jQuery Study Notes - Ajax Operation (1) - Data Loading_jquery
Load HTML
We usually use the method of loading HTML to load HTML fragments and insert them into the specified position. Assume that the current page is:
<div></div> <button>load</button>
The content of the test.html file in the same directory is:
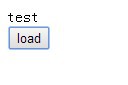
<span>test</span>
We can use the load method to load HTML and bind it to the button's click event:
$('button').click(function() {
$('div').load('test.html');
});
After clicking the button:
Loading JSON
JSON is Javascript Object Notation, literally translated as Javascript Object Notation, so it can easily represent and transmit data. It stipulates that keys and values must be enclosed in double quotes, and functions are illegal JSON values.
{
"name": "stephenlee",
"sex": "male"
}
Save the above JSON data in the test.json file. We can use the getJSON method to load JSON data and also bind it to the click event of the button:
$('button').click(function() {
$.getJSON('test.json');
});
Since the getJSON method is defined as a global object of jQuery, you need to use $ to call this method. Here $ refers to the global jQuery object, not the individual jQuery objects that $() refers to. Therefore we also call the getJSON function a global function.
But we will find that the above code only obtains JSON data, but does not see any effect. Here we can use the second parameter of the getJSON method as the callback function to test the effect:
$('button').click(function() {
$.getJSON('test.json', function(data) {
console.log(data);
$.each(data, function(index, content) {
console.log(content);
})
});
});
After clicking the button, let’s take a look at the output in the console:
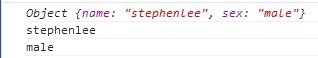
The first parameter of each function here can receive an array or object, and the second parameter is the value callback function, which takes the current index and value of the array or object in each loop as parameters.
Loading JS
Sometimes we don’t want to load all JS files when the page is first loaded, but dynamically load them based on demand. Suppose there is a JS file in the current directory with a simple alert:
$(function() {
alert('test');//
})
We can use the global function getScript to load the file and bind it to the click event of the button:
$('button').click(function() {
$.getScript('test.js');
});
After clicking the button, the test.js file is loaded and the alert is successfully triggered.
Load XML
The loading operation of XML is similar to JSON, because the role of XML documents is also related to data storage. Create a text.xml file in the same directory with the content:
<person> <name>stephenlee</name> <sex>male</sex> </person>
You can directly use the get method to load XML documents. Why it looks like a default method can be seen from the full name of AJAX - Asynchronous JavaScript And XML.
Also bind it to the button click event:
$('button').click(function() {
$.get('test.xml', function(data) {
console.log(data);
});
});
View the console and the result is:
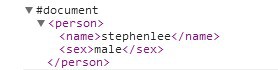
It should be noted here that if the format in the XML document is incorrect, although no error will be reported, the callback function will not be executed.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMThis article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future ProspectsApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future ProspectsApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AMThe latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It MattersApr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It MattersApr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software





