Last time [JS-implementing navigation bar hover] mentioned that when the page where the navigation bar is hovered is run on IE, the navigation bar will keep shaking.
The solution is as follows:
Changed the positioning method of the navigation bar from absolute to fixed. I don’t know why it was changed to fixed, but it stopped shaking. . -_-||
div.navigation{
width: 800px;
height: 40px;
background: red;
margin: 4px auto 0;
top: 400px;
left: 0px;
position: fixed;
}
For this reason, JS must also be modified accordingly.
Because fixed positioning is based on the browser’s visible area, the original positioning of the navigation bar must be changed.
//Record the original position of the navigation bar on the page
var naviga_offsetTop = 0;
var naviga_offsetLeft = 0;
//IE7 does not recognize getElementsByClassName. For compatibility, customize a
function my_getElementsByClassName(class_name) {
var el = [] ;
//Get all elements
_el = document.getElementsByTagName('*');
//Select by className
for (var i=0; i<_el.length i>if (_el[i].className == class_name ) {
el[el.length] = _el[i];
}
}
return el;
}
//Navigation bar, hover at the top
function naviga_stay_top(){
var a_navigation_bar = [];
if(document.getElementsByClassName){//Chrome, FF
a_navigation_bar = document.getElementsByClassName("navigation");
} else {//IE
a_navigation_bar = my_getElementsByClassName("navigation");
}
var scrollTop = document.body.scrollTop || document .documentElement.scrollTop;
document.title = scrollTop;
//If the scrolling distance is greater than the distance between the original navigation bar and the top
//Directly fix the navigation bar to the visual area Top
if( scrollTop > naviga_offsetTop ){
a_navigation_bar[0].style.top = 0 "px";
} else {
//If the scrolling distance is smaller than the original navigation bar distance from the top, recalculate the position of the navigation bar
a_navigation_bar[0].style.top = (naviga_offsetTop - scrollTop) "px";
}
}
//give Four tabs on the navigation bar, plus click events.
window.onload=function(){
var a_tabs = [];
if( document.getElementsByClassName ){//Chrome, FF
a_tabs = document.getElementsByClassName("tab");
}else{ //IE
a_tabs = my_getElementsByClassName("tab");
}
var a_contents = [];
if( document.getElementsByClassName ){//Chrome, FF
a_contents = document.getElementsByClassName("content");
}else{//IE
a_contents = my_getElementsByClassName("content");
}
//Get offsetLeft , that is, the distance between the navigation bar and the left border
var a_main_div = [];
if( document.getElementsByClassName ){//Chrome, FF
a_main_div = document.getElementsByClassName("main");
}else{ //IE
a_main_div = my_getElementsByClassName("main");
}
naviga_offsetLeft = a_main_div[0].offsetLeft;
a_tabs[0].onclick=function() {
window.scrollTo(0, a_contents[2].offsetTop);
}
a_tabs[1].onclick=function(){
window.scrollTo(0, a_contents[3]. offsetTop);
}
a_tabs[2].onclick=function(){
window.scrollTo(0, a_contents[4].offsetTop);
}
a_tabs[3]. onclick=function(){
window.scrollTo(0, a_contents[5].offsetTop);
}
//Get the position of the navigation bar to the top on the page
var a_navigation_bar = [];
if(document.getElementsByClassName){//Chrome, FF
a_navigation_bar = document.getElementsByClassName("navigation");
} else {//IE
a_navigation_bar = my_getElementsByClassName(" navigation");
}
//Get offsetTop
naviga_offsetTop = a_navigation_bar[0].offsetTop;
a_navigation_bar[0].style.left = naviga_offsetLeft "px";
//Add scrolling events to the scroll bar and mouse
if( window.attachEvent) //IE
{
window.attachEvent("onmousewheel", naviga_stay_top);
window.attachEvent("onscroll ", naviga_stay_top);
document.attachEvent("onmousewheel", naviga_stay_top);
document.attachEvent("onscroll", naviga_stay_top);
} else {//Chrome ,FF
window.addEventListener("mousewheel", naviga_stay_top,false);
window.addEventListener("scroll", naviga_stay_top,false);
document.addEventListener("mousewheel", naviga_stay_top,false);
document.addEventListener("scroll", naviga_stay_top,false);
}
}
In this question, it is important to understand the difference between CSS DIV positioning (relative, absolute, static, fixed).
