 Web Front-end
Web Front-end HTML Tutorial
HTML Tutorial The selection mechanism of DOCTYPE mode by well-known browsers_HTML/Xhtml_Web page production
The selection mechanism of DOCTYPE mode by well-known browsers_HTML/Xhtml_Web page productionDocument Scope
The mode switching included in this article applies to Firefox and other Gecko-based browsers, Safari, Chrome and other Webkit-based browsers, Opera, Konqueror, Internet Explorer for Mac, Internet Explorer for Windows, and embedded IE browser. Avoid mentioning the name of the browser engine and instead mention the name of the most well-known browser using that engine.
This article focuses on the mode selection mechanism rather than documenting the exact behavior of each mode.
Mode
Here are the different modes:
Mode with content type text/html
The mode selection for text/html content depends on doctype sniffing (discussed later in this article). In IE8, the mode depends on other factors as well. However, by default in IE8, the mode for non-intranet sites that are not on Microsoft's blacklist depends on the document type.
It cannot be overemphasized that the precise behavior of modes differs in each browser, even though it is discussed uniformly in this article.
- Quirks Mode
- In Quirks Mode, the browser violates modern web formats in order to avoid "breaking" pages created based on practices popular in the late 1990s. specification. Different browsers implement different quirks. In Internet Explorer 6, 7, and 8, quirks mode effectively freezes IE 5.5. In other browsers, quirks mode is a small deviation from standards mode.
- If you are creating a new web page, you should comply with relevant specifications (especially CSS2.1) and use standards mode.
- Standards Mode
- In Standards Mode, the browser attempts to treat standards-compliant documents as normatively correct as in the specified browser .
- Different browsers follow different stages, so standards mode is not a single goal.
- HTML5 calls this mode "no quirks mode"
- Almost Standards Mode (Almost Standards Mode)
- irefox, Safari, Chrome, Opera( Starting from 7.5) and IE8 also have a mode called "quasi-standard mode", which implements the vertical size of table cells according to traditional methods instead of strictly following CSS2 specifications. Mac IE5, Windows IE6 and 7, versions prior to Opera 7.5, and Konqueror do not need quasi-standards mode because they at least do not strictly follow the CSS2 specification to implement table cell vertical dimensions in their respective standards modes. In fact, their standards mode is closer to Mozilla's quasi-standards mode than Mozilla's standards mode.
- HTML5 calls this mode "limited quirks mode".
- IE7 mode
- IE8 has a mode that mainly freezes a copy of IE7 standards mode. No other browsers have a mode like this, and it is not specified by HTML5.
Mode with content type application/xhtml xml (XML mode)
In Firefox, Safari, Chrome and Opera, the application/xhtml xml HTTP content type (not a meta element nor a doctype!) will trigger XML mode. In XML mode, the browser attempts to give the XML document specification-correct processing to the extent specified in the browser.
IE6, 7 and 8 do not support application/xhtml xml, nor does Mac IE5.
In the Nokia S60 browser based on WebKit, the application/xhtml xml HTTP content type cannot trigger XML mode, because the focus in mobile walled gardens is compatibility with non-standard content. (Older “mobile browsers” cannot use real XML parsers because non-canonical content is tagged as XML.)
Having not tested Konqueror enough, I can't say exactly what will happen in this browser.
Non-Web Modes
Some engines have modes that have nothing to do with web content. For completeness, they are only mentioned here. Opera has a WML2.0 mode. WebKit on Leopard has a specific mode for legacy Dashboard widgets.
Impact
Here are the main impacts of these patterns:
Layout
The text/html mode mainly affects CSS layout. For example, it's a quirk that tables don't inherit styles. In some browser quirks mode, the box model becomes the IE5.5 box model. This document does not list all layout quirks.
In semi-standard mode (in browsers with this mode), only the height of the table cell containing the image is different from that in standard mode.
In XML mode, selectors have different case-sensitive behavior. Additionally, the specific rules for the HTML body element do not apply to older browsers that do not implement the latest CSS 2.1 changes.
