一、DOM
DOM: DOM= Document Object Model,文档对象模型,DOM可以以一种独立于平台和语言的方式访问和修改一个文档的内容和结构。换句话说,这是表示和处理一个HTML或XML文档的常用方法。有一点很重要,DOM的设计是以对象管理组织(OMG)的规约为基础的,因此可以用于任何编程语言.
D:文档 – html 文档 或 xml 文档
O:对象 – document 对象的属性和方法
M:模型
DOM 是针对xml(html)的基于树的API。
DOM树:节点(node)的层次。
DOM 把一个文档表示为一棵家谱树(父,子,兄弟)
DOM定义了Node的接口以及许多种节点类型来表示XML节点的多个方面
二、DOM的结构
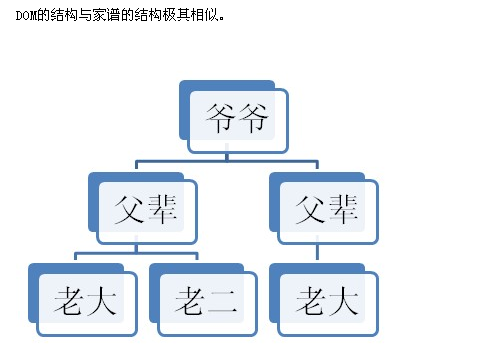


三、节点
根据 DOM,HTML 文档中的每个成分都是一个节点。DOM 是这样规定的:
整个文档是一个文档节点
每个 HTML 标签是一个元素节点
包含在 HTML 元素中的文本是文本节点
每一个 HTML 属性是一个属性节点
注释属于注释节点
四、Node 层次
节点彼此都有等级关系。
HTML 文档中的所有节点组成了一个文档树(或节点树)。HTML 文档中的每个元素、属性、文本等都代表着树中的一个节点。树起始于文档节点,并由此继续伸出枝条,直到处于这棵树最低级别的所有文本节点为止。
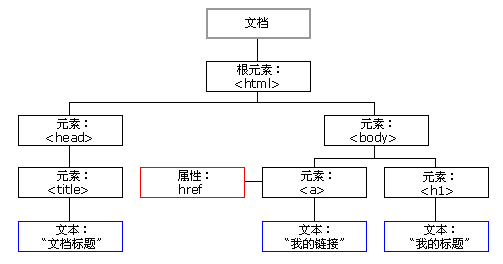
五、节点及其类型
节点
* 由结构图中我们可以看到,整个文档就是一个文档节点。
* 而每一个HMTL标签都是一个元素节点。
* 标签中的文字则是文本节点。
* 标签的属性是属性节点。
* 一切都是节点……
节点树
节点树的概念从图中一目了然,最上面的就是“树根”了。节点之间有父子关系,祖先与子孙关系,兄妹关系。这些关系从图中也很好看出来,直接连线的就是父子关系了。而有一个父亲的就是兄妹关系……
六、查找并访问节点
你可通过若干种方法来查找您希望操作的元素:
通过使用 getElementById() 和 getElementsByTagName() 方法
通过使用一个元素节点的 parentNode、firstChild 以及 lastChild 属性
七、查找元素节点
getElementById()
寻找一个有着给定 id 属性值的元素,返回值是一个有着给定 id 属性值的元素节点。如果不存在这样的元素,它返回 null.