relative,absolute,static,fixed
Let’s first look at the definition of each attribute value:
1. static: default value. Without positioning, the element appears in normal flow (ignoring top, bottom, left, right or z-index declarations).
2. Relative: Generate a relatively positioned element and position it relative to its normal position through the settings of top, bottom, left, and right. Hierarchical classification can be done through z-index.
3. Absolute: Generate an absolutely positioned element and position it relative to the first parent element other than static positioning. The position of the element is specified via the "left", "top", "right" and "bottom" attributes. Hierarchical classification can be done through z-index.
4. fixed: Generate absolutely positioned elements and position them relative to the browser window. The position of the element is specified via the "left", "top", "right" and "bottom" attributes. Hierarchical classification can be done through z-index.
The positioning methods of static and fixed are easy to understand and will not be analyzed here. The following is an analysis of the commonly used relative and absolute:
1. relative. An element positioned relative is removed from the normal text flow, but its position in the text flow still exists. As shown in Figure 1:
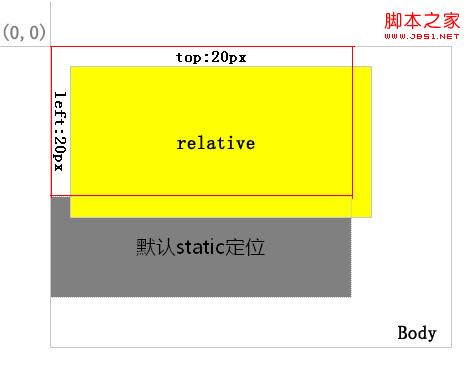
Figure 1
The layer with the yellow background is positioned relative, and the red border area is its position in the normal flow. After positioning it through top and left, you can see from the position of the gray background layer that its normal position still exists.
2. Absolute. A layer positioned as absolute is separated from the normal text flow, but the difference from relative is that its position in the normal flow no longer exists. As shown in Figure 2:
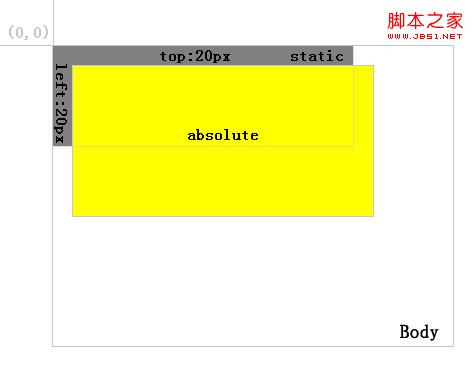
Figure 2
As you can see, after positioning the yellow background layer as absolute, the gray background layer is automatically filled in.
3. The main difference between relative and absolute:
First of all, it is whether the position in the normal flow exists or not as mentioned above.
