- Super Cool Page Title
Figure 2-1: Using title tags after breaking away from styles Page content
Screen readers, PDAs, mobile phones and other visual and non-visual browsers can also recognize and correctly process the content of the title tag, highlighting its importance above other content on the page. Use < ;span> tag, browsers that don’t support (or can’t support) CSS won’t think it’s anything special.
Annoying default styles
In the history of web design, designers People avoid using title tags simply because without styling, title tags look like monsters. Choose one of the two, and some of them avoid usingbecause the default font size is too large. Or
instead use a smaller font size and a higher label title tag.
However, there is an important point worth emphasizing. We can easily change the style of these title tags according to our own preferences by defining css - for example For example,may not necessarily be a giant thing that takes up half the screen. Later, I will demonstrate how to simply use CSS styles to define title tags to help you overcome your fear of
.
Friendly to search engines
This is the biggest advantage. Search engines like title tags very much. Bold fonts in tags or paragraphs do not mean much to search engines. Using the correct~
tag title does not take much time, but it can help search engines index your page and make it easier for users to find your page.
Search engine robots attach great importance to The content in the title tag, maybe, you will want to pile a few keywords in it. After they process theand <meta> tags, they will then process the title tag in the page content. If If you do not use title tags on your page, then these keywords in your title will not attract their attention and will be ignored by them.<br>So, it only takes a little time to make it easier for others Finding your page by content sounds good, right? <br><strong>A side note on tag order</strong><br>In the example above, the most important thing on the page is the title, because it is The title of the entire document. Therefore, we will use the most important title tag <h1>. According to W3C, some people think that skipping the title layer is not a good practice. For example, suppose we have the following web page: <br><span class="code"><h1>Super Cool Page Title" class="fixed_tab_a">, even if all style definitions are removed from the page, You can still see the structure of the document, because the correct title tag describes the meaning of the content, not the presentation. (Figure 2-1)<br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/d403782309c7ce2ffc51499ef1aa3159-0.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-1: Using title tags after breaking away from styles Page content<br>Screen readers, PDAs, mobile phones and other visual and non-visual browsers can also recognize and correctly process the content of the title tag, highlighting its importance above other content on the page. Use < ;span> tag, browsers that don’t support (or can’t support) CSS won’t think it’s anything special.<br><strong>Annoying default styles</strong><br>In the history of web design, designers People avoid using title tags simply because without styling, title tags look like monsters. Choose one of the two, and some of them avoid using <h1> because the default font size is too large. Or <h2> instead use a smaller font size and a higher label title tag. <br> However, there is an important point worth emphasizing. We can easily change the style of these title tags according to our own preferences by defining css - for example For example, <h1> may not necessarily be a giant thing that takes up half the screen. Later, I will demonstrate how to simply use CSS styles to define title tags to help you overcome your fear of <h1>.<br><strong>Friendly to search engines</strong><br>This is the biggest advantage. Search engines like title tags very much. Bold fonts in <span> tags or paragraphs do not mean much to search engines. Using the correct <h1>~<h6> tag title does not take much time, but it can help search engines index your page and make it easier for users to find your page.<br>Search engine robots attach great importance to The content in the title tag, maybe, you will want to pile a few keywords in it. After they process the <title> and <meta> tags, they will then process the title tag in the page content. If If you do not use title tags on your page, then these keywords in your title will not attract their attention and will be ignored by them.