Analysis
There are also quirks that affect the parsing of HTML and CSS and can cause standards-compliant web pages to be parsed incorrectly. Quirk layout determines whether these quirks are enabled or not. Regardless, it's important to understand the main similarities and differences between Quirks mode and Standards mode in CSS layout and parsing (not HTML parsing).
Some people mistakenly refer to standards mode as "strict parsing mode", which misunderstands the browser's ability to enforce HTML syntax rules and the browser's ability to evaluate markup for correctness. This is not the case. Even when standards mode layout is in effect, browsers still do tag soup (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tag_soup) correction work. (Before the release of Netscape 6 in 2000, Mozilla did have parsing modes for enforcing HTML syntax rules. These modes were incompatible with existing Web content and were abandoned.)
Another common misconception is about XHTML parsing. It is generally believed that using the XHTML doctype results in different parsing. In fact, this is not the case. XHTML documents with content type text/html use the same parser as HTML documents. Currently all browsers care about is that XHTML with document type text/html is just "tag soup with croutons" (extra slashes everywhere).
Only when documents using XML document type (for example: application/xhtml xml or xmapplication/) will trigger XML mode for parsing, the parser at this time is completely different from the HTML parser.
Script
While Quirks Mode is mostly about CSS, there is also a bit about scripting. For example, in Firefox's quirks mode, the HTML id attribute establishes a global script-scoped object reference just like in IE. The impact of scripting in IE8 deserves more attention than in other browsers.
In XML mode, the behavior of some DOM APIs is completely different, because the behavior of XML's DOM API is not compatible with the behavior of HTML when it is defined.
doctype sniffing (also called doctype conversion)
Modern browsers use doctype sniffing to determine the engine mode of text/html documents. This means that the choice of mode is based on the document type declaration (or lack thereof) at the beginning of the HTML document. (This does not apply to documents using the XML document type.)
The document type declaration (doctype) is a grammatical forgery of SGML. SGML is an old-style markup framework, and HTML before HTML5 was defined based on it. In the HTML4.01 specification, the document type declaration describes the version information of HTML. Despite the name "Document Type Declaration" and the HTML 4.01 specification describing "version information", a Document Type Declaration does not classify an SGML or XML document as a specific type of document, even if it looks like it (because of the name) . (More in the appendix)
Neither the HTML4.01 specification nor ISO 8879 (SGML) say anything about using document type declarations as engine mode conversions. Doctype sniffing is based on the observation that at the time doctype sniffing was designed, the vast majority of quirky documents had neither a document type declaration nor a reference to an older DTD. HTML5 accepts this fact and defines the doctype in text/html as the only mode conversion.
A typical pre-HTML5 document type declaration contains (separated by whitespace) the " string, the universal identifier of the root element ("html"), and the "PUBLIC" string, between quotes The DTD public identifier in the DTD, the possible system identifier (URL) of the same DTD and the character ">". The document type declaration is placed before the opening tag of the document's root element.
Select doctype
text/html
Here is a simple guide on how to choose a doctype when creating a new text/html document:
- Standard mode, cutting-edge validation
- If you want to verify such as , and new features like ARIA, then this is the right thing to do. Note that the effective definition of HTML5 is still changing, please be sure to test image alignment in Firefox, Safari, Chrome, Opera9 or Opera10. Testing image alignment in Internet Explorer is not sufficient, anyway make sure you test in IE8 as well.
- Standards mode, more stable verification target
- This doctype will also trigger standards mode, and the 10-year-old HTML4.01 valid definition is stable. Please make sure to test image alignment in Firefox, Safari, Chrome, Opera9 or Opera10. Testing image alignment in Internet Explorer is not sufficient, anyway make sure you test in IE8 as well.
- To use standards mode, but still verify that markup or using sliced images in table layouts is not recommended and you don't want to fix them.
- gt ;
- It triggers semi-standards mode (and the old full Standards mode in Mozilla). Please note that layouts based on sliced images implemented using tables may be broken if ported to HTML5 in the future (and the same goes for full standards mode).
- Using quirks mode on purpose
- No doctype.
- Please don’t do this. Intentionally designing for quirks mode will bother you, and in the future no one your colleagues or successors will even care about Windows IE6 (no one cares about Netscape 4.x and IE5 anymore). Designing for quirks mode is a bad idea. Believe me.
- If you want to still support Windows IE6, it's better to make a special hack for it using conditional comments than to make other browsers fall back to quirks mode.
I do not recommend any XHTML doctype because XHTML used as text/html is considered harmful . Regardless, if you choose to use the XHTML doctype, be aware that XML declarations will trigger quirks mode in IE6 (but not IE7!).
application/xhtml xml
A simple guideline for application/xhtml xml is to never use doctype. Web pages in this manner are not "strictly consistent" with XHMTL 1.0, but that doesn't matter. (Please see the Appendix at the back)
IE8 complications
A List Apart once introduced that in addition to doctype, IE8 will use mode conversion based on meta elements as one of the factors in mode selection. (See Ian Hickson, David Baron, David Baron again, Robert O'Callahan and Maciej Stachowiak comments. )
IE8 has 4 modes: IE5.5 quirks mode, IE7 standards mode, IE8 quasi-standards mode and IE8 standards mode. The choice of mode depends on data from several sources: doctype, meta elements, HTTP headers, periodic download data from Microsoft, LAN domain, settings made by the user, settings made by the LAN administrator, and the mode of the parent frame (if any) Compatible with the address bar view button is triggered by the user. (For other apps embedded in the engine, the mode also depends on the embedded app.)
Fortunately, IE8 will generally use doctype sniffing like other browsers if:
- The author did not set the X-UA-Compatible HTTP header
- The author did not set the X-UA-Compatible meta tag
- Microsoft has not placed this site’s domain name on the blacklist
- The LAN administrator did not place this site on the blacklist
- The user did not press the Compatibility View button (or was otherwise added to a specific user blacklist)
- This site is not in the LAN domain
- User did not choose to show all sites in IE7
- The page is not embedded into the compatibility mode page through the frame
Except for the two cases above regarding X-UA-Compatible, IE8 performs doctype sniffing like IE7. IE7 emulation is called compatibility view.
In the case of X-UA-Compatible, IE8 behaves completely differently from other browsers. I would like to see the Appendix or the flow chart in PDF and PNG formats on this page.
Unfortunately, without the X-UA-Compatible HTTP header or meta tag, even with the appropriate doctype, IE8 allows users to inadvertently downgrade the page from IE8's standards mode to IE7 mode, which is an emulation IE7 standards mode. Worse, LAN administrators can do this too. Microsoft can also blacklist all domain names you use.
To deal with these effects, doctype is not enough, you need X-UA-Compatible HTTP header and meta tag.
The following is a simple guide on how to select the X-UA-Compatible HTTP header or meta tag for new text/html documents that already have a doctype that triggers standards mode or quasi-standards mode in other browsers:
- Your domain is not on Microsoft's blacklist, and you are more concerned with not having browser-specific nuisances than making sure users can't fall back to IE7 behavior.
- You do not need to include the X-UA-Compatible HTTP header or meta tag.
- Your domain name is on Microsoft's blacklist. Because other authors in your domain name have damaged the site or caused users to enable compatibility view for the entire domain, you are worried about Google or Digg using frames to embed your site or your To ensure that users cannot use compatible views
- First, include the following meta element in your page (it is illegal in HTML5) (before any script element), or set the following HTTP header: Breaking
- in IE8 First, include the following meta element in your page (it is illegal in HTML5) (before any script element), or set the following HTTP header:
- Related links
Eric Meyer writes about Mac IE5 patterns in
- Using the correct doctype
- doctype sniffing for Mozilla
- by David Baron Lance Silver discusses mode and doctype sniffing in Windows IE6 in CSS Enhancements in IE6
- doctype conversion for Opera9
- Faruk Ateş’s IE8 and X-UA-Compatible solution
- Addendum: A plea to XML implementers and specification authors
Please do not bring doctype sniffing to XML.
