 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Open source! V2Xverse: handed over and released the first simulation platform and end-to-end model for V2X
Open source! V2Xverse: handed over and released the first simulation platform and end-to-end model for V2XOpen source! V2Xverse: handed over and released the first simulation platform and end-to-end model for V2X

Synchronized driving data of vehicle-road collaboration

Autonomous driving V2X-AD (Vehicle- to-everything-aided autonomous driving) has great potential in providing safer driving strategies. Researchers have conducted a lot of research on the communication and communication aspects of V2X-AD, but the effect of these infrastructure and communication resources in improving driving performance has not been fully explored. This highlights the need to study collaborative autonomous driving, that is, how to design efficient information sharing strategies for driving planning to improve the driving performance of each vehicle. This requires two key basic conditions: one is a platform that can provide a data environment for V2X-AD, and an end-to-end driving system with complete driving-related functions and information sharing mechanisms. In terms of the platform that provides the data environment, it can be achieved by utilizing the communication network between vehicles and the support of the infrastructure. In this way, vehicles can share real-time and environmental information needed for driving, thereby improving driving performance. On the other hand, end-to-end driving systems need to have complete driving functions and be able to share information. This means that the driving system should be able to obtain driving-related information from other vehicles and infrastructure and combine this information with its own driving planning to provide more efficient driving performance. While achieving these two basic conditions, security and privacy protection also need to be considered. Therefore, when designing the driving planning strategy of V2X-AD, we should pay attention to the efficiency of the information sharing strategy and thereby improve the driving performance of each vehicle. To sum up, vehicle-road collaborative assisted autonomous driving V2X-AD has huge potential
" For this reason, researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory published a new research article "Towards Collaborative Autonomous Driving: Simulation Platform and End-to-End System" proposes CoDriving: an end-to-end collaborative driving system that uses an information sharing strategy for driving planning to achieve efficient communication and collaboration. A simulation platform V2Xverse was built, which provides a complete training and testing environment for collaborative driving, including the generation of vehicle-road collaborative driving data sets, the deployment of full-stack collaborative driving systems, and closed-loop driving performance evaluation and driving tasks in customizable scenarios. Evaluation. "
At the same time, the simulation platform V2Xverse integrates the training and deployment test codes of multiple existing collaborative sensing methods, using a variety of test tasks to test comprehensive driving capabilities: 3D target detection, path planning, and loop closure. Autopilot. V2Xverse breaks through the limitations of existing collaborative sensing methods that can only "see" but not "control". It supports embedding existing collaborative sensing methods into a complete driving system and testing driving performance in a simulation environment. The researchers of this article believe that this will bring better functional extensions and a test benchmark that is more suitable for actual driving scenarios for vision-based vehicle-road collaboration research in autonomous driving.
- Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.09496
- Code link: https://github.com/CollaborativePerception /V2Xverse
Research background and significance
The research of this article focuses on collaborative autonomous driving based on V2X (Vehicle-to-everything) communication. Compared with single-vehicle autonomous driving, collaborative autonomous driving improves vehicle perception and driving performance through information exchange between the vehicle and the surrounding environment (such as roadside units, pedestrians equipped with smart devices, etc.), which will benefit people with limited vision. Safe driving in complex scenarios (Figure 1).
 Figure 1. Dangerous "ghost probe" scene, the bicycle cannot sense the occluded object
Figure 1. Dangerous "ghost probe" scene, the bicycle cannot sense the occluded object
Currently, V2X-based vehicle-road collaborative work mostly focuses on optimizing module-level perception capabilities. However, how to use cooperative sensing capabilities to improve the final driving performance in integrated systems is still underexplored.