<br>So, it only takes a little time to make it easier for others Finding your page by content sounds good, right? <br><strong>A side note on tag order</strong><br>In the example above, the most important thing on the page is the title, because it is The title of the entire document. Therefore, we will use the most important title tag <h1>. According to W3C, some people think that skipping the title layer is not a good practice. For example, suppose we have the following web page: <br><span class="code"><h1>Super Cool Page Title</a></li><li><span></span><a href="#tags-in-the-page-if-you-use-an-external-style-sheet-you-can-apply-the-style-to-the-entire-website-If-you-want-to-change-the-entire-website-later-For-each-h-color-size-or-font-you-only-need-to-modify-a-few-css-rules-and-the-effects-of-the-modifications-can-be-seen-immediately-This-sounds-very-tempting-right-br-Let-s-super-Cool-title-to-tell-ourselves-br-span-class-code-h-Super-Cool-Page-Title" title=" tags in the page (if you use an external style sheet, you can apply the style to the entire website). If you want to change the entire website later For each <h1> color, size or font, you only need to modify a few css rules, and the effects of the modifications can be seen immediately! This sounds very tempting, right? <br> Let’s super Cool title to tell ourselves:<br><span class="code"><h1>Super Cool Page Title" class="fixed_tab_a"> tags in the page (if you use an external style sheet, you can apply the style to the entire website). If you want to change the entire website later For each <h1> color, size or font, you only need to modify a few css rules, and the effects of the modifications can be seen immediately! This sounds very tempting, right? <br> Let’s super Cool title to tell ourselves:<br><span class="code"><h1>Super Cool Page Title</a></li></ul></div><div class="m_editormain12_close"><a href="" title="" title="" id="fixed_tab_close">close</a></div></div></div><div class="Article_Details_main1M"><div class="phpgenera_Details_mainL1"><a href="https://m.php.cn/" title="Home" class="phpgenera_Details_mainL1a">Home</a><img class="lazy" data-src="/static/imghwm/top_right.png" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="" /><a href="https://m.php.cn/web-designer.html" class="phpgenera_Details_mainL1a">Web Front-end</a><img class="lazy" data-src="/static/imghwm/top_right.png" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="" /><a href="https://m.php.cn/div-tutorial.html" class="phpgenera_Details_mainL1a">HTML Tutorial</a><img class="lazy" data-src="/static/imghwm/top_right.png" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="" /><span>Markup language - title_HTML/Xhtml_web page production</span></div><div class="Articlelist_txts"><div class="Articlelist_txts_info"><a href="" title="" class="Articlelist_txts_title">Markup language - title_HTML/Xhtml_web page production</a><div class="Articlelist_txts_info_head"><div class="author_info"><a href="https://m.php.cn/member/1.html" class="author_avatar"><img class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/avatar/000/000/001/6251028808086368.png" alt="PHP中文网" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="author avatar" onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"></a><div class="author_detail"><a href="https://m.php.cn/member/1.html" class="author_name">PHP中文网</a></div></div></div><span class="Articlelist_txts_time">May 16, 2016 pm 04:45 PM</span><div class="Articlelist_txts_infos"><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss on">css</span><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss ">use</span><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss ">icon</span><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss ">us</span><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss ">Label</span><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss ">mark</span><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss ">title</span><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss ">style</span><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss ">language</span><span class="Articlelist_txts_infoss ">page</span></div></div></div><hr /><div class="article_main"><p><strong>Standardized Design Solutions - Markup Language and Style Handbook<br>Web Standards Solutions The