Doctype sniffing is a tag chowder-like approach to solving a tag chowder problem. Doctype sniffing is a heuristic designed after the release of the HTML4 and CSS2 specifications that distinguishes stale documents from documents that conform to behavior that their authors might have expected.
Occasionally it is suggested to use doctype sniffing on XML to schedule different processing, identify the vocabulary in use or activate features. This is a bad idea. Scheduling and vocabulary identification should be based on namespaces, while feature activation should be based on explicit processing instructions or elements.
The whole idea of well-formedness is to introduce DTD-free parsing of XML and promote doctype-free documentation. In the formal case where two XML documents have the same canonical form and the application processes them differently (and the difference is not due to a lack of choice to process external entities), the application may be broken. In practice, if two XML documents cause the same content to be reported (qnames ignored) to a SAX2
content handler and the application processes the documents differently, the application may be broken. Considering that as web authors you can't trust that everyone will use an XML processor that resolves extra entities to parse their pages (even though some browsers appear to do so because they map certain public identifiers to a truncated entity-defining DTD), Inserting doctypes into XML for the Web is pointless and often leads to cargo cultish habits. (You still use W3C Validator's DTD override feature to validate a DTD, although W3C Validator will say that the result is only temporarily valid. Or better yet, you can relax NG with Validate , it doesn't pollute the document referenced by the schema. ) Requiring a doctype in order to sniff is pretty stupid, even if that's the workaround in HTML practice. Also, when a lower-level specification defines two things as equal, a higher-level specification should not try to give them different meanings. Please consider gt ;. If you remove the public identifier, the same DTD is still specified, so doctype means the same as the previous doctype. Should they be sniffed differently? Can further theorize. Assume that a DTD called foobar.dtd is copied to example.com: . How to sniff this? It should mean the same thing. Even the entire DTD can be attached to the document. In other words, if there is #include "foo.h", you should not bind any black magic to the name foo.h, because it should allow copying the contents of foo.h into the document or copying foo.h into in bar.h and means #include "bar.h". The reason I'm not worried about HTML and SGML constructing the same parameters is that web browsers don't use real SGML parsers to parse HTML, so I don't think pretending to be SGML is useful. Anyway, if you’re not convinced yet, here’s W. Eliot Kimber’s article on the matter comp.text.sgml In the table below, quirk mode, standard mode and quasi-standard are represented by Q, S and A respectively. When the browser has only two modes, if the row height of the table cell is consistent with Mozilla's standard mode, the standard mode is marked "S". If the row height of the table cell is consistent with Mozilla's quasi-standard mode, , then it is marked as "A". Please note that XHTML served using the XML content model is rendered in XML mode. The purpose of this table is not to say that all doctypes in the table are reasonable choices for new pages. The purpose of this table is to show what data my recommendations are based on. The following abbreviation symbols are used for column headers: Appendix: How to handle some doctypes in text/html
History
Moziila's doctype sniffing code was significantly modified in October 2000, September 2001 and June 2002. The status of the Mozilla (and Netscape 6.x) build described in this document can be seen at ftp.mozilla.org as of 2000.10.19. This document does not cover how doctype sniffing works in Mozilla M18 (and Netscape 6.0 PR3). Safari's doctype sniffing code has also been significantly modified since the first public beta version. This document does not cover behavior earlier than version V73 also called 0.9.
The doctype sniffing code before Konqueror 3.5 seems to come from a very early version of Safari. Konqueror now matches Safari, and its doctype sniffing code comes from Mozilla.
As can be seen from the table, Opera's doctype sniffing is regularly changing from being similar to IE to being similar to Mozilla, although Opera 9.5 and 9.6 are on the way back. At the same time, Opera's quirks mode layout behavior has been switched from emulating IE6's quirks mode to Mozilla's quirks mode.
Appendix: Mode selection for IE8
- Start: Enter "X-UA-Compatible meta?"
- X-UA-Compatible meta?
- IE=7: Use IE7 standard
- IE=EmulateIE7: Enter "quirks or no doctype? (compatibility mode)"
- IE=IE8 or IE=IE7 or IE=a or IE=EmulateIE8 or no or first script: enter "X-UA- Compatible HTTP header?"
- IE=8 or IE=Edge or IE=99 or IE=9.9: Enter "quasi-standards mode?"
- IE=5: Use quirks mode (IE5. 5)
- )"
- IE=IE8 or IE=IE7 or IE=a or IE=EmulateIE8 or none: Enter "Show all sites...Preset?"
- IE=8 or IE=Edge or IE=99 or IE=9.9: Enter "quasi-standards mode?"
- IE=5: Use quirks mode (IE5.5)
- Quacks mode or no doctype? (compatibility mode)
- Yes: Use quirks mode (IE5.5)
- No: Use IE7 standards mode
- Show all sites... Preset?
- Yes: Enter "quirks mode or no doctype? (compatibility mode)"
- No: Enter "Show LAN site...preset?"
- Show LAN site...preset set up?
- Yes: Enter "The site is located in the LAN domain?"
- No: Enter "The domain name is on the list maintained by Microsoft?"
- The domain name is on the list maintained by Microsoft?
- Yes: Enter "Quirk mode or no doctype? (Compatibility mode)"
- No: Enter "Embedded in Frame with compatibility mode page?"
- Compatibility mode page Embedding with Frame?
- Yes: Go to "Quirk mode or no doctype? (compatibility mode)"
