PHP速学视频免费教程(入门到精通)
PHP怎么学习?PHP怎么入门?PHP在哪学?PHP怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了PHP速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!
观察函数
ajaxStart 和 ajaxStop 函数可以用来作为观察函数,我们可以使用观察函数的回调函数来做相应的处理。
当 Ajax 请求开始且尚未进行其他传输时,会触发 ajaxStart 的回调函数。
当最后一次活动请求终止时,则会执行通过 ajaxStop 注册的回调函数。
由于观察函数具备全局性,所以需要使用 $(document) 来调用。我们通过使用 Ajax 方法取得一个图片的例子来测试两个函数:
当前页面为:
<div></div> <button>load</button>

同目录下的 test.html 内容为:
<img src="avatar.jpg">
点击按钮后希望载入图像:
$('button').click(function() {
$('div').load('test.html');
});

此时我们可以使用 ajaxStart 和 ajaxStop 函数来增加提示:
$(document).ajaxStart(function() {//
alert('load a picture');
}).ajaxStop(function() {
alert('show a picture');
});
$('button').click(function() {
$('div').load('test.html');
});
此时点击按钮后,再图像载入前先提示 load a picture,载入后提示 show a picture。
错误处理
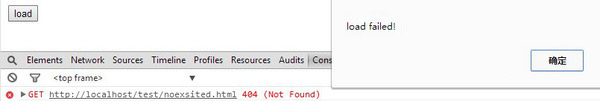
最常用的方式是全局的 ajaxError 方法,以上例为例,如果我们像一个不存在的页面发送数据请求:
$(document).ajaxError(function() {//
alert('load failed!');
});
$('button').click(function() {
$('div').load('noexsited.html');
});
此时点击按钮后:
对于非 load 方法,还可以使用 fail 方法来连缀处理:
$('button').click(function() {
$.get('noexsited.html', function(data) {
}).fail(function(jqXHR) {
alert('status is ' + jqXHR.status);
});
});

JSONP
JSONP 即 JSON with padding,填充式 JSON,利用的是 <script> 标签可以跨域获取 Javascript 文件的思路,故可以跨域获取 JSON 数据。<br /> JSONP 的格式是把标准 JSON 文件包装在一对圆括号中,圆括号又前置一个任意字符串。这个字符串,即所谓的 P,由请求数据的客户端来决定。<br /> 同样是上例的按钮,首先我们将外域页面 otherdomain.com/index.php 内容设置为:</script>
我们使用特殊的占位符 ? 来实现跨域获取 JSON 数据:
$('button').click(function() {
$.getJSON('otherdomain.com/index.php?callback=?', function(data) {
console.log(data);
});
});

数据获取成功。