有同行问到了全局索引和本地索引如何选择,全局索引可以分区也可以不分区,而本地索引只包含各自分区的数据。 本地索引是分区的,而且是根据分区表的分区键值来对应,就是分区表的每个分区都有对应的分区索引,而全局索引可以分区也可以不分区,全局索引对应
有同行问到了全局索引和本地索引如何选择,全局索引可以分区也可以不分区,而本地索引只包含各自分区的数据。
本地索引是分区的,而且是根据分区表的分区键值来对应,就是分区表的每个分区都有对应的分区索引,而全局索引可以分区也可以不分区,全局索引对应的表可以是分区表也可以不是分区表。
比如这里t_global01是heap table并不是partition table
SQL> create table t_global01 as select * from dba_objects;
Table created.
SQL> CREATE INDEX index_t_objid
2 ON t_global01 (object_id) global
3 PARTITION BY RANGE(object_id)
4 (PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN(10000),
5 PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN(20000),
6 PARTITION pmax VALUES LESS THAN(MAXVALUE));
Index created.
索引又可以分为前缀索引和非前缀索引,前缀索引是指索引的分区键包含在索引中,并且是索引的前导列,而非前缀索引则是分区键不在索引中或者不是索引的前导列,本地索引可以建立前缀索引和非前缀索引,而全局索引只能建立前缀索引。
SQL> create table t_local01 partition by range(object_id)
2 (partition p1 values less than(10000),
3 partition p2 values less than(20000),
4 partition p3 values less than(30000),
5 partition p4 values less than(40000),
6 partition p5 values less than(maxvalue))
7 as select * from dba_objects;
Table created.
建立本地的前缀索引
SQL> CREATE INDEX index_t_pre01 on t_local01(object_id,object_name) local;
Index created.
建立本地的非前缀索引
SQL> CREATE INDEX index_t_nonpre01 on t_local01(object_name) local;
Index created.
全局索引不允许建立非前缀索引
SQL> create index ind_t_objid_nonpre on t_local01(object_id) global
2 partition by range(data_object_id)
3 (partition p1 values less than(10000),
4 partition pmax values less than(maxvalue));
partition by range(data_object_id)
*
ERROR at line 2:
ORA-14038: GLOBAL partitioned index must be prefixed
分区表的全局索引可能会因为分区表的ddl而导致全局索引失效,这个需要我们特别注意,一般来说oltp建立全局索引,而在olap系统建立本地索引。
Partitioned Indexes: Global, Local, Prefixed and Non-Prefixed (文档 ID 69374.1)
To illustrate the usefulness of global indexes, imagine that we have a large
fact table partitioned on a DATE column. We frequently need to search the table
on a VARCHAR2 column (VCOL) which is not part of the table's partition key.
Assume that there are currently 12 partitions in the table.
We could use 2 possible methods:
A local non-prefixed index on VCOL:
| |
------- -------
| | (10 more | |
Values: A.. Z.. partitions here) A.. Z..
Or a global prefixed index on VCOL:
| |
------- -------
| | (10 more | |
Values: A.. D.. partitions here) T.. Z..
A global prefixed index would usually be the best choice for a unique index on
our example VCOL column. For nonunique indexes, the issue is whether we can use
parallel index searches (local non-prefixed) or whether we need a serial search,
even at the expense of the greater maintenance problems of global indexes.
这里提出了对于唯一列建立全局索引较合适
Common Questions on Indexes on Partitioned Table (文档 ID 1481609.1)记录了local index和global index的适用特点
What are the performance implications of local indexes
Partition elimination/pruning during SQLs against the partitioned table with predicate on the partition key (prefixed more often allows for partition elimination than non prefixed).
这里提出了如果查询条件中有分区键,建立本地索引可以让分区裁剪生效(前缀索引通常比非前缀索引更容易发生分区裁剪)
Non prefixed local index is useful if it is important to have quick access according to a column which is not the partition key (e.g. look up for value account_number column, hence the account_number is placed as a leading column of the index), while it is also important to have the index equipartitioned with the table e.g. to support the time interval for rolling out old data and rolling in new data (e.g. partition key is time_id column, rolling out/in data is done by partition maintenance commands). This scenario often happens in historical databases.
