Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >深入解析Python中的变量和赋值运算符
深入解析Python中的变量和赋值运算符
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-06-10 15:07:501581browse
Python 变量类型
变量存储在内存中的值。这就意味着在创建变量时会在内存中开辟一个空间。
基于变量的数据类型,解释器会分配指定内存,并决定什么数据可以被存储在内存中。
因此,变量可以指定不同的数据类型,这些变量可以存储整数,小数或字符。
变量赋值
Python中的变量不需要声明,变量的赋值操作既是变量声明和定义的过程。
每个变量在内存中创建,都包括变量的标识,名称和数据这些信息。
每个变量在使用前都必须赋值,变量赋值以后该变量才会被创建。
等号(=)用来给变量赋值。
等号(=)运算符左边是一个变量名,等号(=)运算符右边是存储在变量中的值。例如:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- counter = 100 # 赋值整型变量 miles = 1000.0 # 浮点型 name = "John" # 字符串 print counter print miles print name
以上实例中,100,1000.0和"John"分别赋值给counter,miles,name变量。
执行以上程序会输出如下结果:
100 1000.0 John
多个变量赋值
Python允许你同时为多个变量赋值。例如:
a = b = c = 1
以上实例,创建一个整型对象,值为1,三个变量被分配到相同的内存空间上。
您也可以为多个对象指定多个变量。例如:
a, b, c = 1, 2, "john"
以上实例,两个整型对象1和2的分配给变量a和b,字符串对象"john"分配给变量c。
Python赋值运算符
以下假设变量a为10,变量b为20:
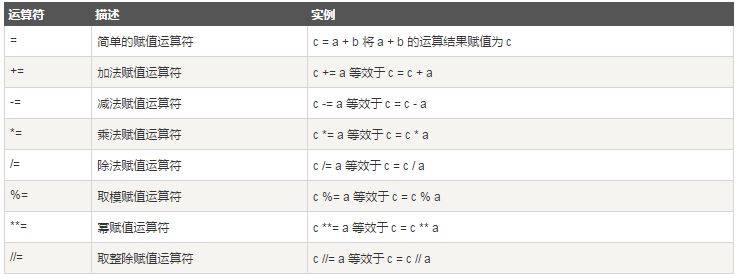
以下实例演示了Python所有赋值运算符的操作:
#!/usr/bin/python a = 21 b = 10 c = 0 c = a + b print "Line 1 - Value of c is ", c c += a print "Line 2 - Value of c is ", c c *= a print "Line 3 - Value of c is ", c c /= a print "Line 4 - Value of c is ", c c = 2 c %= a print "Line 5 - Value of c is ", c c **= a print "Line 6 - Value of c is ", c c //= a print "Line 7 - Value of c is ", c
以上实例输出结果:
Line 1 - Value of c is 31 Line 2 - Value of c is 52 Line 3 - Value of c is 1092 Line 4 - Value of c is 52 Line 5 - Value of c is 2 Line 6 - Value of c is 2097152 Line 7 - Value of c is 99864
Statement:
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn
Previous article:Python实现身份证号码解析Next article:Python2.x版本中基本的中文编码问题解决

