YOLOv10 is here! True real-time end-to-end target detection
In the past few years, YOLOs has become a mainstream paradigm in the field of real-time object detection due to its effective balance between computational cost and detection performance. Researchers have conducted in-depth exploration of the structural design, optimization goals, data enhancement strategies, etc. of YOLOs and have made significant progress. However, the post-processing reliance on non-maximum suppression (NMS) hinders end-to-end deployment of YOLOs and negatively impacts inference latency. Furthermore, the design of various components in YOLOs lacks comprehensive and thorough review, resulting in significant computational redundancy and limiting model performance. This results in suboptimal efficiency, and huge potential for performance improvements. In this work, we aim to further advance the performance-efficiency boundary of YOLOs from both post-processing and model architecture. To this end, we first propose persistent dual allocation for NMS-free training of YOLOs, which simultaneously brings competitive performance and lower inference latency. Furthermore, we introduce a comprehensive efficiency-accuracy driven model design strategy for YOLOs. We have comprehensively optimized each component of YOLOs from the perspectives of efficiency and accuracy, which greatly reduces computational overhead and enhances model capabilities. The result of our efforts is a new generation of the YOLO series designed for real-time end-to-end object detection, called YOLOv10. Extensive experiments show that YOLOv10 achieves state-of-the-art performance and efficiency at various model scales. For example, on the COCO dataset, our YOLOv10-S is 1.8 times faster than RT-DETR-R18 under similar AP, while reducing parameters and floating point operations (FLOPs) by 2.8 times. Compared with YOLOv9-C, YOLOv10-B reduces latency by 46% and reduces parameters by 25% under the same performance. Code link: https://github.com/THU-MIG/yolov10.
What improvements are there in YOLOv10?
First solves the redundant prediction problem in post-processing by proposing a persistent dual allocation strategy for NMS-free YOLOs. This strategy includes dual label assignment and consistent matching metrics. This enables the model to obtain rich and harmonious supervision during training while eliminating the need for NMS during inference, achieving competitive performance while maintaining high efficiency.
This time, a comprehensive efficiency-accuracy driven model design strategy is proposed for the model architecture, and each component in YOLOs is comprehensively examined. In terms of efficiency, lightweight classification heads, space-channel decoupled downsampling, and rank-guided block designs are proposed to reduce obvious computational redundancy and achieve a more efficient architecture.
In terms of accuracy, large kernel convolutions are explored and effective partial self-attention modules are proposed to enhance model capabilities and tap performance improvement potential at low cost.
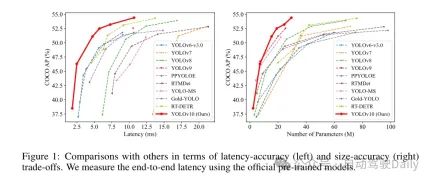
Based on these methods, the author successfully implemented a series of real-time end-to-end detectors with different model sizes, namely YOLOv10-N/S/M/B/L/X. Extensive experiments on standard object detection benchmarks show that YOLOv10 demonstrates the ability to outperform previous state-of-the-art models in terms of computation-accuracy trade-offs at various model sizes. As shown in Figure 1, under similar performance, YOLOv10-S/X is 1.8 times/1.3 times faster than RT-DETR R18/R101 respectively. Compared with YOLOv9-C, YOLOv10-B achieves 46% latency reduction under the same performance. In addition, YOLOv10 shows extremely high parameter utilization efficiency. YOLOv10-L/X is 0.3 AP and 0.5 AP higher than YOLOv8-L/X with the number of parameters reduced by 1.8 times and 2.3 times respectively. YOLOv10-M achieves similar AP to YOLOv9-M/YOLO-MS while reducing the number of parameters by 23% and 31% respectively.
During the training process, YOLOs usually utilize TAL (Task Assignment Learning) to assign multiple samples to each instance. Adopting a one-to-many allocation method generates rich supervision signals, which helps optimize and achieve stronger performance. However, this also makes YOLOs must rely on NMS (non-maximum suppression) post-processing, which results in suboptimal inference efficiency when deployed. While previous works have explored one-to-one matching approaches to suppress redundant predictions, they often add additional inference overhead or result in suboptimal performance. In this work, we propose an NMS-free training strategy that adopts dual label assignment and consistent matching metric, achieving high efficiency and competitive performance. Through this strategy, our YOLOs no longer require NMS in training, achieving high efficiency and competitive performance.

#Efficiency-driven model design. The components in YOLO include the stem, downsampling layers, stages with basic building blocks, and the head. The computational cost of the backbone part is very low, so we perform efficiency-driven model design for the other three parts.
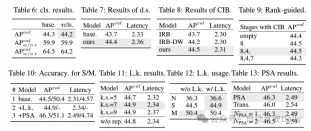
(1)轻量级的分类头。在YOLO中,分类头和回归头通常有相同的架构。然而,它们在计算开销上存在显着的差异。例如,在YOLOv8-S中,分类头(5.95G/1.51M的FLOPs和参数数量)和回归头(2.34G/0.64M)的FLOPs和参数数量分别是回归头的2.5倍和2.4倍。然而,通过分析分析分类错误和回归错误的影响(见表6),我们发现回归头对YOLO的性能更为重要。因此,我们可以在不担心性能损害的情况下减少分类头的开销。因此,我们简单地采用了轻量级的分类头架构,它由两个深度可分离卷积组成,卷积核大小为3×3,后跟一个1×1的卷积核。 通过以上改进,我们可以简化轻量级的分类头的架构,它由两个深度可分离卷积组成,卷积核大小为3×3,后跟一个1×1的卷积核。这种简化的架构可以实现分类的功能,并且具有更小的计算开销和参数数量。
(2)空间-通道解耦下采样。 YOLO通常使用步长为2的常规3×3标准卷积,同时实现空间下采样(从H × W到H/2 × W/2)和通道变换(从C到2C)。这引入了不可忽视的计算成本 和参数计数。相反,我们提出将空间缩减和通道增加操作解耦,以实现更高效的下采样。具体来说,首先利用逐点卷积来调制通道维度,然后利用深度卷积进行空间下采样。这将计算成本降低到并将参数计数降低到。同时,它在下采样过程中最大限度地保留了信息,从而在降低延迟的同时保持了竞争性能。
(3)基于rank引导的模块设计。 YOLOs通常对所有阶段都使用相同的基本构建块,例如YOLOv8中的bottleneck块。为了彻底检查YOLOs的这种同构设计,我们利用内在秩来分析每个阶段的冗余性。具体来说,计算每个阶段中最后一个基本块中最后一个卷积的数值秩,它计算大于阈值的奇异值的数量。图3(a)展示了YOLOv8的结果,表明深层阶段和大型模型更容易表现出更多的冗余性。这一观察表明,简单地对所有阶段应用相同的block设计对于实现最佳容量-效率权衡来说并不是最优的。为了解决这个问题,提出了一种基于秩的模块设计方案,旨在通过紧凑的架构设计来降低被证明是冗余的阶段的复杂性。
首先介绍了一种紧凑的倒置块(CIB)结构,它采用廉价的深度卷积进行空间混合和成本效益高的逐点卷积进行通道混合,如图3(b)所示。它可以作为有效的基本构建块,例如嵌入在ELAN结构中(图3(b))。然后,倡导一种基于秩的模块分配策略,以在保持竞争力量的同时实现最佳效率。具体来说,给定一个模型,根据其内在秩的升序对所有阶段进行排序。进一步检查用CIB替换领先阶段的基本块后的性能变化。如果与给定模型相比没有性能下降,我们将继续替换下一个阶段,否则停止该过程。因此,我们可以在不同阶段和模型规模上实现自适应紧凑块设计,从而在不影响性能的情况下实现更高的效率。

基于精度导向的模型设计。 论文进一步探索了大核卷积和自注意力机制,以实现基于精度的设计,旨在以最小的成本提升性能。
(1)大核卷积。采用大核深度卷积是扩大感受野并增强模型能力的一种有效方法。然而,在所有阶段简单地利用它们可能会在用于检测小目标的浅层特征中引入污染,同时也在高分辨率阶段引入显着的I/O开销和延迟。因此,作者提出在深层阶段的跨阶段信息块(CIB)中利用大核深度卷积。这里将CIB中的第二个3×3深度卷积的核大小增加到7×7。此外,采用结构重参数化技术,引入另一个3×3深度卷积分支,以缓解优化问题,而不增加推理开销。此外,随着模型大小的增加,其感受野自然扩大,使用大核卷积的好处逐渐减弱。因此,仅在小模型规模上采用大核卷积。
(2)部分自注意力(PSA)。自注意力机制因其出色的全局建模能力而被广泛应用于各种视觉任务中。然而,它表现出高计算复杂度和内存占用。为了解决这个问题,鉴于普遍存在的注意力头冗余,作则提出了一种高效的部分自注意力(PSA)模块设计,如图3.(c)所示。具体来说,在1×1卷积之后将特征均匀地按通道分成两部分。只将一部分特征输入到由多头自注意力模块(MHSA)和前馈网络(FFN)组成的NPSA块中。然后,将两部分特征通过1×1卷积进行拼接和融合。此外,将MHSA中查询和键的维度设置为值的一半,并将LayerNorm替换为BatchNorm以实现快速推理。PSA仅放置在具有最低分辨率的第4阶段之后,以避免自注意力的二次计算复杂度带来的过多开销。通过这种方式,可以在计算成本较低的情况下将全局表示学习能力融入YOLOs中,从而很好地增强了模型的能力并提高了性能。
实验对比
这里就不做过多介绍啦,直接上结果!!!latency减少,性能继续增加。


The above is the detailed content of YOLOv10 is here! True real-time end-to-end target detection. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
![Can't use ChatGPT! Explaining the causes and solutions that can be tested immediately [Latest 2025]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/242/473/174717025174979.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40) Can't use ChatGPT! Explaining the causes and solutions that can be tested immediately [Latest 2025]May 14, 2025 am 05:04 AM
Can't use ChatGPT! Explaining the causes and solutions that can be tested immediately [Latest 2025]May 14, 2025 am 05:04 AMChatGPT is not accessible? This article provides a variety of practical solutions! Many users may encounter problems such as inaccessibility or slow response when using ChatGPT on a daily basis. This article will guide you to solve these problems step by step based on different situations. Causes of ChatGPT's inaccessibility and preliminary troubleshooting First, we need to determine whether the problem lies in the OpenAI server side, or the user's own network or device problems. Please follow the steps below to troubleshoot: Step 1: Check the official status of OpenAI Visit the OpenAI Status page (status.openai.com) to see if the ChatGPT service is running normally. If a red or yellow alarm is displayed, it means Open
 Calculating The Risk Of ASI Starts With Human MindsMay 14, 2025 am 05:02 AM
Calculating The Risk Of ASI Starts With Human MindsMay 14, 2025 am 05:02 AMOn 10 May 2025, MIT physicist Max Tegmark told The Guardian that AI labs should emulate Oppenheimer’s Trinity-test calculus before releasing Artificial Super-Intelligence. “My assessment is that the 'Compton constant', the probability that a race to
 An easy-to-understand explanation of how to write and compose lyrics and recommended tools in ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 05:01 AM
An easy-to-understand explanation of how to write and compose lyrics and recommended tools in ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 05:01 AMAI music creation technology is changing with each passing day. This article will use AI models such as ChatGPT as an example to explain in detail how to use AI to assist music creation, and explain it with actual cases. We will introduce how to create music through SunoAI, AI jukebox on Hugging Face, and Python's Music21 library. Through these technologies, everyone can easily create original music. However, it should be noted that the copyright issue of AI-generated content cannot be ignored, and you must be cautious when using it. Let’s explore the infinite possibilities of AI in the music field together! OpenAI's latest AI agent "OpenAI Deep Research" introduces: [ChatGPT]Ope
 What is ChatGPT-4? A thorough explanation of what you can do, the pricing, and the differences from GPT-3.5!May 14, 2025 am 05:00 AM
What is ChatGPT-4? A thorough explanation of what you can do, the pricing, and the differences from GPT-3.5!May 14, 2025 am 05:00 AMThe emergence of ChatGPT-4 has greatly expanded the possibility of AI applications. Compared with GPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4 has significantly improved. It has powerful context comprehension capabilities and can also recognize and generate images. It is a universal AI assistant. It has shown great potential in many fields such as improving business efficiency and assisting creation. However, at the same time, we must also pay attention to the precautions in its use. This article will explain the characteristics of ChatGPT-4 in detail and introduce effective usage methods for different scenarios. The article contains skills to make full use of the latest AI technologies, please refer to it. OpenAI's latest AI agent, please click the link below for details of "OpenAI Deep Research"
 Explaining how to use the ChatGPT app! Japanese support and voice conversation functionMay 14, 2025 am 04:59 AM
Explaining how to use the ChatGPT app! Japanese support and voice conversation functionMay 14, 2025 am 04:59 AMChatGPT App: Unleash your creativity with the AI assistant! Beginner's Guide The ChatGPT app is an innovative AI assistant that handles a wide range of tasks, including writing, translation, and question answering. It is a tool with endless possibilities that is useful for creative activities and information gathering. In this article, we will explain in an easy-to-understand way for beginners, from how to install the ChatGPT smartphone app, to the features unique to apps such as voice input functions and plugins, as well as the points to keep in mind when using the app. We'll also be taking a closer look at plugin restrictions and device-to-device configuration synchronization
 How do I use the Chinese version of ChatGPT? Explanation of registration procedures and feesMay 14, 2025 am 04:56 AM
How do I use the Chinese version of ChatGPT? Explanation of registration procedures and feesMay 14, 2025 am 04:56 AMChatGPT Chinese version: Unlock new experience of Chinese AI dialogue ChatGPT is popular all over the world, did you know it also offers a Chinese version? This powerful AI tool not only supports daily conversations, but also handles professional content and is compatible with Simplified and Traditional Chinese. Whether it is a user in China or a friend who is learning Chinese, you can benefit from it. This article will introduce in detail how to use ChatGPT Chinese version, including account settings, Chinese prompt word input, filter use, and selection of different packages, and analyze potential risks and response strategies. In addition, we will also compare ChatGPT Chinese version with other Chinese AI tools to help you better understand its advantages and application scenarios. OpenAI's latest AI intelligence
 5 AI Agent Myths You Need To Stop Believing NowMay 14, 2025 am 04:54 AM
5 AI Agent Myths You Need To Stop Believing NowMay 14, 2025 am 04:54 AMThese can be thought of as the next leap forward in the field of generative AI, which gave us ChatGPT and other large-language-model chatbots. Rather than simply answering questions or generating information, they can take action on our behalf, inter
 An easy-to-understand explanation of the illegality of creating and managing multiple accounts using ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 04:50 AM
An easy-to-understand explanation of the illegality of creating and managing multiple accounts using ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 04:50 AMEfficient multiple account management techniques using ChatGPT | A thorough explanation of how to use business and private life! ChatGPT is used in a variety of situations, but some people may be worried about managing multiple accounts. This article will explain in detail how to create multiple accounts for ChatGPT, what to do when using it, and how to operate it safely and efficiently. We also cover important points such as the difference in business and private use, and complying with OpenAI's terms of use, and provide a guide to help you safely utilize multiple accounts. OpenAI


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use







