value of AI. They use AI as an auxiliary tool to explore new aesthetic possibilities, blend different styles, and create novel visual effects. AI helps artists and designers automate repetitive tasks, propose different design elements and provide creative input. AI supports style transfer, which is to apply a style of image
 How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AMZoom, initially known for its video conferencing platform, is leading a workplace revolution with its innovative use of agentic AI. A recent conversation with Zoom's CTO, XD Huang, revealed the company's ambitious vision. Defining Agentic AI Huang d
 The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AMWill AI revolutionize education? This question is prompting serious reflection among educators and stakeholders. The integration of AI into education presents both opportunities and challenges. As Matthew Lynch of The Tech Edvocate notes, universit
 The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AM
The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AMThe development of scientific research and technology in the United States may face challenges, perhaps due to budget cuts. According to Nature, the number of American scientists applying for overseas jobs increased by 32% from January to March 2025 compared with the same period in 2024. A previous poll showed that 75% of the researchers surveyed were considering searching for jobs in Europe and Canada. Hundreds of NIH and NSF grants have been terminated in the past few months, with NIH’s new grants down by about $2.3 billion this year, a drop of nearly one-third. The leaked budget proposal shows that the Trump administration is considering sharply cutting budgets for scientific institutions, with a possible reduction of up to 50%. The turmoil in the field of basic research has also affected one of the major advantages of the United States: attracting overseas talents. 35
 All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AM
All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AMOpenAI unveils the powerful GPT-4.1 series: a family of three advanced language models designed for real-world applications. This significant leap forward offers faster response times, enhanced comprehension, and drastically reduced costs compared t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function