In order to solve this problem, this article aims to expand the collaborative sensing capability into a collaborative driving system covering comprehensive driving capabilities, including key modules such as perception, prediction, planning and control. Achieving collaborative autonomous driving requires two key foundations: a platform that can provide a data environment for V2X-AD; and the second is an end-to-end driving system that integrates complete driving-related functions and information sharing mechanisms. From a platform perspective, this work builds V2Xverse, a comprehensive collaborative autonomous driving simulation platform that provides a complete process from the generation of vehicle-road collaborative driving data sets to the deployment of full-stack collaborative driving systems and closed-loop driving performance evaluation. From the perspective of the driving system, this article introduces CoDriving, a new end-to-end collaborative driving system that designs and embeds a V2X communication-based collaboration module in a complete autonomous driving framework to improve collaborative driving performance by sharing sensory information. . The core idea of CoDriving is a new information sharing strategy for driving planning, which uses spatially sparse but important visual feature information for driving as communication content to optimize communication efficiency while improving driving performance.
V2Xverse: Vehicle-road collaborative driving simulation platform
The key feature of the V2Xverse proposed in this article is the ability to achieve offline benchmark generation of driving-related subtasks and in different scenarios Online closed-loop evaluation of driving performance fully supports the development of collaborative autonomous driving systems. In order to create a V2X-AD scene, V2Xverse sets up multiple smart cars equipped with complete driving capabilities in the scene, and places roadside units on both sides of the road through certain strategies to provide supplementary vision for the smart cars. In order to support the development of collaborative autonomous driving methods, V2Xverse first provides (vehicle-vehicle) and (vehicle-roadside unit) communication modules, and provides complete driving signals and expert annotations for system training, and also provides closed-loop driving evaluation A variety of dangerous scenarios. The simulation platform framework is shown in Figure 2.
 Figure 2. V2Xverse simulation platform framework
Figure 2. V2Xverse simulation platform framework
Compared with the existing Carla-based autonomous driving simulation platform, V2Xverse has three advantages. First of all, V2Xverse supports multi-vehicle driving simulation, while the mainstream carla-leaderboard and its derivative platforms only support single-vehicle driving simulation. Second, V2Xverse supports full driving function simulation, while the existing collaborative perception simulation platform only supports functions related to the perception module. Third, V2Xverse supports comprehensive V2X-AD scenarios, including diverse sensor devices, model integration and flexible scenario customization; see Table 1.
 Table 1. Comparison between V2Xverse and existing Carla-based autonomous driving simulation platform
Table 1. Comparison between V2Xverse and existing Carla-based autonomous driving simulation platform
CoDriving: End-to-end self-driving model for efficient collaboration
CoDriving consists of two components (see Figure 3): 1) End-to-end single-vehicle autonomous driving network, which converts sensor inputs into driving control signals; 2) Driving-oriented collaboration, where collaborators share information critical to driving Perceptual features are used to achieve efficient communication, and the perceptual features of bicycle BEVs are enhanced through feature aggregation. The enhanced perceptual features will help the system produce more accurate perceptual identification results and planning prediction results.
 Figure 3. The overall framework of CoDriving
Figure 3. The overall framework of CoDriving
End-to-end autonomous driving network
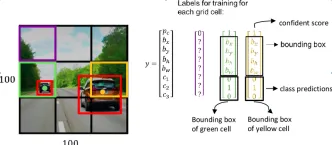
The end-to-end single-vehicle autonomous driving network is based on the Modal inputs are used to learn output waypoint predictions, and a control module converts the waypoints into driving control signals. To achieve this, CoDriving integrates the modular components required for driving into an end-to-end system, including 3D object detectors, waypoint predictors and controllers. CoDriving uses Bird's Eye View (BEV) representation because it provides a unified global coordinate system, avoids complex coordinate transformation, and better supports collaboration based on spatial information.
Driving-oriented collaboration strategy
V2X collaboration solves the inevitable problem of limited visibility of bicycles through information sharing. In this work, this paper proposes a new driving-oriented collaboration strategy to simultaneously optimize driving performance and communication efficiency. The scheme includes i) driving intention-based perception communication, where CoDriving exchanges spatially sparse but driving-critical BEV perception features through a driving request module; and ii) BEV feature enhancement, where CoDriving utilizes the received feature information to enhance the performance of each collaborative vehicle. BEV perception characteristics. The enhanced BEV features will help the system produce more accurate perception recognition results and planning prediction results.