Markup and Style Handbook</strong><br><strong>Part 1: Get Down With Markup Starting from Markup Syntax</strong><br><strong>Chapter2 Titles</strong><br><strong>Overview:</strong><br>Not only do all web pages need titles, but if marked up correctly, they can add to a web design and usability Quite a few. <br> In terms of appearance, the title of a web page usually uses a larger font size, and may use a different color or font from the main text. The function of the title is to "briefly describe the topic discussed in the following chapters" , W3C describes it this way - Display a summary of each paragraph in a web page. <br> How to create a page title to make the most effective use of the information we want to display? In this chapter, we will study several commonly used methods for processing titles. methods, try to find one of them that is most helpful to us, and then we will use some CSS tips and tricks to decorate the best method. <br><strong>The best way to create a document title What is a good way?</strong><br>Before answering this question, let us assume that we are now placing the title at the top of the document and let's look at three ways to achieve a similar effect.<br><strong>Method A: Does it make sense?</strong><br><span class="code"><span class="heading">Super Cool Page Title</span></span><br>Although the <span> tag is used in some The occasion is a convenient tag, but for the page title, it doesn't mean much. The only advantage of using this method is that we can specify a css style for the heading class to make the text look like a title. <br> <span class="code">.heading {<br> font-size: 24px;<br> font-weight: bold;<br> color: blue;<br> }</span><br>Now, all titles marked with heading class It will all become bigger, thicker, and blue, which is great, right? But what happens if someone visits this page using a browser that does not support CSS? <br> For example, if we put the CSS style in the old in an external style sheet file that the browser does not support — or what happens when a screen reader reads the page for users with disabilities? Users accessing the page through these means will not be able to see (hear) the title and body text. The difference. Annotation methods such as <br>class="heading" slightly describe the meaning of the tag content, but <span> is just a general-purpose container, which only allows most browsers to change the default display style. .<br>When the search engine crawls this page, it will skip the <span> tag as if it was not there, and will not increase the weight of the keywords that may be included in it. This will be discussed later in this chapter. Mention more about the relationship between search engines and page titles. <br> Finally, since the <span> tag is an inline element, we mostly need to place the content of method A into another block-level container, for example or <p> so that it can occupy a line of its own. This will generate a lot of unnecessary code. Even if you add the necessary containers, browsers that do not support CSS will still display the text in its original way for users to see. There is no difference between the title and the text.<br> #p#<br><strong>Method B: Combination of P and B</strong><br><span class="code"><p><b>Super Cool Page Title</b></p></span> <br>Method B uses the paragraph tag, which will give us the block-level element display we want, and the <b> tag will make the text bold (on most browsers) — but When we mark important titles in this way, we still have to face the same lack of semantic results. <br> Unlike method A, the existence of the <b> tag even if it lacks the definition of CSS style, in most browsers The text will still be presented in bold style. However, like the <span> tag, search engines will not increase the keyword weight for bold text within the paragraph. <br><strong>It is difficult to add styles</strong><br>Using a simple combination of p and b tags prevents us from adding a different style to this title from other paragraphs. Perhaps we want to emphasize the title in a unique way and add definition and structure to the page content - but using After using this method to make it appear bold, we have no way to do these things.<br><strong>Method C: Style and substance</strong><br><span class="code"><h1 id="Super-Cool-Page-Title">Super Cool Page Title</h1></span><br>Haha, here comes our good friend the title tag. Title tags have been around since the beginning, but many web designers still fail to use them in a consistent way. If used properly, title tags can Provides an anchor point for page content and provides a flexible, indexable, and style-changeable structure. <br> From the perspective of the tags themselves, you will love its simplicity. They do not require additional container tags. You It can even be said that this method can save some bytes compared to the first two methods, which may be ignored, but every byte smaller is a change.<br><h1> to <h6> represent six layers of headings respectively, from the most important <h1> to the least important <h6>. They are block-level elements themselves and can be self-contained without an additional container. One line, simple and efficient - the best tool for the job.<br><strong>Easy to define styles</strong><br>Because the <h1> tag has a unique meaning, unlike <b> Or the </b> </h1> </h6> </h1> </h6> </h1> <p> tag will be used multiple times in the text, so we can use CSS to add various styles to it (we will discuss it in depth in "More Techniques" in this chapter). <br> More importantly, even without adding any style definitions, the title tag clearly looks like a title! The browser will use large fonts and bold fonts to render the content of </p> <h1>, even if all style definitions are removed from the page, You can still see the structure of the document, because the correct title tag describes the meaning of the content, not the presentation. (Figure 2-1)<br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/d403782309c7ce2ffc51499ef1aa3159-0.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-1: Using title tags after breaking away from styles Page content<br>Screen readers, PDAs, mobile phones and other visual and non-visual browsers can also recognize and correctly process the content of the title tag, highlighting its importance above other content on the page. Use < ;span> tag, browsers that don’t support (or can’t support) CSS won’t think it’s anything special.<br><strong>Annoying default styles</strong><br>In the history of web design, designers People avoid using title tags simply because without styling, title tags look like monsters. Choose one of the two, and some of them avoid using <h1> because the default font size is too large. Or <h2> instead use a smaller font size and a higher label title tag. <br> However, there is an important point worth emphasizing. We can easily change the style of these title tags according to our own preferences by defining css - for example For example, <h1> may not necessarily be a giant thing that takes up half the screen. Later, I will demonstrate how to simply use CSS styles to define title tags to help you overcome your fear of <h1>.<br><strong>Friendly to search engines</strong><br>This is the biggest advantage. Search engines like title tags very much. Bold fonts in <span> tags or paragraphs do not mean much to search engines. Using the correct <h1>~<h6> tag title does not take much time, but it can help search engines index your page and make it easier for users to find your page.<br>Search engine robots attach great importance to The content in the title tag, maybe, you will want to pile a few keywords in it. After they process the <title> and <meta> tags, they will then process the title tag in the page content. If If you do not use title tags on your page, then these keywords in your title will not attract their attention and will be ignored by them.<br>So, it only takes a little time to make it easier for others Finding your page by content sounds good, right? <br><strong>A side note on tag order</strong><br>In the example above, the most important thing on the page is the title, because it is The title of the entire document. Therefore, we will use the most important title tag <h1>. According to W3C, some people think that skipping the title layer is not a good practice. For example, suppose we have the following web page: <br><span class="code"><h1 id="Super-Cool-Page-Title">Super Cool Page Title</h1></span><br>Then the next title (if it is not another <h1>) should be <h2>, and then Use <h3> and so on, you may not skip a certain level of headings, for example, use <h3> directly after <h1>. I agree, and think that the structure and outline are the same, and each one should be used in order. Levels, this allows you to easily add titles and styles to existing pages. At the same time, it is less likely to use up all the title levels. <br> As mentioned earlier, designers may use represents the most important title on the page, just because its default font size is not as scary as <h1>. But remember, write the structure first, and then adjust the style. We can adjust it at any time according to our own Prefer changing the font size of the title tag through css.<br> #p#<br><strong>Summary</strong><br>Let’s briefly review why it is better to use title tags (<h1> to <h6>) to mark the titles within the page.<br><strong>Method A:</strong><br>Visual browsers will display the title in the same style as normal text when the css function is disabled or does not support it. Non-visual browsers have no idea about the relationship between the title and the text. The difference. <br>Search engines will not pay special attention to titles marked with <span><br>We can develop unique styles, but when we add titles, we will be trapped by the heading class. <br><strong>Method B:</strong><br>The visual browser will only display content in bold and continue to use the default font size. <br>We cannot add a unique style to the title that is different from the body text<br>Search engines also do not pay special attention to <p> <b>The content of the created title. <br><strong>Method C: </strong><br> conveys the exact meaning of the text in the title tag. <br>Whether it is a visual or non-visual browser, it will process the title content correctly no matter what format it reads<br>Search engines will pay attention to the keywords in the title tag.<br><strong>Extension of techniques</strong><br>Here we will adopt method C and use it to experiment with some simple css styles. We will fully utilize the uniqueness of the title tag Advantages of sex. We can use the title tag with great peace of mind, because the title content can be processed correctly no matter what browser and device it is on. Next, let’s dress it up and take it to the street (if you can bring it If you go out on the street with an html tag...)<br><strong>Simple style</strong><br>Using css, the simplest and easiest effect is to set different fonts for the title. We can write a css rules, and then apply them to all <h1> tags in the page (if you use an external style sheet, you can apply the style to the entire website). If you want to change the entire website later For each <h1> color, size or font, you only need to modify a few css rules, and the effects of the modifications can be seen immediately! This sounds very tempting, right? <br> Let’s super Cool title to tell ourselves:<br><span class="code"><h1 id="Super-Cool-Page-Title">Super Cool Page Title</h1></span><br>Let’s use css to change its color, font and size:<br><span class="code">h1 {<br> font-family: Arial, sans-serif;<br> font-size: 24px;<br> color: #369;<br> }</span><br>Just like we just did What I said is very simple. All <h1> on the entire page are set to 24 pixels in size and blue Arial (or the default sans-serif) font, as shown in Figure 2-2: <br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/d403782309c7ce2ffc51499ef1aa3159-1.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-2: Title style example<br>Next we continue to add a 1 pixel wide gray border under the title text (Figure 2-3):<br><span class="code">h1 {<br> font- family: Arial, sans-serif;<br> font-size: 24px;<br> color: #369;<br> padding-bottom: 4px;<br> border-bottom: 1px solid #999;<br> } </span><br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/abb61a1e8f6ba9fd01fda63afb390085-2.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-3: Example of title style with gray bottom border <br> We left some more inner patches at the bottom of the text so that the lower border will not have difficulty breathing. Because of the title Labels are block-level elements, so the border will not only fill the bottom of the text, but will continue to extend to the right until it fills the entire page width. <br> It is also worth mentioning that we use the abbreviation of border - that is, in a line The declaration also defines width, style, and color. You can try other settings to see what other effects there are.<br> #p#<br><strong>Adding a background</strong><br>The background can add a subtle effect to the title. As long as we add the background color and some white space, we can create a fresh and fresh one without using pictures. Title style. For example: <br><span class="code">h1 {<br> font-family: Arial, sans-serif;<br> font-size: 24px;<br> color: #fff;<br> padding: 4px;<br> background-color: #696;<br> }</span><br>We change the text in the title to white, leave a 4-pixel inner patch space around it, and change the background to green. For example As shown in Figure 2-4, there will be a wide green band with the color of a pool table running through the entire page, dividing the two paragraphs. <br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/abb61a1e8f6ba9fd01fda63afb390085-3.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-4: Setting the inner patch and background color Title example <br><strong>Background and border</strong><br> Just add a thin border under the title and a light background, and you can create a three-dimensional effect without using an image. .<br>This css is very similar to the one above, only changing a few colors and adding a 2-pixel border at the bottom<br><span class="code">h1 {<br> font-family: Arial, sans-serif; <br> font-size: 24px;<br> color: #666;<br> padding: 4px;<br> background-color: #ddd;<br> border-bottom: 2px solid #ccc;<br> } </span><br>By using the same color with different brightness, you can create a realistic three-dimensional effect as shown in Figure 2-5: <br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/abb61a1e8f6ba9fd01fda63afb390085-4.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-5: Setting the background and bottom edge The title <br><strong>Tile background</strong><br>If you use pictures, you can be more creative. Let us use photoshop to create a 10X10 small picture with a black border on the top. Then the following is the gray gradient from top to bottom (as shown in Figure 2-6): <br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/fa27560271db57237aa907152e753926-5.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-6 Small picture created with Photoshop<br>We can use css to put this small picture at the bottom of our <h1>:<br><span class="code">h1 {<br> font -family: Arial, sans-serif;<br> font-size: 24px;<br> color: #369;<br> padding-bottom: 14px;<br> background: url(10x10.gif) repeat-x bottom ;<br> }</span><br>Set repeat-x to make the browser only arrange the background image in the horizontal direction (the opposite repeat-y is to arrange it in the vertical direction), and we set In order to place the picture at the bottom of the title, and add some lower inner patches to adjust the distance between the picture and the text (Figure 2-7) <br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/fa27560271db57237aa907152e753926-6.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-7: Set Example of a title with a tiled background<br><strong>Icon for easy replacement</strong><br>We can also use the cssdebackground attribute to set a small icon to the left of the text to replace the hard-coded image tag. Add a small decorative icon to the title. This method will make it very easy to change the display effect of the website in the future - you only need to replace one css rule to change the display effect of the entire website at the same time.<br>The code is roughly the same as the tiled background above: <br><span class="code">h1 {<br> font-family: Arial, sans-serif;<br> font-size: 24px;<br> color: #369;<br> padding-left: 30px;<br> background: url(icon.gif) no-repeat 0 50%;<br> }</span><br>We leave an extra space on the left side of the text to prevent us from thinking The desired icon, and then set no-repeat to specify that the background image will not be tiled (as shown in Figure 2-8). At the same time, we want the icon to be positioned at 0 pixels on the left and opposite to the vertical center line. <br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/fa27560271db57237aa907152e753926-7.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-8: Example of title with icon set<br> #p#<br><strong>Easy to update</strong><br>Let us imagine a scenario: in a website containing 100 pages, we do not use the above method, but use the <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="http://images.fastcompany.com/icon/first_imp.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Markup language - title_HTML/Xhtml_web page production" > tag to write The icons next to each title are integrated with the website style. After a few weeks, the owner of the website plans to change the website style, and the new icon size is different from the old one. Oops! Now we will How annoying it is to have to go back and modify the <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="http://images.fastcompany.com/icon/first_imp.