而非前缀索引通常在查询中没有分区键过滤时比较适用。
下面来通过测试来看看上面文章提供的结论:
SQL> create table tab01
2 partition by range(object_id)
3 (partition p1 values less than(10000),
4 partition p2 values less than(20000),
5 partition p3 values less than(30000),
6 partition p4 values less than(40000),
7 partition p5 values less than(maxvalue))
8 as
9 select * from dba_objects;
Table created.
SQL> create index ind_type_local_pre on tab01(object_id,object_type) local;
Index created.
SQL> create index ind_type_local_nonpre on tab01(object_type) local;
Index created.
SQL> analyze table tab01 compute statistics;
Table analyzed.
上面已经建立了前缀和非前缀的本地索引,然后如果我们的查询中没有分区键,那么看看两个索引的实用性
SQL> select /*+index(tab01 ind_type_local_nonpre)*/* from tab01 where object_typ
e='INDEX';
1726 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 4022647995
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Byt
es | Cost (%CPU)| Time | Pstart| Pstop |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1481 | 1
27K| 74 (0)| 00:00:01 | | |
| 1 | PARTITION RANGE ALL | | 1481 | 1
27K| 74 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 5 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY LOCAL INDEX ROWID| TAB01 | 1481 | 1
27K| 74 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 5 |
|* 3 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IND_TYPE_LOCAL_NONPRE | 1481 |
| 10 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='INDEX')
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
1 recursive calls
0 db block gets
353 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
87737 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
1757 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
117 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1726 rows processed
SQL> select /*+index(tab01 ind_type_local_pre)*/* from tab01 where object_type='
INDEX';
1726 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1706313756
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes
| Cost (%CPU)| Time | Pstart| Pstop |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1481 | 127K
| 198 (1)| 00:00:03 | | |
| 1 | PARTITION RANGE ALL | | 1481 | 127K
| 198 (1)| 00:00:03 | 1 | 5 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY LOCAL INDEX ROWID| TAB01 | 1481 | 127K
| 198 (1)| 00:00:03 | 1 | 5 |
|* 3 | INDEX FULL SCAN | IND_TYPE_LOCAL_PRE | 1481 |
| 176 (1)| 00:00:03 | 1 | 5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='INDEX')
filter("OBJECT_TYPE"='INDEX')
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
1 recursive calls
0 db block gets
521 consistent gets
174 physical reads
0 redo size
87699 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
1757 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
117 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1726 rows processed
这里看来对于本地索引,在查询条件中没有分区键时非前缀索引比较实用。
而如果有分区键的查询,本地索引是可以走分区裁剪的
SQL> select /*+index(tab01 ind_type_local_pre)*/* from tab01 where object_type='
INDEX' and object_id
920 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 4238522555
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes
| Cost (%CPU)| Time | Pstart| Pstop |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 281 | 21075
| 34 (0)| 00:00:01 | | |
| 1 | PARTITION RANGE SINGLE | | 281 | 21075
| 34 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY LOCAL INDEX ROWID| TAB01 | 281 | 21075
| 34 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 |
|* 3 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IND_TYPE_LOCAL_PRE | 281 |
| 30 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='INDEX' AND "OBJECT_ID" filter("OBJECT_TYPE"='INDEX')
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
244 recursive calls
0 db block gets
244 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
45241 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
1163 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
63 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
920 rows processed
SQL> select /*+index(tab01 ind_type_local_nonpre)*/* from tab01 where object_typ
e='INDEX' and object_id
920 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1322437935
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Byt
es | Cost (%CPU)| Time | Pstart| Pstop |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 281 | 210
75 | 21 (0)| 00:00:01 | | |
| 1 | PARTITION RANGE SINGLE | | 281 | 210
75 | 21 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY LOCAL INDEX ROWID| TAB01 | 281 | 210
75 | 21 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 |
|* 3 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IND_TYPE_LOCAL_NONPRE | 281 |
| 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='INDEX')
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
1 recursive calls
0 db block gets
182 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
45241 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
1163 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
63 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
920 rows processed
这里我们看出执行计划中都出现了PARTITION RANGE SINGLE单个分区扫描(pstart和pstop都是1),这个是因为执行计划的INDEX RANGE SCAN索引范围扫描时pstart 1和pstop 1,此时索引扫描就只会扫描指定的索引分区,这个也就是索引的分区裁剪,当然还有表的分区裁剪,关于分区裁剪的内容小鱼后面有时间会列出来单独讨论。
而如果是全局索引,索引默认不分区,所以也就无法发生索引的分区裁剪:
SQL> drop index ind_type_local_nonpre;
Index dropped.
SQL> create index ind_type_global on tab01(object_type) global;
Index created.
SQL> select /*+index(tab01 ind_type_global)*/* from tab01 where object_type='IND
EX' and object_id
920 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3954671853
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | C
ost (%CPU)| Time | Pstart| Pstop |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 281 | 21075 |
69 (0)| 00:00:01 | | |
|* 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY GLOBAL INDEX ROWID| TAB01 | 281 | 21075 |
69 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IND_TYPE_GLOBAL | 1481 | |
5 (0)| 00:00:01 | | |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter("OBJECT_ID" 2 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='INDEX')
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
1 recursive calls
0 db block gets
185 consistent gets
6 physical reads
0 redo size
45241 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
1163 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
63 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
920 rows processed
What are the performance implications of global indexes?
Global index can be useful where rapid access, data integrity, and availability are important. In an OLTP system, a table may be partitioned by one key, for example, the employees.department_id column, but an application may need to access the data with many different keys, for example, by employee_id or job_id. Global indexes can be useful in this scenario as global indexes are prefixed and can provide better performance than local nonprefixed indexes because they minimize the number of index partition probes (cf. local prefixed more often allows for partition elimination than non prefixed mentioned in the previous section).
全局索引多用于OLTP系统,可以快速的返回查询的数据,特别适用于查询条件中不包含分区键的查询,这种情况全局索引相比本地索引更加高效。
Global indexes are harder to manage than local indexes. At partition maintenance of the table, all partitions of a global index are affected.
这里提出全局索引难以维护,如果分区修改了,所有分区的索引都会影响
Partition elimination/pruning during SQLs against the partitioned table: prefixed - always allows for partition elimination.
同样全局索引也是可以发生分区裁剪的
SQL> create table t_global01 as select * from dba_objects;
Table created.
SQL> CREATE INDEX index_t_objid
2 ON t_global01 (object_id) global
3 PARTITION BY RANGE(object_id)
4 (PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN(10000),
5 PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN(20000),
6 PARTITION pmax VALUES LESS THAN(MAXVALUE));
Index created.
SQL> select * from t_global01 where object_id
9568 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1223163610
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CP
U)| Time | Pstart| Pstop |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 9194 | 897K| 177 (
0)| 00:00:03 | | |
| 1 | PARTITION RANGE SINGLE | | 9194 | 897K| 177 (
0)| 00:00:03 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T_GLOBAL01 | 9194 | 897K| 177 (
0)| 00:00:03 | | |
|* 3 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | INDEX_T_OBJID | 9194 | | 43 (
0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("OBJECT_ID"
这里看出也发生了所谓的分区裁剪,index range scan的pstart和pstop都是1,说明是扫描了索引的一个分区,这也和上面partition range single相对应(出现partition range single并不一定表示该表是分区表,有可能有分区的索引)
The hash index partitioning can improve performance of indexes where a small number leaf blocks in the index have high contention in multiuser OLTP environment. In some OLTP applications, index insertions happen only at the right edge of the index. This situation could occur when the index is defined on monotonically increasing columns (e.g. column value is populated by a sequence). In such situations, the right edge of the index becomes a hotspot because of contention for index pages, buffers, latches for update, and additional index maintenance activity, which results in performance degradation.
这里提出了一个hash index partition,在高并发情况下,索引的数据会不停往右边倾斜(比如列是序列填充时),这种情况下索引右边叶块会成为热点块,造成大量的buffer latches竞争和额外的维护(比如索引分裂)而导致性能下降。
关于本地索引和全局索引小鱼也没有较多的实战案例,个人而言小鱼维护的大多是OLTP系统,所以一般都是建立的全局索引,可以参考以下建立:
Global index和local index适用范围
non-prefixed Local indexes特别适用于基于历史数据查询分析的数据库,在这样的数据库中,历史数据一般都是根据时间来分区的。
prefixed Local index适用于对分区主键进行索引,可以明显减少查询所搜索到的分区数目,极大的加快查询速度。
Global prefixed index适用于对非分区主键进行索引,特别对于唯一列的查询是比较适合建立全局索引的,但是Global pre- fixed index难以维护,任何对基表的分区信息的修改都会不可避免的导致索引的失效。
原文地址:全局索引和本地索引分析, 感谢原作者分享。
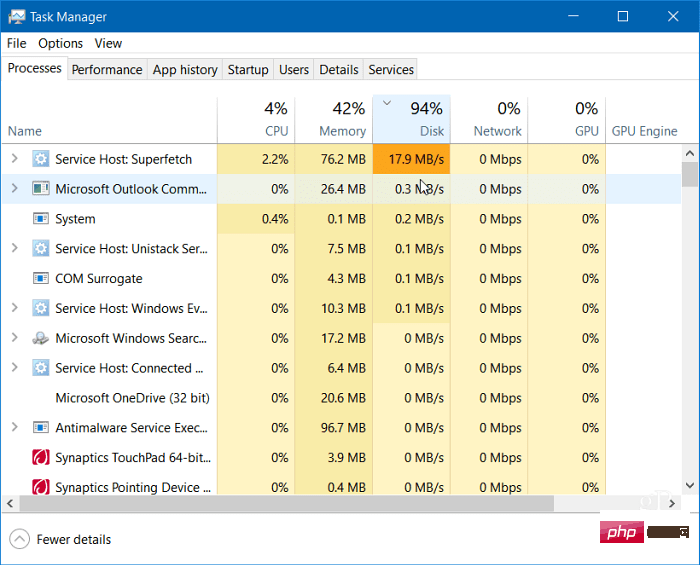 如何在 Windows 11 上修复 100% 的磁盘使用率Apr 20, 2023 pm 12:58 PM
如何在 Windows 11 上修复 100% 的磁盘使用率Apr 20, 2023 pm 12:58 PM如何在Window11上修复100%的磁盘使用率查找导致100%磁盘使用的有问题的应用程序或服务的直接方法是使用任务管理器。要打开任务管理器,请右键单击开始菜单并选择任务管理器。单击磁盘列标题,查看占用最多资源的内容。从那里开始,您将很好地了解从哪里开始。但是,问题可能比仅仅关闭应用程序或禁用服务更严重。继续阅读以查找问题的更多潜在原因以及如何解决这些问题。禁用SuperfetchSuperfetch功能(在Windows11中也称为SysMain)有助于通过访问预取文件来减少启动时
 如何在 Windows 11 中隐藏文件和文件夹并从搜索中移除?Apr 26, 2023 pm 11:07 PM
如何在 Windows 11 中隐藏文件和文件夹并从搜索中移除?Apr 26, 2023 pm 11:07 PM<h2>如何在Windows11上从搜索中隐藏文件和文件夹</h2><p>我们首先要看的是自定义Windows搜索文件的位置。通过跳过这些特定位置,您应该可以更快地看到结果,同时还可以隐藏您想要保护的任何文件。</p><p>如果要从Windows11上的搜索中排除文件和文件夹,请使用以下步骤:</p><ol&
 以下是6种修复Windows 11搜索栏不可用的方法。May 08, 2023 pm 10:25 PM
以下是6种修复Windows 11搜索栏不可用的方法。May 08, 2023 pm 10:25 PM如果您的搜索栏在Windows11中不起作用,有几种快速方法可以立即启动并运行!任何微软操作系统有时都可能遇到故障,最新的操作系统不能免除该规则。此外,正如Reddit上的用户u/zebra_head1所指出的那样,同样的错误出现在Windows11的22H2Build22621.1413上。用户抱怨切换任务栏搜索框的选项随机消失。因此,您必须为任何情况做好准备。为什么我无法在计算机上的搜索栏中键入内容?无法在计算机上键入可归因于不同的因素和过程。以下是您应该注意的一些事项:Ctfmon.
 Windows 11 Outlook 搜索不工作:6 个修复方法Apr 22, 2023 pm 09:46 PM
Windows 11 Outlook 搜索不工作:6 个修复方法Apr 22, 2023 pm 09:46 PM在Outlook中运行搜索和索引疑难解答您可以开始的更直接的修复之一是运行搜索和索引疑难解答。要在Windows11上运行疑难解答,请执行以下操作:单击开始按钮或按Windows键并从菜单中选择设置。当设置打开时,选择系统>疑难解答>其他疑难解答。在右侧向下滚动,找到SearchandIndexing,然后单击Run按钮。选择Outlook搜索不返回结果并继续屏幕上的说明。当您运行它时,疑难解答程序将自动识别并修复问题。运行疑难解答后,打开Outlook并查看搜索是否正常。如
 Vue中如何实现全局loading效果Jun 11, 2023 am 09:05 AM
Vue中如何实现全局loading效果Jun 11, 2023 am 09:05 AM在前端开发中,我们经常会有一种场景:用户在与网页交互过程中需要等待数据的加载,此时通常会有一个loading效果显示,提醒用户等待。在Vue框架中,实现一个全局loading效果并不困难,下面我们来介绍一下如何实现。第一步:创建Vue插件我们可以创建一个名为loading的Vue插件,该插件可以在所有的Vue实例中引用。在插件中,我们需要实现以下两个方法:s
 Python程序将多个元素插入到数组中的指定索引位置Sep 03, 2023 pm 10:13 PM
Python程序将多个元素插入到数组中的指定索引位置Sep 03, 2023 pm 10:13 PM数组是以有组织的方式存储的同类数据元素的集合。数组中的每个数据元素都由一个索引值来标识。Python中的数组Python没有原生的数组数据结构。因此,我们可以使用列表数据结构来替代数组。[10,4,11,76,99]同时我们可以使用PythonNumpy模块来处理数组。由numpy模块定义的数组是−array([1,2,3,4])Python中的索引从0开始,因此可以使用各自的索引值来访问上述数组元素,如0、1、2、直到n-1。在下面的文章中,我们将看到在指定索引处插入多个元素的不同方法。输入输
 如何在MySQL中使用索引来提高查询性能?Jul 30, 2023 pm 10:43 PM
如何在MySQL中使用索引来提高查询性能?Jul 30, 2023 pm 10:43 PM如何在MySQL中使用索引来提高查询性能?引言:MySQL是一款常用的关系型数据库,随着数据量的增加,查询性能成为一个重要的考量因素。在MySQL中,索引是提高查询性能的关键因素之一。本文将介绍什么是索引,为什么使用索引可以提高查询性能,并给出一些在MySQL中使用索引的示例代码。一、什么是索引?索引是对数据库表中一个或多个列的值进行排序的一种结构,它可以快
 深入剖析MySQL索引优化策略Jun 14, 2023 pm 12:01 PM
深入剖析MySQL索引优化策略Jun 14, 2023 pm 12:01 PM作为一种常用的关系型数据库,MySQL在今天的互联网应用中扮演着至关重要的角色。而在MySQL优化策略中,索引的使用更是至关重要。在MySQL中,索引是一种数据结构,用于快速定位数据中的特定行。使用索引可以大大提高查询效率,减少数据库处理数据的时间和资源。但不正确的索引使用方式,同样会导致数据库性能的下降。下面我们来深入剖析MySQL索引的优化策略,帮助您更


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.