Experimental results
Using the V2Xverse simulation platform, this article tests the performance of CoDriving on three tasks: closed-loop driving, 3D target detection, and waypoint prediction. In the key closed-loop driving test, compared with the previous single-vehicle end-to-end autonomous driving SOTA method, CoDriving's driving score significantly improved by 62.49%, and the pedestrian collision rate dropped by 53.50%. In the target detection and waypoint prediction tasks, CoDriving performs better than other collaborative methods, as shown in Table 2.
 Table 2. CoDriving is better than SOTA's single driving method in the closed-loop driving task, and is better than other collaborative sensing methods in the modular perception and planning subtasks
Table 2. CoDriving is better than SOTA's single driving method in the closed-loop driving task, and is better than other collaborative sensing methods in the modular perception and planning subtasks
This article At the same time, the collaborative performance of CoDriving under different communication bandwidths was verified. In the three tasks of closed-loop driving, 3D target detection, and waypoint prediction, CoDriving outperformed other collaboration methods under different communication bandwidth restrictions, as shown in Figure 4.
 Figure 4. Collaboration performance of CoDriving under different communication bandwidths
Figure 4. Collaboration performance of CoDriving under different communication bandwidths
Figure 5 shows a driving case of CoDriving in the V2Xverse simulation environment. In the scene in Figure 5, a pedestrian in the blind spot suddenly rushed out of the road. It can be seen that the autonomous driving bicycle had a limited field of vision and was unable to avoid the pedestrian in advance, causing a serious car accident. CoDriving uses the shared vision characteristics of roadside units to detect pedestrians in advance and avoid them safely.

Figure 5(1). Compared to bicycle self-driving with limited vision, CoDriving uses the information provided by the roadside unit to detect pedestrians in the blind spot Figure 5 (2). CoDriving successfully avoided pedestrians, but the self-driving bicycle did not avoid the situation in time, causing a collision
Figure 5 (2). CoDriving successfully avoided pedestrians, but the self-driving bicycle did not avoid the situation in time, causing a collision
Summary
This work helps collaborative autonomous driving by building a simulation platform V2Xverse method development and proposes a new end-to-end self-driving system. Among them, V2Xverse is a V2X collaborative driving simulation platform that supports closed-loop driving testing. This platform provides a complete development channel for the development of collaborative autonomous driving systems with the goal of improving final driving performance. It is worth mentioning that V2Xverse also supports the deployment of a variety of existing single-vehicle autonomous driving systems, as well as the training and closed-loop driving testing of a variety of existing collaborative sensing methods. At the same time, this paper proposes a new end-to-end collaborative autonomous driving system CoDriving, which improves driving performance and optimizes communication efficiency by sharing key driving perception information. A comprehensive evaluation of the entire driving system shows that CoDriving is significantly better than the single-vehicle self-driving system in different communication bandwidths. The researchers of this article believe that the V2Xverse platform and CoDriving system provide potential solutions for more reliable autonomous driving.