Secondly, the relative positioned layer is always relative to its nearest parent element, no matter how its parent element is positioned. As shown in Figure 3:
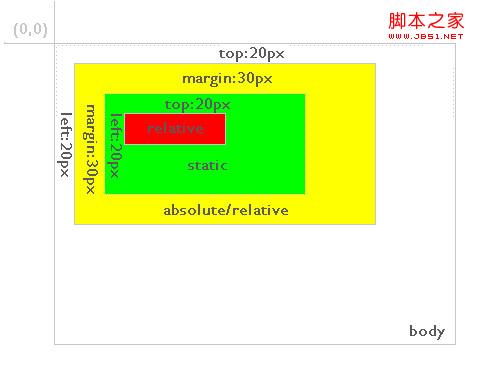
Figure 3
In the figure, the red background layer is relative positioned, and the green background layer of its direct parent element is static positioned by default. The position of the red background layer is the top and left 20 elements relative to the green background layer. And if the red background layer is positioned as absolute, the situation is as shown in Figure 4:
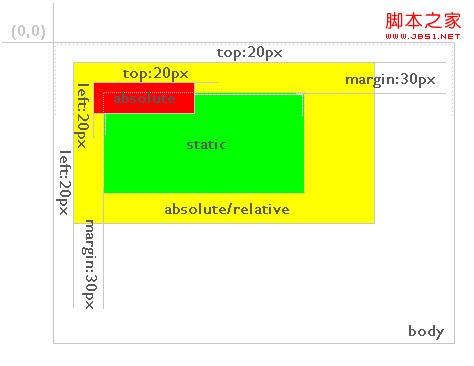
Figure 4
As you can see, the red background layer still defines top:20px; left: 20px; but its relative element becomes a yellow background layer with absolute or relative positioning mode. Therefore, a layer positioned for absolute is always relative to its nearest parent layer defined as absolute or relative, and this parent layer is not necessarily its direct parent layer. If absolute or relative is not defined in its parent layer, it will be positioned relative to the body, as shown in Figure 5:
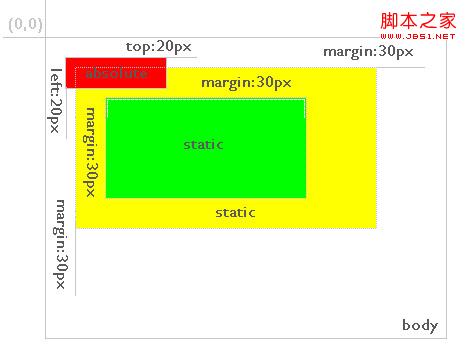
Figure 5
Except top, left, and right In addition to bottom positioning, the definition of margin attribute value also conforms to the above rules.
 抖音顶部的导航栏如何调整?其他导航栏调整选项Mar 07, 2024 pm 02:50 PM
抖音顶部的导航栏如何调整?其他导航栏调整选项Mar 07, 2024 pm 02:50 PM抖音界面的导航栏位于顶部,是用户快速访问不同功能和内容的重要通道。随着抖音的不断更新,用户可能希望能够根据个人喜好和需求对导航栏进行自定义和调整。一、抖音顶部的导航栏如何调整?通常,抖音的顶部导航栏会展示一些热门频道,让用户方便快速浏览和查看感兴趣的内容。如果您想调整顶部频道的设置,只需按照以下步骤操作即可:打开抖音应用并登录您的账号。在主界面上方找到导航栏,通常位于屏幕中间或顶部。点击导航栏上方的“+”符号或类似的按钮,进入频道编辑界面。在频道编辑界面中,您可以看到默认的热门频道列表。您可以通
 纯CSS实现带阴影效果的菜单导航栏的实现步骤Oct 16, 2023 am 08:27 AM
纯CSS实现带阴影效果的菜单导航栏的实现步骤Oct 16, 2023 am 08:27 AM纯CSS实现带阴影效果的菜单导航栏的实现步骤,需要具体代码示例在网页设计中,菜单导航栏是一个非常常见的元素。通过给菜单导航栏添加阴影效果,不仅可以增加其美观度,还可以提升用户体验。在本文中,我们将使用纯CSS来实现一个带阴影效果的菜单导航栏,并提供具体的代码示例供参考。实现步骤如下:创建HTML结构首先,我们需要创建一个基本的HTML结构来容纳菜单导航栏。以
 如何使用PHP开发简单的导航栏和网址收藏功能Sep 20, 2023 pm 03:14 PM
如何使用PHP开发简单的导航栏和网址收藏功能Sep 20, 2023 pm 03:14 PM如何使用PHP开发简单的导航栏和网址收藏功能导航栏和网址收藏功能是网页开发中常见并且实用的功能之一。本文将介绍如何使用PHP语言开发一个简单的导航栏和网址收藏功能,并提供具体的代码示例。创建导航栏界面首先,我们需要创建一个导航栏界面。导航栏通常包含一些链接,用于快速导航到其他页面。我们可以使用HTML和CSS来设计并排列这些链接。以下是一个简单的导航栏界面的
 Discuz导航栏个性化定制,让论坛更具特色!Mar 11, 2024 pm 01:45 PM
Discuz导航栏个性化定制,让论坛更具特色!Mar 11, 2024 pm 01:45 PM在Discuz论坛中,导航栏是用户访问网站时经常接触到的部分之一,因此定制导航栏可以为论坛增添独特的个性化风格,提升用户体验。接下来将介绍如何在Discuz论坛中进行导航栏的个性化定制,并提供具体的代码示例。首先,我们需要登录到Discuz的后台管理系统,进入“界面”->“导航设置”页面。在这个页面上,我们可以对导航栏进行各种设置和定制。以下是一些
 纯CSS实现响应式导航栏的下拉选项卡菜单效果的实现步骤Oct 28, 2023 am 09:58 AM
纯CSS实现响应式导航栏的下拉选项卡菜单效果的实现步骤Oct 28, 2023 am 09:58 AM纯CSS实现响应式导航栏的下拉选项卡菜单效果的实现步骤导航栏是网页中常见的元素之一,而下拉选项卡菜单则是导航栏中经常使用的一种效果,能够提供更多的导航选项。本文将介绍如何使用纯CSS实现一个响应式的导航栏下拉选项卡菜单效果。步骤一:搭建基础HTML结构我们首先需要搭建一个基础的HTML结构来进行演示,并且为这个导航栏添加一些样式。下面是一个简单的HTML结构
 纯CSS实现菜单导航栏的悬浮效果的实现步骤Oct 19, 2023 am 10:13 AM
纯CSS实现菜单导航栏的悬浮效果的实现步骤Oct 19, 2023 am 10:13 AM纯CSS实现菜单导航栏的悬浮效果的实现步骤随着Web设计的不断进步,用户对于网站的需求也越来越高。为了提供更好的用户体验,悬浮效果在网站设计中得到了广泛应用。本文将介绍如何使用纯CSS来实现菜单导航栏的悬浮效果,以提升网站的可用性和美观性。创建基本菜单结构首先,我们需要在HTML文档中创建菜单的基本结构。以下是一个简单的示例:<navclass=&q
 如何使用 JavaScript 实现网页底部固定导航栏的背景颜色渐变效果?Oct 20, 2023 pm 07:36 PM
如何使用 JavaScript 实现网页底部固定导航栏的背景颜色渐变效果?Oct 20, 2023 pm 07:36 PM如何使用JavaScript实现网页底部固定导航栏的背景颜色渐变效果?在现代网页设计中,固定导航栏已成为一种常见的布局方式。如果你想为网页底部固定导航栏添加一个背景颜色渐变效果,JavaScript是一个非常适合的选择。本文将向你介绍如何使用JavaScript来实现这一效果,并提供具体的代码示例。步骤1:HTML结构首先,我们需要在HTML
 如何使用 Vue 实现导航栏动态效果?Jun 25, 2023 pm 12:17 PM
如何使用 Vue 实现导航栏动态效果?Jun 25, 2023 pm 12:17 PMVue是一款非常流行的JavaScript框架,可以用于构建动态Web应用程序。在Vue中,可以很方便地实现导航栏动态效果,为用户提供更好的界面交互体验。下面是一些基本步骤,用于使用Vue实现导航栏动态效果。创建Vue实例首先,需要在HTML中引入Vue库,然后创建一个Vue实例。可以使用如下代码创建Vue实例:var


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)