var oElement = document.getElementById ( sID )
该方法只能用于 document 对象
function test(){
var usernameElement=document.getElementById(“tid");
//获取元素的值
alert("usernameElement.value: "+usernameElement.value)
//获取元素的类型
alert("usernameElement.type: "+usernameElement.type)
}
getElementsByName()
寻找有着给定name属性的所有元素,这个方法将返回一个节点集合,这个集合可以当作一个数组来处理。这个集合的 length 属性等于当前文档里有着给定name属性的所有元素的总个数。
function test(){
var tnameArray=document.getElementsByName("tname");
alert(tnameArray.length);
for(var i=0;i
}
}
<input type="text" name="username" value="国庆60年_1"><br> <input type="text" name="username" value="国庆60年_2"><br> <input type="text" name="username" value="国庆60年_3"><br> <input type="button" name="ok" value="保存" id="ok"><br><script language="JavaScript"> //该方法返回是数组类型 var usernameElements=document.getElementsByName("username"); for (var i = 0; i < usernameElements.length; i++) { //获取元素的类型 //alert(usernameElements[i].type) //获取元素value的值 //alert(usernameElements[i].value); //采用函数直接量的方法 usernameElements[i].onchange = function(){ alert(this.value); }} </script><br>
getElementsByTagName()
寻找有着给定标签名的所有元素,这个方法将返回一个节点集合,这个集合可以当作一个数组来处理。这个集合的 length 属性等于当前文档里有着给定标签名的所有元素的总个数。
var elements = document.getElementsByTagName(tagName);
var elements = element.getElementsByTagName(tagName);
该方法不必非得用在整个文档上。它也可以用来在某个特定元素的子节点当中寻找有着给定标签名的元素。
var container = document.getElementById(“sid”);
var elements = container.getElementsByTagName(“p”);
alert(elements .length);
// //处理input
// var inputElements=document.getElementsByTagName("input");
// //输出input标签的长度
// //alert(inputElements.length);
// for(var i=0;i
// alert(inputElements[i].value);
// }
// }
//处理select
// //获取select标签
// var selectElements=document.getElementsByTagName("select");
// //获取select下的子标签
// for(var j=0;j
// for(var i=0;i
// }
// }
var textareaElements=document.getElementsByTagName("textarea");
alert(textareaElements[0].value);
// //处理input// var inputElements=document.getElementsByTagName("input");// //输出input标签的长度// //alert(inputElements.length);// for(var i=0;i<inputelements.length if alert var selectelements='document.getElementsByTagName("select");//' for j="0;j<selectElements.length;j++){//" optionelements='selectElements[j].getElementsByTagName("option");//' i="0;i<optionElements.length;i++){//" textareaelements='document.getElementsByTagName("textarea");'><div class="codetitle">
<span><a style="CURSOR: pointer" data="39839" class="copybut" id="copybut39839" onclick="doCopy('code39839')"><u>复制代码</u></a></span> 代码如下:</div>
<div class="codebody" id="code39839">
<br>var inputElements=document.getElementsByTagName("input");<br>for(var i=0;i<inputelements.length>if (inputElements.type != 'submit') {<br>inputElements[i].onchange = function(){<br>alert(this.value)<br>};<br>}<br><br>var selectElements=document.getElementsByTagName("select");<br>for (var i = 0; i selectElements[i].onchange=function(){ <br>alert(this.value);<br>}<br>}<br></inputelements.length>
</div> <pre style="DISPLAY: none" class="html" name="code"> var inputElements=document.getElementsByTagName("input"); for(var i=0;i<inputelements.length if inputelements function alert var selectelements='document.getElementsByTagName("select");' for i="0;" selectelements.length>
<p><br></p>
<p><strong>八、parentNode、firstChild以及lastChild</strong></p>
<p>这三个属性 parentNode、firstChild 以及 lastChild 可遵循文档的结构,在文档中进行“短距离的旅行”。<br>请看下面这个 HTML 片段:</p>
<div class="codetitle">
<span><a style="CURSOR: pointer" data="79360" class="copybut" id="copybut79360" onclick="doCopy('code79360')"><u>复制代码</u></a></span> 代码如下:</div>
<div class="codebody" id="code79360">
<br><table> <br><tr>
<br><td>John</td> <br><td>Doe</td>
<br><td>Alaska</td> <br>
</tr>
<br>
</table> <br>
</div>
<p><br>在上面的HTML代码中,第一个 </p>
<td> 是 </td>
<tr> 元素的首个子元素(firstChild),而最后一个 <td> 是 </td>
</tr>
<tr>元素的最后一个子元素(lastChild)。<br>此外,</tr>
<tr> 是每个 <td>元 素的父节点(parentNode)。
<p></p>
<div class="codetitle">
<span><a style="CURSOR: pointer" data="60797" class="copybut" id="copybut60797" onclick="doCopy('code60797')"><u>复制代码</u></a></span> 代码如下:</div>
<div class="codebody" id="code60797">
<br>var textareaElements=document.getElementsByTagName("textarea");<br>for (var i = 0; i textareaElements[i].onchange = function(){<br>alert(this.value);<br>};<br>}<br>
</div>
<pre style="DISPLAY: none" class="html" name="code"> var textareaElements=document.getElementsByTagName("textarea"); for (var i = 0; i
九、查看是否存在子节点
hasChildNodes()
该方法用来检查一个元素是否有子节点,返回值是 true 或 false.
var booleanValue = element.hasChildNodes();
文本节点和属性节点不可能再包含任何子节点,所以对这两类节点使用 hasChildNodes 方法的返回值永远是 false.
如果 hasChildNodes 方法的返回值是 false,则 childNodes,firstChild,lastChild 将是空数组和空字符串。
hasChildNodes()
var selectElements=document.getElementsByTagName("select");
alert(selectElements[0].hasChildNodes())
var inputElements=document.getElementsByTagName("input");
for(var i=0;i
}
var selectElements=document.getElementsByTagName("select"); alert(selectElements[0].hasChildNodes())var inputElements=document.getElementsByTagName("input");for(var i=0;i<inputelements.length alert>
</inputelements.length>
十、根节点
有两种特殊的文档属性可用来访问根节点:
document.documentElement
document.body
第一个属性可返回存在于 XML 以及 HTML 文档中的文档根节点。
第二个属性是对 HTML 页面的特殊扩展,提供了对
十一、DOM节点信息
每个节点都拥有包含着关于节点某些信息的属性。这些属性是:
nodeName(节点名称)
nodeName 属性含有某个节点的名称。
var name = node.nodeName;
元素节点的 nodeName 是标签名称
属性节点的 nodeName 是属性名称
文本节点的 nodeName 永远是 #text
文档节点的 nodeName 永远是 #document
注释:nodeName 所包含的 html 元素的标签名称永远是大写的
nodeValue(节点值)
nodeValue:返回给定节点的当前值(字符串)
如果给定节点是一个属性节点,返回值是这个属性的值。
如果给定节点是一个文本节点,返回值是这个文本节点的内容。
如果给定节点是一个元素节点,返回值是 null
nodeValue 是一个 读/写 属性,但不能对元素节点的 nodeValue 属性设置值,
但可以为文本节点的 nodeValue 属性设置一个值。
var li = document.getElementById(“li”);
if(li.firstChild.nodeType == 3)
li.firstChild.nodeValue = “国庆60年”;
nodeType(节点类型)
nodeType:返回一个整数,这个数值代表着给定节点的类型。
nodeType 属性返回的整数值对应着 12 种节点类型,常用的有三种:
Node.ELEMENT_NODE ---1 -- 元素节点
Node.ATTRIBUTE_NODE ---2 -- 属性节点
Node.TEXT_NODE ---3 -- 文本节点
nodeType 是个只读属性
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr
 Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AM
Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AMNode.js excels at efficient I/O, largely thanks to streams. Streams process data incrementally, avoiding memory overload—ideal for large files, network tasks, and real-time applications. Combining streams with TypeScript's type safety creates a powe
 Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AMThe differences in performance and efficiency between Python and JavaScript are mainly reflected in: 1) As an interpreted language, Python runs slowly but has high development efficiency and is suitable for rapid prototype development; 2) JavaScript is limited to single thread in the browser, but multi-threading and asynchronous I/O can be used to improve performance in Node.js, and both have advantages in actual projects.
 The Origins of JavaScript: Exploring Its Implementation LanguageApr 29, 2025 am 12:51 AM
The Origins of JavaScript: Exploring Its Implementation LanguageApr 29, 2025 am 12:51 AMJavaScript originated in 1995 and was created by Brandon Ike, and realized the language into C. 1.C language provides high performance and system-level programming capabilities for JavaScript. 2. JavaScript's memory management and performance optimization rely on C language. 3. The cross-platform feature of C language helps JavaScript run efficiently on different operating systems.
 Behind the Scenes: What Language Powers JavaScript?Apr 28, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Behind the Scenes: What Language Powers JavaScript?Apr 28, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript runs in browsers and Node.js environments and relies on the JavaScript engine to parse and execute code. 1) Generate abstract syntax tree (AST) in the parsing stage; 2) convert AST into bytecode or machine code in the compilation stage; 3) execute the compiled code in the execution stage.
 The Future of Python and JavaScript: Trends and PredictionsApr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AM
The Future of Python and JavaScript: Trends and PredictionsApr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AMThe future trends of Python and JavaScript include: 1. Python will consolidate its position in the fields of scientific computing and AI, 2. JavaScript will promote the development of web technology, 3. Cross-platform development will become a hot topic, and 4. Performance optimization will be the focus. Both will continue to expand application scenarios in their respective fields and make more breakthroughs in performance.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and ToolsApr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and ToolsApr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AMBoth Python and JavaScript's choices in development environments are important. 1) Python's development environment includes PyCharm, JupyterNotebook and Anaconda, which are suitable for data science and rapid prototyping. 2) The development environment of JavaScript includes Node.js, VSCode and Webpack, which are suitable for front-end and back-end development. Choosing the right tools according to project needs can improve development efficiency and project success rate.
 Is JavaScript Written in C? Examining the EvidenceApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Is JavaScript Written in C? Examining the EvidenceApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AMYes, the engine core of JavaScript is written in C. 1) The C language provides efficient performance and underlying control, which is suitable for the development of JavaScript engine. 2) Taking the V8 engine as an example, its core is written in C, combining the efficiency and object-oriented characteristics of C. 3) The working principle of the JavaScript engine includes parsing, compiling and execution, and the C language plays a key role in these processes.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!