The above is the detailed content of Open source! V2Xverse: handed over and released the first simulation platform and end-to-end model for V2X. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
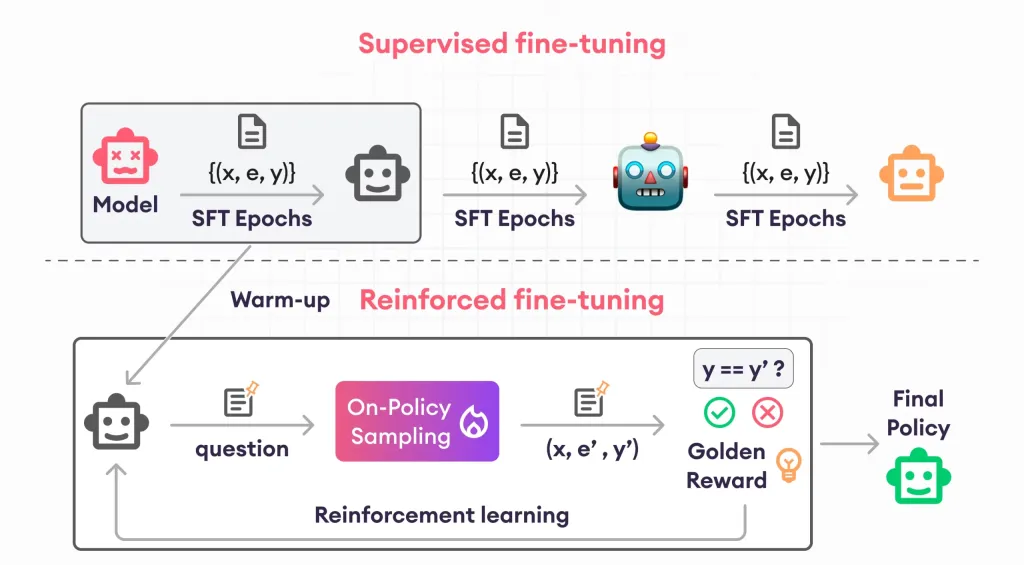 Guide to Reinforcement Finetuning - Analytics VidhyaApr 28, 2025 am 09:30 AM
Guide to Reinforcement Finetuning - Analytics VidhyaApr 28, 2025 am 09:30 AMReinforcement finetuning has shaken up AI development by teaching models to adjust based on human feedback. It blends supervised learning foundations with reward-based updates to make them safer, more accurate, and genuinely help
 Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AMScientists have extensively studied human and simpler neural networks (like those in C. elegans) to understand their functionality. However, a crucial question arises: how do we adapt our own neural networks to work effectively alongside novel AI s
 New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AM
New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AMGoogle's Gemini Advanced: New Subscription Tiers on the Horizon Currently, accessing Gemini Advanced requires a $19.99/month Google One AI Premium plan. However, an Android Authority report hints at upcoming changes. Code within the latest Google P
 How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AMDespite the hype surrounding advanced AI capabilities, a significant challenge lurks within enterprise AI deployments: data processing bottlenecks. While CEOs celebrate AI advancements, engineers grapple with slow query times, overloaded pipelines, a
 MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AM
MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AMHandling documents is no longer just about opening files in your AI projects, it’s about transforming chaos into clarity. Docs such as PDFs, PowerPoints, and Word flood our workflows in every shape and size. Retrieving structured
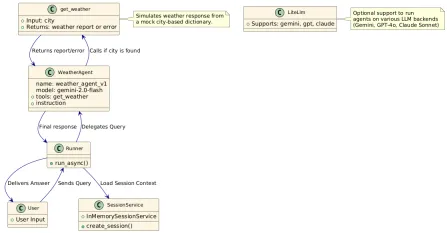 How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AMHarness the power of Google's Agent Development Kit (ADK) to create intelligent agents with real-world capabilities! This tutorial guides you through building conversational agents using ADK, supporting various language models like Gemini and GPT. W
 Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AM
Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AMsummary: Small Language Model (SLM) is designed for efficiency. They are better than the Large Language Model (LLM) in resource-deficient, real-time and privacy-sensitive environments. Best for focus-based tasks, especially where domain specificity, controllability, and interpretability are more important than general knowledge or creativity. SLMs are not a replacement for LLMs, but they are ideal when precision, speed and cost-effectiveness are critical. Technology helps us achieve more with fewer resources. It has always been a promoter, not a driver. From the steam engine era to the Internet bubble era, the power of technology lies in the extent to which it helps us solve problems. Artificial intelligence (AI) and more recently generative AI are no exception
 How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AM
How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AMHarness the Power of Google Gemini for Computer Vision: A Comprehensive Guide Google Gemini, a leading AI chatbot, extends its capabilities beyond conversation to encompass powerful computer vision functionalities. This guide details how to utilize


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft