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Markup language - title_HTML/Xhtml_web page production" > tags on 100 pages to update the path of the new icon! Think about the impact these events will have on the project budget and the pressure on the completion deadline? Time is money. !<br>If you integrate these not very important, decorative icons into a css file, it only takes a few minutes to replace all the icons on the entire site at once, giving you a brand new look! From this you can You should be able to gradually understand the benefits of separating structural markup and display effects. <br><strong>Chameleon Effect</strong><br> The technique below is somewhat contradictory to what I just said, but I think this technique is useful in a certain way. It is very useful in some situations. This is a technique I used extensively when doing standard refactoring for Fast Company magazine’s website (www.fastcompany.com) in April 2003. <br> At that time, we had < in the website Many 13X13 small icons are used next to the ;h3> tag, like this: <br><span class="code"><h3> <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="http://images.fastcompany.com/icon/first_imp.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" style="max-width:90%" alt="Markup language - title_HTML/Xhtml_web page production"> FIRST IMPRESSION</h3></span><br>There are two reasons why we decided to write the icon into the web page like this. First, according to the type of title Different icons are used (book club is a book, daily quotes are quotation marks, etc.). The second reason is that we change the color of the entire website every month to match the current magazine cover theme. Of course, this replacement work is very simple because of the use of CSS. <br> In order to make the icon change color along with other page elements (so that we don’t have to re-create the icon for new colors all the time), we only use two A set of icons are made in two colors: white and transparent (the background color will be displayed except for each change). Figure 2-9 is the icon placed before the introduction on the homepage: <br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/cc8f41f111a40b045665e6a7f3838712-8.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-9: 13X13 transparent icon (enlarged) <br> In order to fill in the transparent part with color, we use a simple CSS background attribute to set the color. We hope that this color will only appear behind the chart and not behind the title text. , we used the css selector to only use this rule for images within the <h3> tag, in order to achieve the effect we want: <br><span class="code">h3 img {<br> background: #696;<br> }</span><br>This css code means that all <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/cc8f41f111a40b045665e6a7f3838712-9.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Markup language - title_HTML/Xhtml_web page production" > tags within the <h3> tag will set the background to green. The background color will be displayed through transparent pixels, but the white part will still be white. In this way, only You need to modify this css rule and change it to a different color, and you can instantly change the color of every icon on the website, just like magic. <br><strong>Align <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/cc8f41f111a40b045665e6a7f3838712-9.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Markup language - title_HTML/Xhtml_web page production" > tags</strong><br> In order to align the icon and text correctly (we want it to be vertically centered), we add this css rule: <br><span class="code">h3 img {<br> background: #696;<br> vertical-align: middle ;<br> }</span><br>This rule will vertically center the icon and <h3> text content. Figure 2-20 is the title of the game: <br><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/cc8f41f111a40b045665e6a7f3838712-9.