- No: Go to "Compatibility mode button pressed?"
- Compatibility mode pressed Button?
- Yes: Enter "quirks mode or no doctype? (compatibility mode)"
- No: Enter "quirks mode or no doctype? (IE8)"
- Quirks mode or No doctype? (IE8)
- Yes: Enter "Use quirks mode (IE5.5)"
- No: Enter "quasi-standards mode?"
- Pre-standards mode?
- Yes: Use IE8 semi-standard mode
- No: Use IE8 standards mode
- These steps can be seen as flowcharts in
formats. Thanks Thanks to Simon Pieters, Simon Pieters and Anne van Kesteren for helping me correct the pattern sheets for various Opera versions and for their comments. Thanks to Simon Pieters for creating another IE8 flowchart.
 火狐浏览器是哪个国家的Sep 15, 2022 pm 02:55 PM
火狐浏览器是哪个国家的Sep 15, 2022 pm 02:55 PM火狐浏览器是“美国”的。Firefox火狐浏览器是开源基金组织Mozilla研发的一个自由及开放源代码的网页浏览器;而Mozilla基金会成立于2003年7月,是一家美国公司,现位于美国加利福尼亚州的芒廷维尤。
 电脑浏览器打不开网页但能上网怎么解决Jun 28, 2023 am 11:26 AM
电脑浏览器打不开网页但能上网怎么解决Jun 28, 2023 am 11:26 AM电脑浏览器打不开网页但能上网解决方法:1、网络设置问题,将路由器断电并等待几分钟,然后再重新插上电源;2、浏览器设置问题,清除浏览器缓存和浏览历史记录,确保浏览器没有设置代理服务器或虚拟专用网络;3、DNS设置问题,将DNS设置更改为公共DNS服务器地址;4、杀毒软件或防火墙问题,禁用杀毒软件或防火墙,再尝试打开网页;5、网页本身的问题,等待一段时间或联系网站管理员了解情况。
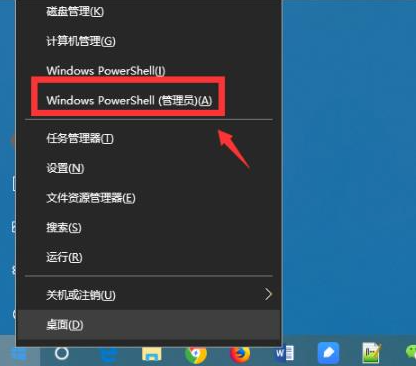 教你如何强制卸载edge浏览器Jul 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
教你如何强制卸载edge浏览器Jul 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PMWindows10自带的Edge浏览器在程序面板上是不能被卸载的,但是有些网友不喜欢使用edge浏览器,想要卸载掉它。那么我们可以尝试如何卸载edge浏览器呢?下面小编就教下大家强制卸载edge浏览器的方法。具体的方法如下:1、右击左下角开始,点击“windowspowershell(管理员)”打开。2、进入命令界面,输入代码get-appxpackage*edge*,查找edge包。3、在edge包中找到packagefullname,选中并复制。4、接着输入命令Remove-appxpack
 如何修复 Microsoft Edge 浏览器中的黑屏问题May 16, 2023 am 10:04 AM
如何修复 Microsoft Edge 浏览器中的黑屏问题May 16, 2023 am 10:04 AM微软于2020年初发布了基于Chromium(谷歌的开源引擎)的NewEdge版本。新Edge的感觉与谷歌Chrome相似,并且具有Chrome中可用的功能。但是,许多用户报告说他们在启动MicrosoftNewEdge后立即看到黑屏。用户可以访问设置菜单,但是当他们单击菜单中的任何选项时,它不起作用,只有黑屏可见。当计算机鼠标悬停在选项上并且用户可以关闭浏览器时,它会突出显示选项。在PC上打开新的Edge浏览器时是否遇到黑屏?那么这篇文章将对你有用。在这篇文章中,
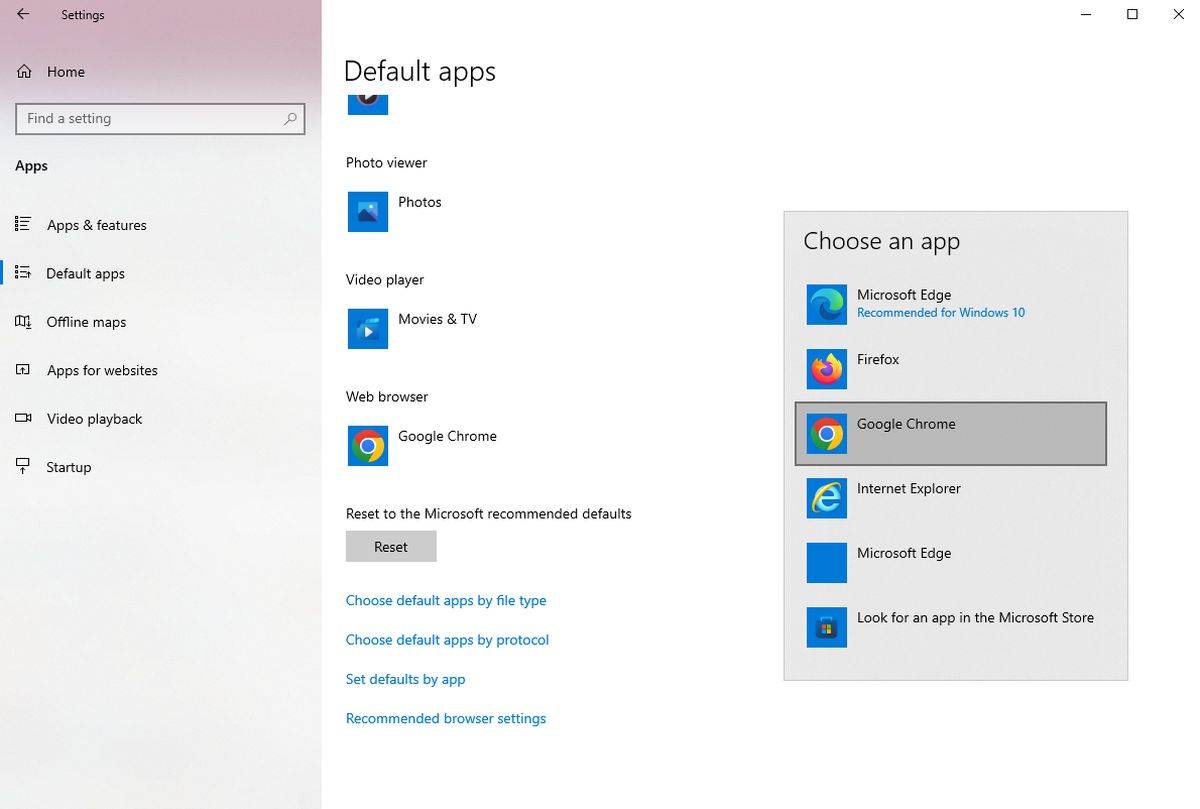 如何禁止 Outlook 在 Edge 浏览器中打开链接Aug 03, 2023 am 11:49 AM
如何禁止 Outlook 在 Edge 浏览器中打开链接Aug 03, 2023 am 11:49 AM如何阻止Outlook在Edge中打开链接在继续之前,请确保您的首选浏览器在Windows中设置为默认浏览器。这可确保在所需的浏览器中打开Outlook链接。要检查并设置默认浏览器:对于Windows10:单击“开始”菜单,然后选择“设置”转到“应用程序”,然后转到“默认应用程序”在默认应用程序列表的底部查找“Web浏览器”如果列出了您的首选浏览器,则一切就绪。如果列出了MicrosoftEdge,请单击它,然后从列表中选择您喜欢的浏览器。如果出现提示,请单击“仍然切换”。修复Edge问题中Ou
 简化三步骤,轻松删除Microsoft Edge中的边框Sep 02, 2023 pm 02:57 PM
简化三步骤,轻松删除Microsoft Edge中的边框Sep 02, 2023 pm 02:57 PM许多用户对MicrosoftEdge中网页周围的白色边框不满意。他们认为这是不必要的和分散注意力的,他们要求Microsoft完全删除MicrosoftEdge的边框。这类似于“不要修复没有损坏的东西”的说法,但Microsoft似乎没有考虑到这一点。当然,它是一种流行的网络浏览器,提供多种功能,包括内置广告拦截器、跟踪预防和密码管理器。但是,某些用户可能会发现浏览器在网页周围有边框。此边框可能会分散注意力或难看,有几种方法可以将其删除。在关于r/Edge的冗长对话中,一些普通的非内部用户发现,
 edge是什么浏览器Jul 19, 2022 pm 12:41 PM
edge是什么浏览器Jul 19, 2022 pm 12:41 PMedge是由微软开发的基于Chromium开源项目及其他开源软件的网页浏览器。Edge浏览器主要特点是能够支持目前主流的Web技术,作为Windows10自带浏览器,给微软用户带来更好的功能体验。
 Web 端实时防挡脸弹幕(基于机器学习)Jun 10, 2023 pm 01:03 PM
Web 端实时防挡脸弹幕(基于机器学习)Jun 10, 2023 pm 01:03 PM防挡脸弹幕,即大量弹幕飘过,但不会遮挡视频画面中的人物,看起来像是从人物背后飘过去的。机器学习已经火了好几年了,但很多人都不知道浏览器中也能运行这些能力;本文介绍在视频弹幕方面的实践优化过程,文末列举了一些本方案可适用的场景,期望能开启一些脑洞。mediapipeDemo(https://google.github.io/mediapipe/)展示主流防挡脸弹幕实现原理点播up上传视频服务器后台计算提取视频画面中的人像区域,转换成svg存储客户端播放视频的同时,从服务器下载svg与弹幕合成,人像


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!






