1. 过程概述
Python先把代码(.py文件)编译成字节码,交给字节码虚拟机,然后虚拟机一条一条执行字节码指令,从而完成程序的执行。
2. 字节码
字节码在Python虚拟机程序里对应的是PyCodeObject对象。
.pyc文件是字节码在磁盘上的表现形式。
3. pyc文件
PyCodeObject对象的创建时机是模块加载的时候,即import。
Python test.py会对test.py进行编译成字节码并解释执行,但是不会生成test.pyc。
如果test.py加载了其他模块,如import util,Python会对util.py进行编译成字节码,生成util.pyc,然后对字节码解释执行。
如果想生成test.pyc,我们可以使用Python内置模块py_compile来编译。
加载模块时,如果同时存在.py和.pyc,Python会尝试使用.pyc,如果.pyc的编译时间早于.py的修改时间,则重新编译.py并更新.pyc。
4. PyCodeObject
Python代码的编译结果就是PyCodeObject对象。
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
int co_argcount; /* 位置参数个数 */
int co_nlocals; /* 局部变量个数 */
int co_stacksize; /* 栈大小 */
int co_flags;
PyObject *co_code; /* 字节码指令序列 */
PyObject *co_consts; /* 所有常量集合 */
PyObject *co_names; /* 所有符号名称集合 */
PyObject *co_varnames; /* 局部变量名称集合 */
PyObject *co_freevars; /* 闭包用的的变量名集合 */
PyObject *co_cellvars; /* 内部嵌套函数引用的变量名集合 */
/* The rest doesn't count for hash/cmp */
PyObject *co_filename; /* 代码所在文件名 */
PyObject *co_name; /* 模块名|函数名|类名 */
int co_firstlineno; /* 代码块在文件中的起始行号 */
PyObject *co_lnotab; /* 字节码指令和行号的对应关系 */
void *co_zombieframe; /* for optimization only (see frameobject.c) */
} PyCodeObject;
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
int co_argcount; /* 位置参数个数 */
int co_nlocals; /* 局部变量个数 */
int co_stacksize; /* 栈大小 */
int co_flags;
PyObject *co_code; /* 字节码指令序列 */
PyObject *co_consts; /* 所有常量集合 */
PyObject *co_names; /* 所有符号名称集合 */
PyObject *co_varnames; /* 局部变量名称集合 */
PyObject *co_freevars; /* 闭包用的的变量名集合 */
PyObject *co_cellvars; /* 内部嵌套函数引用的变量名集合 */
/* The rest doesn't count for hash/cmp */
PyObject *co_filename; /* 代码所在文件名 */
PyObject *co_name; /* 模块名|函数名|类名 */
int co_firstlineno; /* 代码块在文件中的起始行号 */
PyObject *co_lnotab; /* 字节码指令和行号的对应关系 */
void *co_zombieframe; /* for optimization only (see frameobject.c) */
} PyCodeObject;
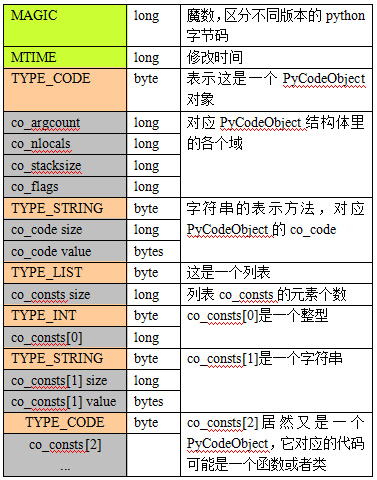
5. pyc文件格式
加载模块时,模块对应的PyCodeObject对象被写入.pyc文件,格式如下:
6. 分析字节码
6.1 解析PyCodeObject
Python提供了内置函数compile可以编译Python代码和查看PyCodeObject对象,如下:
Python代码[test.py]
s = ”hello” def func(): print s func() s = ”hello” def func(): print s func()
在Python交互式shell里编译代码得到PyCodeObject对象:

dir(co)已经列出co的各个域,想查看某个域直接在终端输出即可:
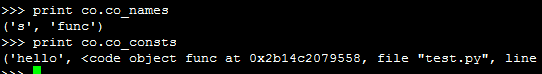
test.py的PyCodeObject
co.co_argcount 0 co.co_nlocals 0 co.co_names (‘s', 'func') co.co_varnames (‘s', 'func') co.co_consts (‘hello', <code object func at 0x2aaeeec57110, file ”test.py”, line 3>, None) co.co_code 'd\x00\x00Z\x00\x00d\x01\x00\x84\x00\x00Z\x01\x00e\x01\x00\x83\x00\x00\x01d\x02\x00S' co.co_argcount 0 co.co_nlocals 0 co.co_names (‘s', 'func') co.co_varnames (‘s', 'func') co.co_consts (‘hello', <code object func at 0x2aaeeec57110, file ”test.py”, line 3>, None) co.co_code 'd\x00\x00Z\x00\x00d\x01\x00\x84\x00\x00Z\x01\x00e\x01\x00\x83\x00\x00\x01d\x02\x00S'
Python解释器会为函数也生成的字节码PyCodeObject对象,见上面的co_consts[1]
func的PyCodeObject
func.co_argcount 0 func.co_nlocals 0 func.co_names (‘s',) func.co_varnames () func.co_consts (None,) func.co_code ‘t\x00\x00GHd\x00\x00S' func.co_argcount 0 func.co_nlocals 0 func.co_names (‘s',) func.co_varnames () func.co_consts (None,) func.co_code ‘t\x00\x00GHd\x00\x00S'
co_code是指令序列,是一串二进制流,它的格式和解析方法见6.2。
6.2 解析指令序列
指令序列co_code的格式

Python内置的dis模块可以解析co_code,如下图:
test.py的指令序列

func函数的指令序列

第一列表示以下几个指令在py文件中的行号;
第二列是该指令在指令序列co_code里的偏移量;
第三列是指令opcode的名称,分为有操作数和无操作数两种,opcode在指令序列中是一个字节的整数;
第四列是操作数oparg,在指令序列中占两个字节,基本都是co_consts或者co_names的下标;
第五列带括号的是操作数说明。
7. 执行字节码
Python虚拟机的原理就是模拟可执行程序再X86机器上的运行,X86的运行时栈帧如下图:
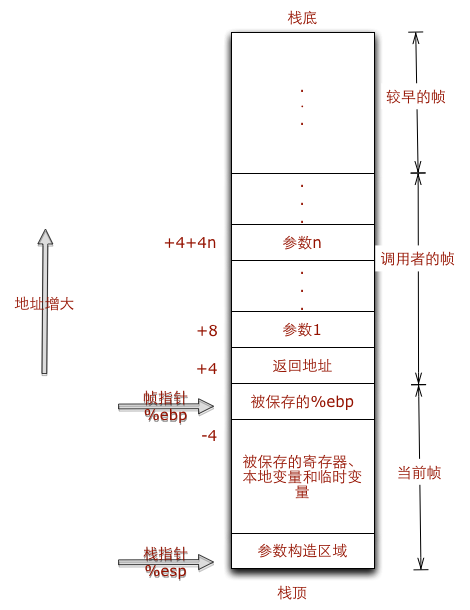
假如test.py用C语言来实现,会是下面这个样子:
const char *s = “hello”;
void func() {
printf(“%s\n”, s);
}
int main() {
func();
return 0;
}
const char *s = “hello”;
void func() {
printf(“%s\n”, s);
}
int main() {
func();
return 0;
}
Python虚拟机的原理就是模拟上述行为。当发生函数调用时,创建新的栈帧,对应Python的实现就是PyFrameObject对象。
7.1 PyFrameObject
typedef struct _frame {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
struct _frame *f_back; /* 调用者的帧 */
PyCodeObject *f_code; /* 帧对应的字节码对象 */
PyObject *f_builtins; /* 内置名字空间 */
PyObject *f_globals; /* 全局名字空间 */
PyObject *f_locals; /* 本地名字空间 */
PyObject **f_valuestack; /* 运行时栈底 */
PyObject **f_stacktop; /* 运行时栈顶 */
…….
}
typedef struct _frame {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
struct _frame *f_back; /* 调用者的帧 */
PyCodeObject *f_code; /* 帧对应的字节码对象 */
PyObject *f_builtins; /* 内置名字空间 */
PyObject *f_globals; /* 全局名字空间 */
PyObject *f_locals; /* 本地名字空间 */
PyObject **f_valuestack; /* 运行时栈底 */
PyObject **f_stacktop; /* 运行时栈顶 */
…….
}
那么对应Python的运行时栈就是这样子:

7.2 执行指令
执行test.py的字节码时,会先创建一个栈帧,以下用f表示当前栈帧,执行过程注释如下:
test.py的符号名集合和常量集合
co.co_names (‘s', 'func') co.co_consts (‘hello', <code object func at 0x2aaeeec57110, file ”test.py”, line 3>, None) co.co_names (‘s', 'func') co.co_consts (‘hello', <code object func at 0x2aaeeec57110, file ”test.py”, line 3>, None)
test.py的指令序列

上面的CALL_FUNCTION指令执行时,会创建新的栈帧,并执行func的字节码指令,以下用f表示当前栈帧,func的字节码执行过程如下:
func函数的符号名集合和常量集合
func.co_names (‘s',) func.co_consts (None,) func.co_names (‘s',) func.co_consts (None,)
func函数的指令序列

7.3 查看栈帧
如果你想查看当前栈帧,Python提供了sys._getframe()方法可以获取当前栈帧,你只需要在代码里加入代码如下:
def func(): import sys frame = sys._getframe() print frame.f_locals print frame.f_globals print frame.f_back.f_locals #你可以打印frame的各个域 print s
 Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AMIs it enough to learn Python for two hours a day? It depends on your goals and learning methods. 1) Develop a clear learning plan, 2) Select appropriate learning resources and methods, 3) Practice and review and consolidate hands-on practice and review and consolidate, and you can gradually master the basic knowledge and advanced functions of Python during this period.
 Python for Web Development: Key ApplicationsApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python for Web Development: Key ApplicationsApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMKey applications of Python in web development include the use of Django and Flask frameworks, API development, data analysis and visualization, machine learning and AI, and performance optimization. 1. Django and Flask framework: Django is suitable for rapid development of complex applications, and Flask is suitable for small or highly customized projects. 2. API development: Use Flask or DjangoRESTFramework to build RESTfulAPI. 3. Data analysis and visualization: Use Python to process data and display it through the web interface. 4. Machine Learning and AI: Python is used to build intelligent web applications. 5. Performance optimization: optimized through asynchronous programming, caching and code
 Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and EfficiencyApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and EfficiencyApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython is better than C in development efficiency, but C is higher in execution performance. 1. Python's concise syntax and rich libraries improve development efficiency. 2.C's compilation-type characteristics and hardware control improve execution performance. When making a choice, you need to weigh the development speed and execution efficiency based on project needs.
 Python in Action: Real-World ExamplesApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python in Action: Real-World ExamplesApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AMPython's real-world applications include data analytics, web development, artificial intelligence and automation. 1) In data analysis, Python uses Pandas and Matplotlib to process and visualize data. 2) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the creation of web applications. 3) In the field of artificial intelligence, TensorFlow and PyTorch are used to build and train models. 4) In terms of automation, Python scripts can be used for tasks such as copying files.
 Python's Main Uses: A Comprehensive OverviewApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python's Main Uses: A Comprehensive OverviewApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AMPython is widely used in data science, web development and automation scripting fields. 1) In data science, Python simplifies data processing and analysis through libraries such as NumPy and Pandas. 2) In web development, the Django and Flask frameworks enable developers to quickly build applications. 3) In automated scripts, Python's simplicity and standard library make it ideal.
 The Main Purpose of Python: Flexibility and Ease of UseApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AM
The Main Purpose of Python: Flexibility and Ease of UseApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AMPython's flexibility is reflected in multi-paradigm support and dynamic type systems, while ease of use comes from a simple syntax and rich standard library. 1. Flexibility: Supports object-oriented, functional and procedural programming, and dynamic type systems improve development efficiency. 2. Ease of use: The grammar is close to natural language, the standard library covers a wide range of functions, and simplifies the development process.
 Python: The Power of Versatile ProgrammingApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python: The Power of Versatile ProgrammingApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AMPython is highly favored for its simplicity and power, suitable for all needs from beginners to advanced developers. Its versatility is reflected in: 1) Easy to learn and use, simple syntax; 2) Rich libraries and frameworks, such as NumPy, Pandas, etc.; 3) Cross-platform support, which can be run on a variety of operating systems; 4) Suitable for scripting and automation tasks to improve work efficiency.
 Learning Python in 2 Hours a Day: A Practical GuideApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Learning Python in 2 Hours a Day: A Practical GuideApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMYes, learn Python in two hours a day. 1. Develop a reasonable study plan, 2. Select the right learning resources, 3. Consolidate the knowledge learned through practice. These steps can help you master Python in a short time.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor