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2- 10: An example of using CSS as an icon and adding a background color <br> This example can also illustrate another important concept - the background color specified with CSS will appear behind the specified icon or CSS icon on any page. <br> Example For example, let's look back at the "conveniently updated icon" example and add a background color to it: <br><span class="code">h1 {<br> font-family: Arial, sans-serif;<br> font -size: 24px;<br> color: #fff;<br> padding-left: 30px;<br> background: #696 url(transparent_icon.gif) no-repeat 0 50%;<br> }</span><br>Now transparent_icon.gif will be displayed on top of the background color defined earlier in the same rule (Figure 2-11) — in this example, the background color is #696, which is the green of the pool table.<br> <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/009/cc8f41f111a40b045665e6a7f3838712-10.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" alt="" style="max-width:90%"><br>Figure 2-11 Example of a title with background image and background color set<br>This little trick is very useful when you add small rounded corners and decorate icons on a color-focused page. . These light pictures can be completely put into the css file, and they can be easily replaced when you plan to update them in the future. If you put more thought now, you can save a lot of work in the future. <br><strong>Summary</strong><br>I hope that by comparing the commonly used methods, you can discover the benefits of using title tags correctly. Whether it is a visual, non-visual browser or other device, you can correctly understand the meaning of previous titles and display them in an appropriate way. , search engines will also index them, and you can easily apply and modify the effects you need to display with css. </h3> </h3> </h3> </h1> </h1> </h1> </h1></b></p></span> </h6> </h1> </h1> </h1> </h3> </h3> </h2> </h1> </h1>
 给语言大模型加上综合视听能力,达摩院开源Video-LLaMAJun 09, 2023 pm 09:28 PM
给语言大模型加上综合视听能力,达摩院开源Video-LLaMAJun 09, 2023 pm 09:28 PM视频在当今社交媒体和互联网文化中扮演着愈发重要的角色,抖音,快手,B站等已经成为数以亿计用户的热门平台。用户围绕视频分享自己的生活点滴、创意作品、有趣瞬间等内容,与他人互动和交流。近期,大语言模型展现出了令人瞩目的能力。我们能否给大模型装上“眼睛”和“耳朵”,让它能够理解视频,陪着用户互动呢?从这个问题出发,达摩院的研究人员提出了Video-LLaMA,一个具有综合视听能力大模型。Video-LLaMA能够感知和理解视频中的视频和音频信号,并能理解用户输入的指令,完成一系列基于音视频的复杂任务,
 光动嘴就能玩原神!用AI切换角色,还能攻击敌人,网友:“绫华,使用神里流·霜灭”May 13, 2023 pm 07:52 PM
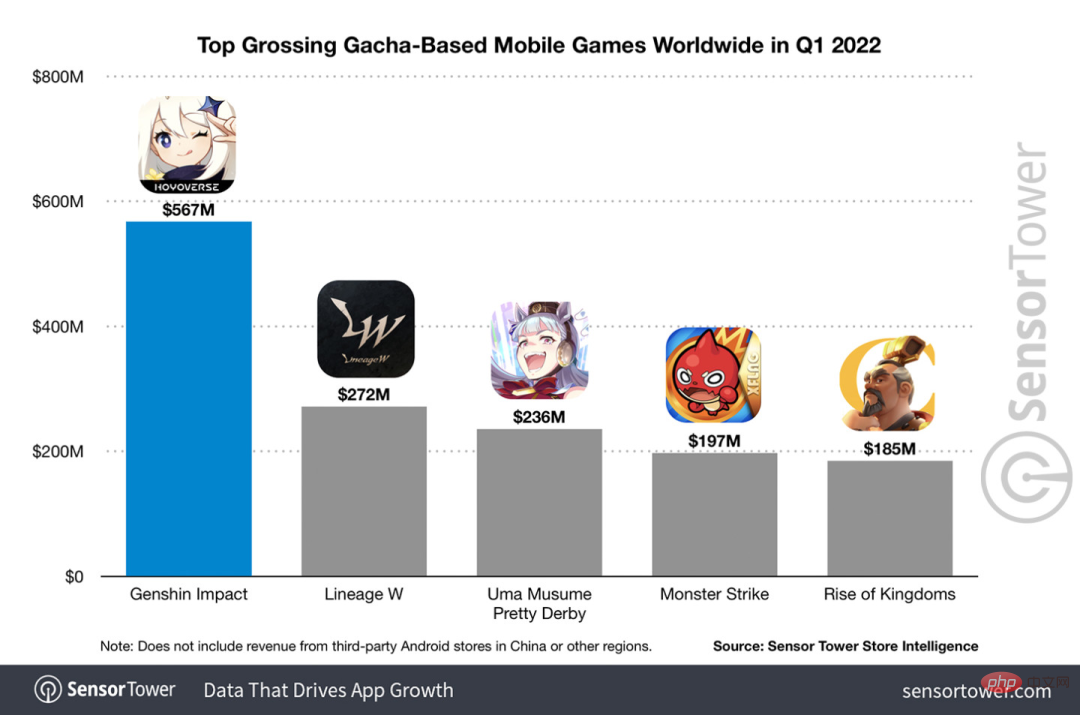
光动嘴就能玩原神!用AI切换角色,还能攻击敌人,网友:“绫华,使用神里流·霜灭”May 13, 2023 pm 07:52 PM说到这两年风靡全球的国产游戏,原神肯定是当仁不让。根据5月公布的本年度Q1季度手游收入调查报告,在抽卡手游里《原神》以5.67亿美金的绝对优势稳稳拿下第一,这也宣告《原神》在上线短短18个月之后单在手机平台总收入就突破30亿美金(大约RM130亿)。如今,开放须弥前最后的2.8海岛版本姗姗来迟,在漫长的长草期后终于又有新的剧情和区域可以肝了。不过不知道有多少“肝帝”,现在海岛已经满探索,又开始长草了。宝箱总共182个+1个摩拉箱(不计入)长草期根本没在怕的,原神区从来不缺整活儿。这不,在长草期间
 PPT文件标题不能删除的处理操作方法Mar 26, 2024 pm 03:21 PM
PPT文件标题不能删除的处理操作方法Mar 26, 2024 pm 03:21 PM1、删除文字当您使用鼠标左键单击文字后,会在文字周围出现许多整齐排列的白色方块,这表示已经选择了该【文本/形状/图形】。一旦选中,只需按下键盘上的【Delete】键,便可轻松删除该文字。2、选不中文字或形状鼠标左键单击【文本/形状/图形】后,没有出现向步骤1中的【选中状态】,出现此类问题原因较多,以母版为例,点击菜单上的【视图】,并找到【母版视图】中的【幻灯片母版】。3、在母版视图中,点击左侧导航的页面,找到需要删除的【文本/形状/图形】后,依旧点击鼠标左键,选中后,按键盘【Delete】删除即
 吵翻天!ChatGPT到底懂不懂语言?PNAS:先研究什么是「理解」吧Apr 07, 2023 pm 06:21 PM
吵翻天!ChatGPT到底懂不懂语言?PNAS:先研究什么是「理解」吧Apr 07, 2023 pm 06:21 PM机器会不会思考这个问题就像问潜水艇会不会游泳一样。——Dijkstra早在ChatGPT发布之前,业界就已经嗅到了大模型带来的变革。去年10月14日,圣塔菲研究所(Santa Fe Institute)的教授Melanie Mitchell和David C. Krakauer在arXiv发布了一篇综述,全面调研了所有关于「大规模预训练语言模型是否可以理解语言」的相关争论,文中描述了「正方」和「反方」的论点,以及根据这些论点衍生的更广泛的智力科学的关键问题。论文链接:https://arxiv.o
 学Python,还不知道main函数吗Apr 12, 2023 pm 02:58 PM
学Python,还不知道main函数吗Apr 12, 2023 pm 02:58 PMPython 中的 main 函数充当程序的执行点,在 Python 编程中定义 main 函数是启动程序执行的必要条件,不过它仅在程序直接运行时才执行,而在作为模块导入时不会执行。要了解有关 Python main 函数的更多信息,我们将从如下几点逐步学习:什么是 Python 函数Python 中 main 函数的功能是什么一个基本的 Python main() 是怎样的Python 执行模式Let’s get started什么是 Python 函数相信很多小伙伴对函数都不陌生了,函数是可
 GPT4ALL:终极开源大语言模型解决方案May 17, 2023 am 11:02 AM
GPT4ALL:终极开源大语言模型解决方案May 17, 2023 am 11:02 AM开源语言模型生态系统正在兴起,这些生态系统为个人提供综合资源以创建用于研究和商业目的的语言应用程序。本文深入研究GPT4ALL,它通过提供全面的搭建模块,使任何人都能开发类似ChatGPT的聊天机器人,从而超越了特定的使用案例。什么是GPT4ALL项目?GPT4ALL可以在使用最先进的开源大型语言模型时提供所需一切的支持。它可以访问开源模型和数据集,使用提供的代码训练和运行它们,使用Web界面或桌面应用程序与它们交互,连接到Langchain后端进行分布式计算,并使用PythonAPI进行轻松集
 计算机硬件能直接识别并执行的语言是什么Dec 25, 2020 pm 03:16 PM
计算机硬件能直接识别并执行的语言是什么Dec 25, 2020 pm 03:16 PM计算机硬件能直接识别并执行的语言是机器语言。机器语言是机器能直接识别的程序语言或指令代码,无需经过翻译,每一操作码在计算机内部都有相应的电路来完成它。
 生成多语种文本与图片的全能工具AltDiffusion-m18May 07, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
生成多语种文本与图片的全能工具AltDiffusion-m18May 07, 2023 pm 06:37 PM当前,非英文文图生成模型选择有限,用户往往要将prompt翻译成英语再输入模型。这样不仅会造成额外的操作负担,并且翻译过程中的语言文化误差,会影响生成图片的准确性。智源研究院FlagAI团队首创高效训练方式,使用多语言预训练模型和StableDiffusion结合,训练多语言文图生成模型——AltDiffusion-m18,支持18种语言的文图生成。包括中文、英文、日语、泰语、韩语、印地语、乌克兰语、阿拉伯语、土耳其语、越南语、波兰语、荷兰语、葡萄牙语、意大利语、西班牙语、德语、法语、俄语。Hu


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!






